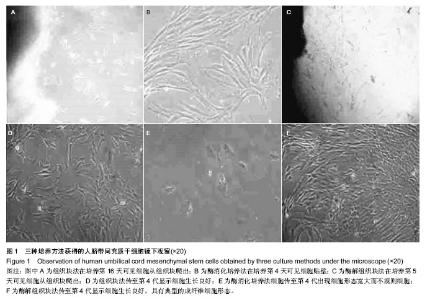
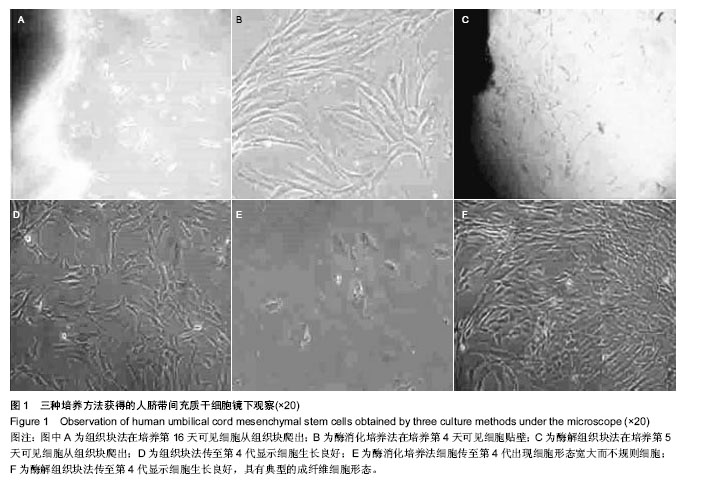
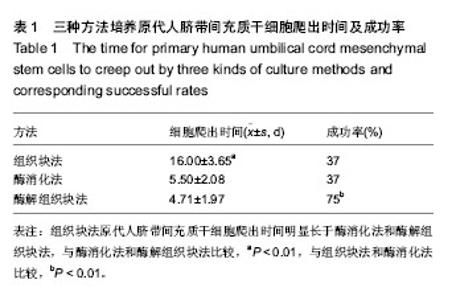
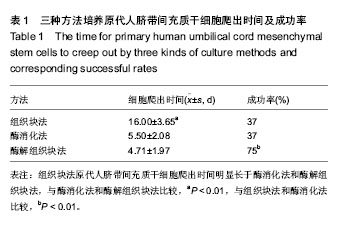
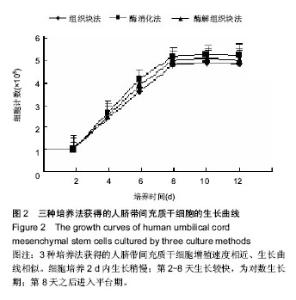
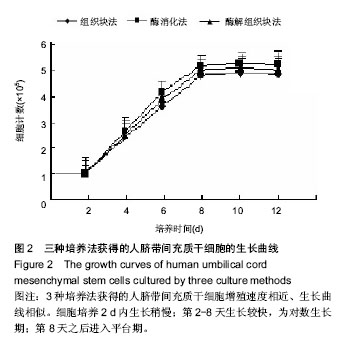
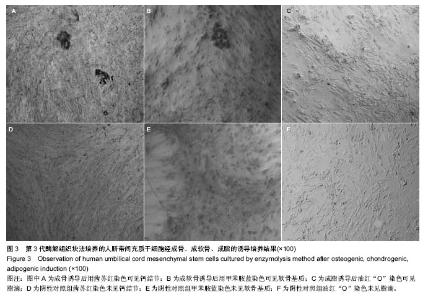
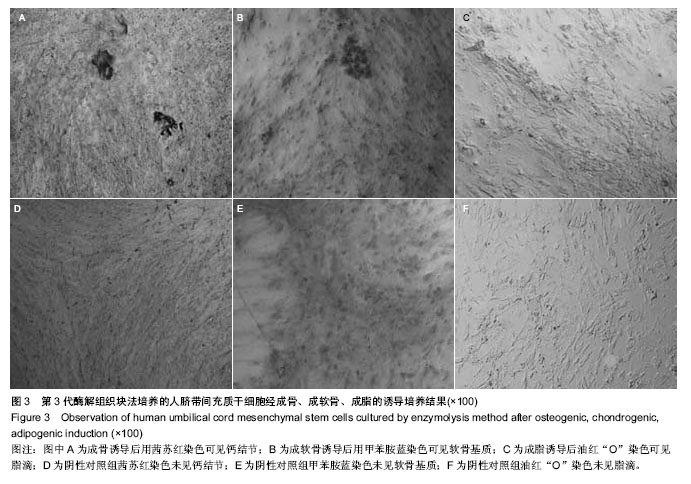
| [1] Zhao L, Weir MD, Xu HH.An injectable calcium phosphate-alginate hydrogel-umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell paste for bone tissue engineering.Biomaterials.2010; 31: 6502-6510.
[2] Mitchell KE, Weiss ML, Mitchell BM,et al.Matrix cells from Wharton's jelly form neurons and glia. Stem Cells.2003;21: 50-60.
[3] Diao Y, Ma Q, Cui F, et al.Human umbilical cord esenchymal stem cells :Osteogenesis in vivo as seed cells for bone tissue engineering.J Biomed Mater Res.2009;91A: 123–131.
[4] Balci D, Can A. The assessment of cryopreservation conditions for human umbilical cord stroma-derived mesenchymal stem cells towards a potential use for stem cell banking. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther.2013;8 (1): 60-72.
[5] Hu L,Hu J,Zhao J,et al.Side-by-side comparison of the biological characteristics of human umbilical cord and adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biomed Res Int.2013; 2013: 438243.
[6] Kim SM, Moon SH, Lee Y, et al.Alternative xeno-free biomaterials derived from human umbilical cord for the self-renewal ex-vivo expansion of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev.2013;22 (22): 3025-3038.
[7] Lonne M, Lavrentieva A, Walter JG, et al. Analysis of oxygen-dependent cytokine expression in human mesenchymal stem cells derived from umbilical cord. Cell Tissue Res.2013;353 (1): 117-122.
[8] Tanaka K, Iwasaki K, Feghali KE,et al.Comparison of characteristics of periodontal ligament cells obtained from outgrowth and enzyme-digested culture methods.Arch Oral Biol. 2011;56 (4): 380-388.
[9] 胡军,陈新民,麻健丰.人牙周膜成纤维细胞原代培养的研究[J]. 现代口腔医学杂志,2002, 16 (2): 176-177.
[10] 江龙,朱亚琴.改良组织块法体外培养人牙周膜细胞和牙髓细胞[J]. 牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志, 2008, 18 (4): 195-199.
[11] Wang HS, Hung SC, Peng ST.Mesenchymal stem cells in the Wharton's jelly of the human umbilical cord. Stem Cells.2004; 22:1330-1337.
[12] Massood E, Maryam K, Parvin S, et al. Vitrification of human umbilical cord wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Cryo Letters.2013;34 (5): 471-480.
[13] Meng HB, Gong J, Zhou B, et al.Therapeutic effect of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in rat severe acute pancreatitis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.2013;6 (12): 2703-2712.
[14] Wu KH, Tsai C, Wu HP, et al. Human application of ex vivo expanded umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells: enhance hematopoiesis after cord blood transplantation. Cell Transplant.2013;22 (11): 2041-2051.
[15] Wu S, Ju GQ, Du T, et al. Microvesicles derived from human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells attenuate bladder tumor cell growth in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One.2013;8 (4): e61366.
[16] Yang H, Yang H, Xie Z, et al.Systemic transplantation of human umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells-educated T regulatory cells improved the impaired cognition in AbetaPPswe/PS1dE9 transgenic mice. PLoS One.2013;8 (7): e69129.
[17] Zhang Y, Zhang M, Zhao S, et al.Effects of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells on anterior chamber-associated immune deviation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013;15 (1): 114-120.
[18] Zhu SF, Zhong ZN, Fu XF, et al.Comparison of cell proliferation, apoptosis, cellular morphology and ultrastructure between human umbilical cord and placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Neurosci Lett.2013;541: 77-82.
[19] Hou T, Xu J, Wu X,et al.Umbilical Cord Wharton's Jelly: A New Potential Cell Source of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells for Bone Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng Part A.2009;15(9): 2325-2334.
[20] Schugar RC, Chirieleison SM, Wescoe KE,et al.High Harvest Yield, High Expansion, and Phenotype Stability of CD146 Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from Whole Primitive Human Umbilical Cord Tissue.J Biomed Biotechnol.2009;2009: 1-11. |