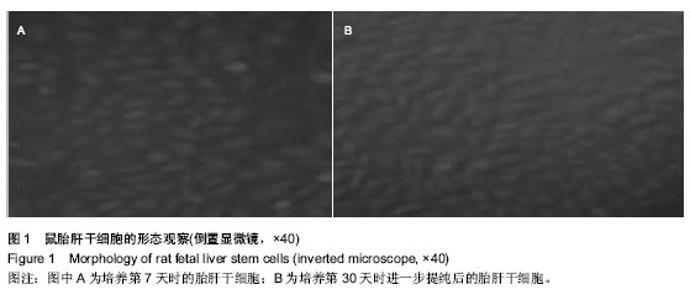
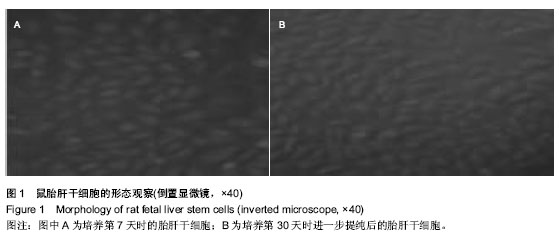
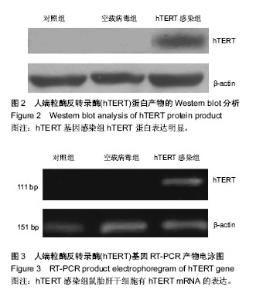
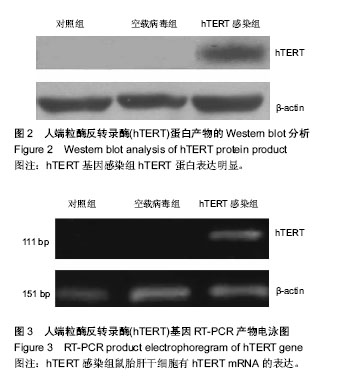
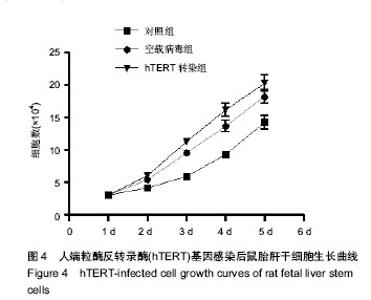
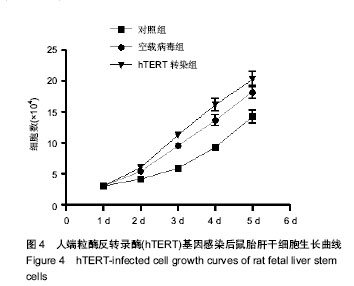
| [1] 王开利,迟淑萍,孙杰,等.外源hTERT基因对人肝细胞增殖及CYP45019A1表达的影响[J].军医进修学院学报, 2011,32(11): 1137-1138.
[2] 靳斌,王伟,刘泽阳,等.外源hTERT基因转染对老年大鼠供肝缺血再灌注损伤的防护作用[J].山东大学学报:医学版, 2013, 51(8):13-16.
[3] 孙来保,李成荣,文建明,等.反义hTERT基因对白血病细胞端粒酶表达及活性的抑制作用[J].中华病理学杂志,2004,33(5): 454-457.
[4] 刘云燕,裘秀春,张殿忠,等. hTERT 反义寡核苷酸对脊索瘤细胞周期及增殖的影响[J].现代肿瘤医学, 2011,19(10):1922-1924.
[5] Röth A, Vercauteren S, Sutherland HJ,et al.Telomerase is limiting the growth of acute myeloid leukemia cells.Leukemia. 2003;17(12):2410-2417.
[6] Akiyama M, Yamada O, Kanda N, et al. Telomerase overexpression in K562 leukemia cells protects against apoptosis by serum deprivation and double-stranded DNA break inducing agents, but not against DNA synthesis inhibitors. Cancer Lett. 2002;178(2):187-197.
[7] 肖扬,张洹.端粒酶HTR反义寡核苷酸对K562细胞端粒酶活性的影响[J].临床血液学杂志,2003,16(1):23 -25.
[8] 吴灵芝,李水彬,程刚卫,等. hTERT基因转染对人神经元活力的影响[J].赣南医学院学报,2014,34(2):170-173.
[9] 杨胜生,曾志勇,程先进,等.胸腺瘤组织中端粒酶活性检测的意义[J].现代肿瘤医学, 2010,18(3):505-506.
[10] 张晓辉,张建宁,康春生,等. hTERT正、反义表达载体转染大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的实验研究[J].中华神经医学杂志,2006,5(3): 217-221.
[11] Autexier C, Lue NF.The structure and function of telomerase reverse transcriptase.Annu Rev Biochem. 2006;75:493-517.
[12] Greider CW.Telomere length regulation.Annu Rev Biochem. 1996;65:337-365.
[13] Karlseder J, Smogorzewska A, de Lange T.Senescence induced by altered telomere state, not telomere loss.Science. 2002;295(5564):2446-2449.
[14] Yamada O, Mizoguchi H.Telomere and telomerase in the differentiation of leukemic cell lines.Nihon Rinsho. 1998;56(5): 1322-1327.
[15] 李梅凤,方美云,王一.质粒介导RNAi靶向hTERT抑制K562细胞端粒酶活性的研究[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2008,16(1):54-60.
[16] Park Y, Chen Y, Ordovas L,et al.Hepatic differentiation of human embryonic stem cells on microcarriers.J Biotechnol. 2014;174:39-48.
[17] Zamule SM, Coslo DM, Chen F, et al. Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells along a hepatic lineage.Chem Biol Interact. 2011;190(1):62-72.
[18] Ishkitiev N, Yaegaki K, Imai T, et al. High-purity hepatic lineage differentiated from dental pulp stem cells in serum-free medium. J Endod. 2012;38(4):475-480.
[19] 赵矫,曾永秋,税青林,等. siRNA表达载体对MCF-7细胞生长及其hTERT基因表达抑制的研究[J].解放军医学杂志,2008,33(3): 246-249.
[20] 张志宏,曾永秋,税青林,等. hTERT-siRNA表达载体的构建及对MCF-7细胞生长、端粒酶活性的抑制作用[J].解放军医学杂志, 2007,32(6):561-564.
[21] 张洁,廖亚平,吴灵芝,等. hTERT基因转染对人胚胎大脑皮质神经元生长的影响[J].解剖学研究,2008,30(4):251-254,260.
[22] 孙冰,安靓. 胎肝干细胞的分离、培养与鉴定[J]. 中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志, 2006, 15(1): 49-53.
[23] 李宏良,曾荣香,陈鹏,等.清毒片和hTERT反义核酸对HL-60细胞增殖及凋亡的协同作用[J].辽宁中医杂志,2010,7(3):395-398.
[24] 宋扬,徐韬,杨明坤,等. RNA干扰端粒酶反转录酶基因慢病毒表达载体的构建及鉴定[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2014,18(11): 1724-1729.
[25] 万世奇,张太平,王天笑.重组腺相关病毒载体表达抗表皮生长因子受体抗体对胰腺癌细胞株抑制作用的研究[J].中华消化外科杂志,2011,10(4):286-289. |