Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (19): 3082-3087.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.19.021
Previous Articles Next Articles
Biological characters of mesenchymal stem cells separated from different components of human placenta
Hong Yan, Huo Si-wei, Lu Yao, Zhang Yi
- Shanghai Cord Blood Bank, Shanghai Stem Cell Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai 201815, China
-
Revised:2014-03-07Online:2014-05-07Published:2014-05-07 -
About author:Hong Yan, Master, Shanghai Cord Blood Bank, Shanghai Stem Cell Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai 201815, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hong Yan, Huo Si-wei, Lu Yao, Zhang Yi. Biological characters of mesenchymal stem cells separated from different components of human placenta[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(19): 3082-3087.
share this article
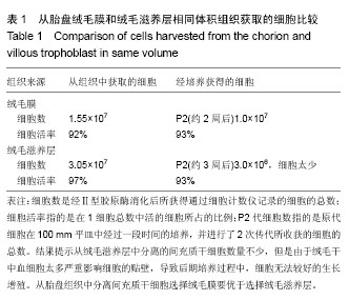
2.1 胎盘间充质细胞的分离及传代培养 从绒毛膜和绒毛滋养层分离细胞的原代及传代扩增培养比较:实验结果表明通过用Ⅱ型胶原酶消化相同体积的绒毛膜和绒毛滋养层都能够得到较均一的胎盘间充质干细胞(表1)。结果表明,相同体积的绒毛膜与绒毛滋养层在原代分离时,绒毛滋养层分离得到的细胞数,超过了绒毛膜分离得到的细胞数,但经过一段时间的培养,由于绒毛滋养层原代分离时,残留的血细胞太多,严重影响了间充质干细胞的贴壁和后续培养,从而导致绒毛滋养层组织细胞分离培养后,无法得到丰富的间充质干细胞,而绒毛膜在清洗的时候可以较为容易的清洗干净,残留的血细胞较少,经培养后得到丰富且状态较好的间充质干细胞。虽有些文献中提出可以添加红细胞裂解液处理,但是考虑到后续处理以及临床要求,这种处理方式是不可取的,故以上结果表面从胎盘组织中分离间充质干细胞选择绒毛膜要优于选择绒毛滋养层。"
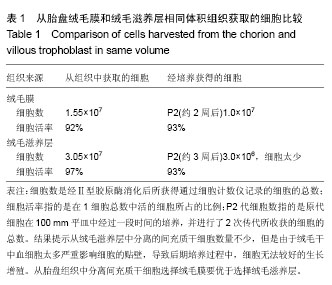
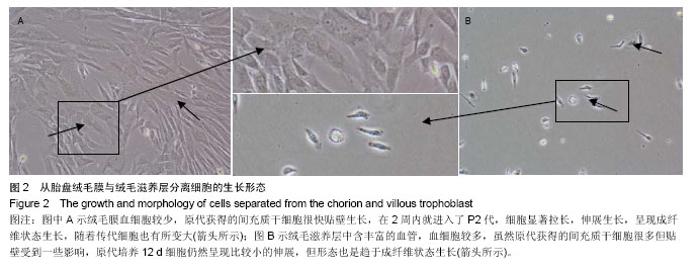
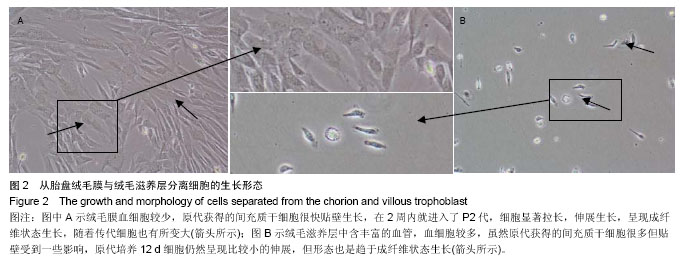
从绒毛膜和绒毛滋养层分离细胞形态比较:倒置相差显微镜下观察,原代细胞接种48 h后,大部分细胞贴壁,形态为典型成纤维细胞样,以长梭形为主,大量细胞呈涡旋状生长,未贴壁细胞圆而亮。其中图2A是从胎盘绒毛膜中分离的间充质干细胞经12 d的培养,细胞已经达到P2代,已经进行了至少2代的扩增繁殖,从图片上可以看出细胞仍然保留间充质干细胞的生长形态;图2B是从同一胎盘中同时期取绒毛滋养层组织分离的间充质干细胞,经12 d的培养,细胞量仍然很少。从绒毛膜中分离的原代间充质干细胞培养7 d左右,可见细胞克隆显著增多并融合成片,即可进行传代。传代培养的细胞接种2-4 h 即可贴壁。传代初期细胞形态以长梭形成纤维细胞为主[31-33]。图2表明采集绒毛膜分离的细胞干净,生长快速,而绒毛滋养层组织中分离得到的原代的间充质干细胞经12 d的培养,细胞仍然很稀少,需要更多时间的培养,由此可见绒毛膜分离的间充质干细胞在细胞后续扩增培养研究方面具有很大优势。究其原因,推测可能是绒毛滋养层血细胞含量高,严重影响了间充质干细胞的贴壁生长,导致后期生长受限制,从前期的分离数据看无论是从绒毛膜还是从绒毛滋养层组织都能得到一定数量的细胞,但在后续培养过程中,从表1和图2表明从绒毛膜分离的间充质干细胞悬液在接种后更易培养。"
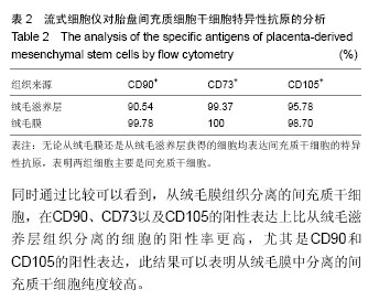
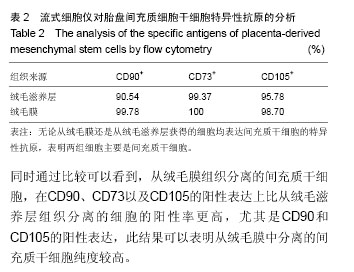
2.2 胎盘间充质细胞干细胞特异性抗原的鉴定 为了进一步鉴定胎盘间充质细胞的干细胞特性,对胎盘间充质细胞进行了干细胞特异性表面抗原的鉴定。利用流式细胞仪对胎盘间充质细胞表面分子CD90、CD73、CD105进行分析,结果表明,胎盘间充质细胞表达CD90、CD73、CD10等间充质干细胞表面标志[34],证明其具有间充质干细胞特性(表2)。表2显示了从绒毛膜以及绒毛滋养层组织中分离间充质干细胞的CD90、CD73以及CD105的阳性表达率,结果表明无论是从绒毛滋养层还是从绒毛膜组织中分离的细胞,它们的CD90、CD73以及CD105的阳性率都在90%以上,充分说明分离得到的细胞具有间充质干细胞的特性。同时通过比较可以看到,从绒毛膜组织分离的间充质干细胞,在CD90、CD73以及CD105的阳性表达上比从绒毛滋养层组织分离的细胞的阳性率更高,尤其是CD90和CD105的阳性表达,此结果可以表明从绒毛膜中分离的间充质干细胞纯度较高。"
| [1] Raggi C, Berardi AC. Mesenchymal stem cells, aging and regenerative medicine. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2012; 2(3):239-242. [2] Zhang L, Tan X, Dong C, et al.In vitro differentiation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hUCMSCs), derived from Wharton's jelly, into choline acetyltransferase (ChAT)-positive cells. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2012;30(6): 471-477. [3] Datta I, Mishra S, Mohanty L, et al.Neuronal plasticity of human Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stromal cells to the dopaminergic cell type compared with human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells.Cytotherapy. 2011;13(8):918-932. [4] Zhang HT, Fan J, Cai YQ, et al. Human Wharton's jelly cells can be induced to differentiate into growth factor-secreting oligodendrocyte progenitor-like cells.Differentiation. 2010; 79(1):15-20. [5] Peng J, Wang Y, Zhang L, et al. Human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into a Schwann-cell phenotype and promote neurite outgrowth in vitro. Brain Res Bull. 2011;84(3):235-243. [6] Shevde N. Stem Cells: Flexible friends. Nature. 2012; 483 (7387):S22-26. [7] Thomas KE, Moon LD. Will stem cell therapies be safe and effective for treating spinal cord injuries? Br Med Bull.2011; 98:127-142. [8] Bao X, Feng M, Wei J, et al. Transplantation of Flk-1+ human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells promotes angiogenesis and neurogenesis after cerebral ischemia in rats. Eur J Neurosci. 2011;34(1):87-98. [9] 刘秀梅,初清,衣明纪,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗Tourette综合征大鼠实验研究[J].中华行为医学与脑科学杂志,2011,20(11): 990-992. [10] 郭淑艳,王华.实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎相关的神经干细胞研究进展[J].国际儿科学杂志,2008,35(2):165-167. [11] 陈国军,方凤,汤永华,等.干细胞治疗脑疾病国内临床资料荟萃分析[J].武警医学,2011,22(3):216-219. [12] Olson SD, Pollock K, Kambal A,et al.Genetically engineered mesenchymal stem cells as a proposed therapeutic for Huntington's disease. Mol Neurobiols.2012;45(1):87-98. [13] Vogel G. Europe: Dismay, confusion greet human stem cell patent ban.Science.2011;334(6055):441-442. [14] Banas A. Purification of adipose tissue mesenchymal stem cells and differentiation toward hepatic-like cells.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;826:61-72. [15] Sacchetti B, Funari A, Michienzi S, et al. Self-renewing osteoprogenitors in bone marrow sinusoids can organize a hematopoietic microenvironment. Cell. 2007;131(2):324-336. [16] Aziz Aly LA, Menoufy HE, Ragae A, et al. Adipose stem cells as alternatives for bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in oral ulcer healing.Int J Stem Cells. 2012;5(2):104-114. [17] 徐志国,刘超,闫铭杰. 人胎盘来源干/祖细胞生物学特性研究进展[J].转化医学杂志,2013,2(6):336-340. [18] 韩忠朝. 胎盘间充质干细胞移植治疗糖尿病足安全有效[J].中华医学信息导报,2012,27(22):19. [19] Ringden O, Keating A. Mesenchymal stromal cells as treatment for chronic GVHD. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2011; 46(2):163-164. [20] Chai M, Barker G, Menon R, et al.Increased oxidative stress in human fetal membranes overlying the cervix from term non-labouring and post labour deliveries.Placenta. 2012; 33(8):604-610. [21] Fukuchi Y, Nakajima H, Sugiyama D,et al.Human placenta-derived cells have mesenchymal stem/progenitor cell potential.Stem Cells. 2004;22(5):649-658. [22] Cunningham FG, MacDonald PC, Gant MF, et al. The placenta and fetal membranes. In: Williams Obstetrics. 20th ed. Stamford, CT: Appleton and Lange. 1997:95-125. [23] Benirschke K, Kaufmann P. Pathology of the human placenta. New York: Springer-Verlag, 2000:42-46, 116, 281-297. [24] 穆晓红,徐林,赵子义,等.人胎盘与骨髓源性间充质干细胞体外培养及生物学特性对比[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009, 13(19):3708-3712. [25] Wang L, Yang Y, Zhu Y, et al.Characterization of placenta- derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in autologous human cord blood serum.Mol Med Rep. 2012;6(4):760-766. [26] 姚旺祥,裴国献,刘勇. 兔胎盘源性间充质干祖细胞的分离方法比较[J].生物医学工程与临床,2007,11(2):85-87. [27] 任红英,赵钦军,刘拥军,等.脐带间充质干细胞体外诱导分化为肝细胞样细胞的研究[J].山东医药,2008,48(30):24-26. [28] Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al.Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006; 8(4):315-317. [29] 周新伏,旷文勇,罗自勉,等.脐带血清体外培养临床用人骨髓间充质干细胞的方法研究[J].临床血液学杂志,2008,21(9):477-480. [30] Wei JP,Zhang TS,Kawa S,et al.Human amnion-isolated cells normalize blood glucose in streptozotocin-Induced diabetic mice.Cell Transplant. 2003;12:545-552. [31] Portmann-Lanz CB, Schoeberlein A, Huber A, et al. Placental mesenchymal stem cells as potential autologous graft for pre- and perinatal neuroregeneration. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006; 194:664-673. [32] Zhang X, Mitsuru A, Igura K, et al. Mesenchymal progenitor cells derived from chorionic villi of human placenta for cartilage tissue engineering. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;340:944-952. [33] Soncini M, Vertua E, Gibelli L, et al. Isolation and characterization of mesenchymal cells from human fetal membranes. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2007;1:296-305. [34] 万振洲,冯亚松,彭海林,等. 体外诱导胎盘间充质干细胞向表皮细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(49): 9223-9226. [35] In’t Anker PS,Scherjon SA,Kleijburg - van der Keur C,et al. Isolation of mesenchymal stem cells of fetal or maternal origin from human placenta. Stem Cells. 2004;22: 1338-1345. [36] 杜莉莉,金玉楠,李昆,等.胎盘来源的间充质干细胞体外分离培养及向软骨细胞分化的研究[J].解剖学进展,2008,14(1):83-86. [37] Lott JP, Savulescu J. Towards a global human embryonic stem cell bank. Am J Bioeth. 2007;7(8):37-44. [38] 连霞.骨髓间充质干细胞生物学特性及其多向分化潜能的理论基础和机制[J].临床医药实践杂志,2006,15(3):163-165. [39] Mattsson J. Recent progress in allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2008;10(4) :343-349. [40] Bojani? I,Golubi? Cepuli? B.Umbilical cord blood as a source of stem cells.Acta Med Croatica.2006;60(3):215-225. |
| [1] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [2] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [3] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [6] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [8] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [9] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [10] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [12] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [13] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| [14] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [15] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||