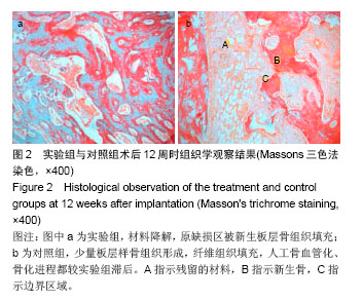
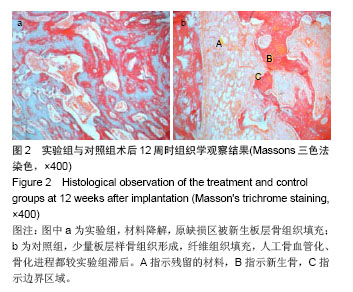
| [1]Nandi SK,Kundu B,Ghosh SK,et al.Efficacy of nano –hydroxyapatite prepared by an aqueous solution combustion technique in healing bone defects of goat.JVet Sci.2007; 9(2): 183-191.
[2]Yuan J,Cui L,ZhangWJ,et al.Repair of canine mandibularbone defects with bone marrow stromal cells and porous β- tricalciumphosphate. Biomaterial.2007;28(6):1005-1013.
[3]Nishida J,Shimamura T.Methods of reconstruction for bone defects after tumor excision:a review of alternatives .Med Sci Monit.2008;14 (8):107-113.
[4]Nuttelman CR,Tripodi MC,Anseth KS.In vitro osteogenic differentiation of hum an m esenchym al stem cells photoencapsulated in PEG hydrogels.J Biomed Mater Res A.2004;68(4):773-782.
[5]Li X ,Li D,Wang L,et al.Developm ent of rotating perfusion bioreactor system and application for bone tissue engineering. ShengWu YiXue Gong Cheng Xue ZaZhi.2007;24(1):66-70.
[6]Walsh WR,Chapman-Shath PJ,Cain S,et al.A resorbable porous ceramic composite bone graft substitute in a rabbit metaphyseal defect model.J Orthop Res.2003;21:655-661.
[7]GauthierO,Biox D,Grimandi G,et al.A new injectable calcium phosphate biomaterial for immediate bone filling of extraction sockets.J Periodontol.1999;70(4):375-383.
[8]Kelly CM,Wilkins RM,Gitelis S,et al. he use of a surgical grade calcium sulfate as a bone graft substitute: results of a multicenter trial. Clin Orthop.2001; 382:42-50.
[9]Cabañas MV,Rodriguez-Lorenzo LM,Vallet-Regi M.Setting behavior and in vitro bioactivity of hydroxypatite/calcium sulfate cements.Chem Mater.2002;14:3550-3555.
[10]Shigeru S,Tomihisa K,Tomoyuki S.Osteogenic response of rabbit tibia to hydroxyapatite particle-Plaster of Paris mixture. Biomaterials.1998;19:1895-1900.
[11]武海军,银和平,李树文,等.密度梯度离心和贴壁筛选法分离培养兔骨髓间充质干细胞的形态学观察[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版), 2012,6(22):7261-7265.
[12]Brandoff JF,Silber JS,Vaccaro AR.Contemporary alternatives to synthetic bone grafts for spine surgery. J Orthop Am. 2008; 37(3):410-414.
[13]Maier S,Pelin I,Bulacovschi V.Study on an injectable biomimetic hydroxyapatite-atelocollagen composite.Rev Med Chi Soc Med Nat Iasi.2007;111(4):1079-1083.
[14]Drosse I,Volkmer E,Capanna R,et al.Tissue engineering for bone defect healing:an update on a mlti-component approach. Injury.2008;39(2):9-20.
[15]Cynthia MK,Ross MW.Treatment of benign bone lesions with an injectable calcium sulfate2based bone graft substitute. Orthopedics.2004;27(1):119-122.
[16]Frame JW.Ridge augmentation using solid and porous hydroxyapatite particles with and without autogenous bone or plaster.J Oral Maxiallofac Surg.1987;45:771-777.
[17]葛亮,苟三怀,杨四川,等.注射式复合纳米人工骨的生物相容性和降解性能的实验研究[J].第二军医大学学报,2006,27(10): 1121-1126.
[18]Dominique J,Reza S,David V,et al.SchaefferChitosan scaffolds: Interconnective pore size and cartilage engineering. Acta Biomaterialia.2006;2(3):313-320.
[19]Wang A,Ao Q,Cao W,et al.Porous chitosan tubular scaffolds withknitted outer wall and controllable inner structure for nerve tissueengineering.J Biomed Mater Res A.2006;79(1): 36-46.
[20]Manjubala I,Scheler S,Bssert J,et al.Mineralisation of chitosan scaffolds with nano-apatite formation by double diffusion technique.Atca Biomater.2006;2(1):75-84.
[21]张民,王建生,卫小春,等.不同配方可注射性羟基磷灰石E硫酸钙骨替代材料的性能分析[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(10):69-71.
[22]Rosset P,Deschaseaux F,Layrolle P.Celltherapyfor bone repair.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res.2014;100(1 Suppl): S107-112.
[23]Tobita M,Mizuno H.Adipose-derived stem cells and periodontal tissue engineering.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2013;28(6):e487-493.
[24]Manialopoulos C, Scdek J,Meleher AH.Boneformationin vitro by stromal cells obtained from boneof young adult rats.Cell TissueRes.1988;254(2):317-330.
[25]杨志明,余希杰,解慧琪,等.不同来源成骨细胞生物特性的比较研究[J].中华创伤杂志,2001,17(1):10-13.
[26]尹战海,韩建,刘淼,等.骨髓间充质干细胞复合骨基质明胶构建组织工程化软骨[J].中华骨科杂志,2005,25(12):170-175.
[27]杨强,彭江,卢氏璧,等.组织工程骨软骨复合体修复犬膝关节负重区骨软骨缺损的实验研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2009,29(5): 480-486. |