Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (6): 883-890.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.06.011
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation combined with core decompression and bone grafting in the repair of osteonecrosis of femoral head
Zhang Yang, Wang Nan, Yang Li-feng, Ma Ji, Li Zhi
- Central Hospital Affiliated to Shenyang Medical College, Shenyang 110024, Liaoning Province, China
-
Online:2015-02-05Published:2015-02-05
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Yang, Wang Nan, Yang Li-feng, Ma Ji, Li Zhi. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation combined with core decompression and bone grafting in the repair of osteonecrosis of femoral head[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(6): 883-890.
share this article
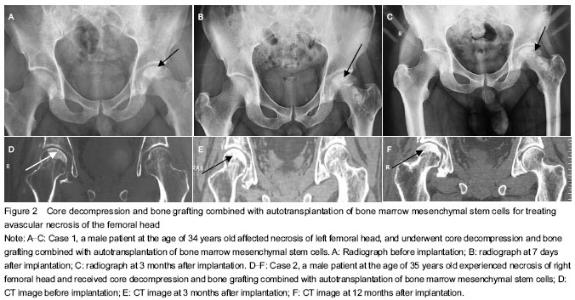
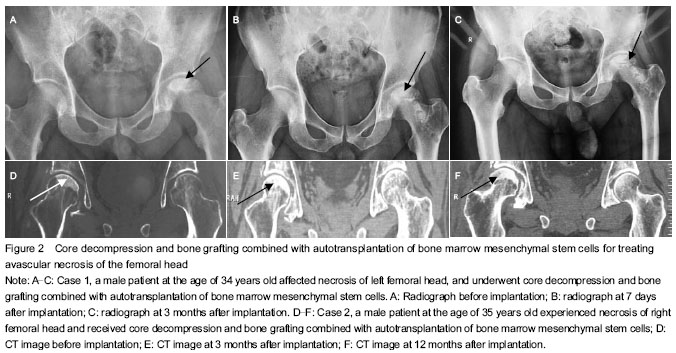
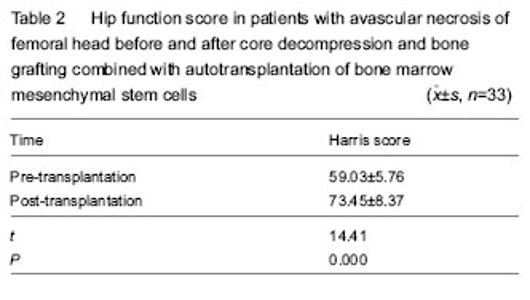
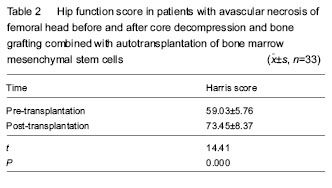
Hip function score in patients with osteonecrosis of femoral head Patients received core decompression and bone grafting combined with autotransplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. A total of 33 patients were followed up at 6-12 months after implantation. Radiographs or CT images did not reveal further collapse of the femoral head. The region of necrosis of the femoral head was controlled and noticeably improved. According to Harris hip function score, pain disappeared and they could do various works. X-ray and CT detection demonstrated that 30 hips had normal femoral head, accounting for 79%; pain apparently lessened; normal walking or slightly limping was detected in 15 hips, accounting for 40%. Walking distance extended in 35 hips, accounting for 92%. Hip dysfunction evidently improved in 24 hips, accounting for 63%. Harris score in patients with osteonecrosis of femoral head before and after implantation is shown in Table 2. Typical cases Case 1: a 34-year-old male patient suffered from necrosis of"
left femoral head, and underwent core decompression and bone grafting combined with autotransplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (Figures 2A-C). Pain in the left hip obviously relieved at 1 week after transplantation, and basically lessened at 3 months. Case 2: a 35-year-old male patient experienced right necrosis of the femoral head, and received core decompression and bone grafting combined with autotransplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (Figures 2D-F). Pain lessened somewhat after implantation, relieved basically at 3 months, and basically disappeared at 12 months. The activity was normal. Adverse reactions One patient suffered from high blood pressure. One patient had joint effusion with a safety factor of 94%. Their bodies recovered to normal after corresponding treatment. Symptoms disappeared after taking corresponding measures."
| [1] Kang WL, Yuan PW. Research progress of femoral head necrosis and mesenchymal stem cells transplantation. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2013;21(19):1954-1957. [2] Korompilias AV, Beris AE, Lykissas MG, et al. Femoral head osteonecrosis: why choose free vascularized fibula grafting. Microsurgery. 2011;31(3):223-228. [3] Aldridge JM 3rd, Urbaniak JR. Avascular necrosis of the femoral head: etiology, pathophysiology, classification, and current treatment guidelines. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2004;33(7):327-332. [4] Chen C, Yang S, Feng Y, et al. Impairment of two types of circulating endothelial progenitor cells in patients with glucocorticoid-induced avascular osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Joint Bone Spine. 2013;80(1):70-76. [5] Teng M, Geng Z, Huang L, et al. Stem cell transplantation in cardiovascular disease: an update. J Int Med Res. 2012; 40(3):833-838. [6] Shen X, Wei BF. Research progress of femoral head necrosis treatment by hip-preserving surgery. Fengshibing yu Guanjieyan. 2014;3(6):68-73. [7] Fu Q, Yan SJ, Wang JY, et al. Analysis of clinical effect of core decompression combined with autologous bone-marrow mesenchymal stem cells treating 45 cases with aseptic necrosis of head of femur. Xiandai Shengwu Yixue Jinzhan. 2013;13(25):4925-4928. [8] Wang JX, Chen YZ, Wei XY. Effects of core decompression combined with transplantation of bmscs for treatment of advanced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Zhonghua Xibao yu Ganxibao Zazhi: Dianzi Ban. 2013;3(2):83-86. [9] Katayama R, Wakitani S, Tsumaki N, et al. Repair of articular cartilage defects in rabbits using CDMP1 gene-transfected autologous mesenchymal cells derived from bone marrow. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2004;43(8):980-985. [10] Väänänen HK. Mesenchymal stem cells. Ann Med. 2005; 37(7):469-479. [11] Li ZH, Liao W, Cui XL, et al. Intravenous transplantation of allogeneic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and its directional migration to the necrotic femoral head. Int J Med Sci. 2011;8(1):74-83. [12] Chinese medical association. Common understanding of diagnosis and treatment for necrotic femoral heads in adults in 2012. Zhongguo Gu yu Guanjie Waike Zazhi. 2012;5(2): 185-192. [13] Li XM, Guo DH, Shi GJ, et al. Clinical study on medullary core decompression conbined with tanshinone IIA mixed with bone grafting in the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head in Ficat II period. Zhongyi Zhenggu. 2014;26(5):9-12. [14] Harris WH. Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty. An end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969;51(4):737-755. [15] Mont MA, Jones LC, Hungerford DS. Nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head: ten years later. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(5):1117-1132. [16] 16 Ficat RP. Idiopathic bone necrosis of the femoral head. Early diagnosis and treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1985; 67(1):3-9. [17] Mont MA, Ragland PS, Etienne G. Core decompression of the femoral head for osteonecrosis using percutaneous multiple small-diameter drilling. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(429): 131-138. [18] Steinberg ME, Larcom PG, Strafford B, et al. Core decompression with bone grafting for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(386):71-78. [19] Rijnen WH, Gardeniers JW, Buma P, et al. Treatment of femoral head osteonecrosis using bone impaction grafting. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;(417):74-83. [20] Sen RK, Tripathy SK, Aggarwal S, et al. Early results of core decompression and autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells instillation in femoral head osteonecrosis: a randomized control study. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(5):679-686. [21] Cheng JG, Yang JS. Progress in the treatment of adult avascular necrosis of femoral head. Zhongguo Xiandai Yiyao Zazhi. 2009;11(9):123-125. [22] Yang M, Li QF. The progress in the study of mesenchymal stem cells in treating ischemic injuries. Zhongguo Meirong Yixue. 2009;18(11):1709-1711. [23] Wu JQ, Cheng LM, Li ZR. Osteogenic differentiation study of bone marrow stromal stem cells in vivo. Zhongguo Gu yu Guanjie Waike. 2010;3(1):73-77. [24] Liang HS, Huang K, Li L, et al. Effect of core decompression and bone grafting combined with autotransplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for early stage of avascular necrosis of femoral head. Zhongguo Xiandai Yiyao Zazhi. 2014;16(8):20-22. [25] Tang J, Huang K, Li L, et al. Treatment of core decompression and bone grafting combined with autotransplantation of bone marrow and platelet-rich plasma for early stage of avascular necrosis of femoral head. Yixue Lilun yu Shijian. 2013;26(10): 1273-1277. [26] Gangji V, Hauzeur JP, Matos C, et al. Treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head with implantation of autologous bone-marrow cells. A pilot study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A(6):1153-1160. [27] Li Z, Chen G, Wang Z, et al. Treatment of avascular necrosis of the femoral head with core decompression and transplantation of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2012;20(5): 411-414. [28] Hernigou P, Beaujean F. Treatment of osteonecrosis with autologous bone marrow grafting. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;(405):14-23. [29] Chu JG, Wang XJ, Wang JW. Clinical curative effect of autologous bone marrow stem cell transplantation combined core decompression treatment for elderly ischemic femoral head necrosis. Zhongguo Laonian Xue Zazhi. 2012;32(16): 3432-3433. [30] Faghihi F, Baghaban Eslaminejad M. The effect of nano-scale topography on osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2014;158(1):5-16. [31] Gentleman E, Swain RJ, Evans ND, et al. Comparative materials differences revealed in engineered bone as a function of cell-specific differentiation. Nat Mater. 2009; 8(9):763-770. [32] Chen QX. Summary of progress on the treatment of femoral head necrosis. Zhongwai Yiliao. 2014(12):197-198. [33] Cai K, Zhou YP, Wu MC. The research towards Bone marrow stem cell transplantation on femoral head necrosis. Jilin Yixue. 2013;34(2):281-282. [34] Stagg J, Galipeau J. Mechanisms of immune modulation by mesenchymal stromal cells and clinical translation. Curr Mol Med. 2013;13(5):856-867. [35] Justesen J, Stenderup K, Eriksen EF, et al. Maintenance of osteoblastic and adipocytic differentiation potential with age and osteoporosis in human marrow stromal cell cultures. Calcif Tissue Int. 2002;71(1):36-44. [36] Kang FD, Pei DX. Treatment of early necrosis of the femoral head at Ficat I, II period and before the collapse. Zhongguo Gu yu Guanjie Sunshang Zazhi. 2010;25(1):91-94. [37] Xiao YJ, Wang SR. Advance in treatment of avascular nerosis of femoral head. Zhongguo Xiandai Yisheng. 2008;46(30): 52-53. [38] Wang XX, Wu QC. Study on the surgical treatment of ischemic necrosis of femoral head. Linchuang Yixue. 2014; 34(1):119. [39] Ma YC, Liao JX, Lin Z, et al. Clinical effect of bone marrow stem cells transplantation on early avascular necrosis of femoral head. Xiandai Yiyuan. 2014;14(9):13-17. |
| [1] | Liu Lihua, Sun Wei, Wang Yunting, Gao Fuqiang, Cheng Liming, Li Zirong, Wang Jiangning. Type L1 steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head through femoral head and neck junction decompression by fenestration: a single-center prospective clinical study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 906-911. |
| [2] | Zeng Xianghong, Liang Bowei. A new strategy for the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 431-437. |
| [3] | Liu Jinyu, Ding Yiwei, Lu Zhengcao, Gao Tianjun, Cui Hongpeng, Li Wen, Du Wei, Ding Yu. Finite element biomechanical study of full endoscopic fenestration decompression for cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3850-3854. |
| [4] |
Wang Tiantian, Wang Jianzhong.
Application and prospect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in the
treatment of early femoral head necrosis |
| [5] | Bu Yueli, Wang Fang, Zhang Jianguo, Li Xiaolin, Cao Zijun, Li Xuemei. Plantar pressure and gait characteristics in older adult patients with diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 736-740. |
| [6] | Wang Jing, Xu Shuai, Liu Haiying. Hidden blood loss during posterior lumbar interbody fusion in lumbar spinal stenosis patients with and without rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(33): 5307-5314. |
| [7] |
Wang Qiuan, Yuan Feng, Wu Jibin, Sun Maji, Wu Dongying, Meng Qiang, Guo Kaijin.
Endoscopic unilateral versus bilateral decompression effects on lumbar disc herniation with contralateral symptoms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5133-5137. |
| [8] | Zhang Chunlin, Shang Lijie, Yan Xu, Cao Zhengming, Shao Chenglong, Feng Yang. Mid-long-term effect of only placed expandable interbody fusion cage in the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis with vertebral instability using micro-endoscopic discectomy system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 335-341. |
| [9] | Liu Jinyu, Ding Yu, Jiang Qiang, Cui Hongpeng, Lu Zhengcao. A finite element model of full endoscope lumbar fenestration and biomechanical characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(27): 4291-4296. |
| [10] | Luo Jin, Lan Hai, Yan Yajing. Comparison of robot-assisted drilling decompression and traditional surgery for treatment of aseptic necrosis of femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(27): 4317-4321. |
| [11] | Chen Dongdong, Hao Yangquan, Zhang Gaokui, Li Huanhuan, Wang Qiuxia, Lu Chao. Three-dimensional printed navigation template assisted core decompression and bone grafting for treatment of ARCO stage II non-traumatic femoral head necrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(27): 4322-4327. |
| [12] | Jiang Shudong, Ren Longxi, Guo Han, Liang Dehua, Zhang Tongtong, Liu Zheng. Robot-assisted unilateral-decompression minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for radiographic bilateral lumbar stenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(24): 3797-3802. |
| [13] | Song Yancheng, Kang Liqing, Shen Canghai, Liu Fenghai, Feng Yongjian. Application of task-state fMRI in evaluating disease severity and prognosis of cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(21): 3341-3346. |
| [14] | Shen Canghai, Feng Yongjian, Song Yancheng, Liu Gang, Liu Zhiwei, Wang Ling, Dai Haiyang. Value of quantitative MRI T2WI parameters in predicting surgical outcome of thoracic ossification of the ligamentum flavum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(18): 2893-2899. |
| [15] | Jiang Qiang, Ding Yu, Liu Jinyu, Cao Shiqi, Lu Zhengcao. Finite element simulation and biomechanical analysis of fully endoscopic precisely laminectomy decompression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(12): 1891-1896. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||