Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (19): 3017-3022.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.19.011
Previous Articles Next Articles
Growth factors promote the therapeutical effects of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on acute myocardial infarction
Wen Ti1, Qi Xun2
- 1Department of Medical Oncology, 2Laboratory of Radiology and Intervention, the First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110001, Liaoning Province, China
-
Revised:2014-03-01Online:2014-05-07Published:2014-05-07 -
About author:Wen Ti, M.D., Lecturer, Department of Medical Oncology, the First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110001, Liaoning Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wen Ti, Qi Xun. Growth factors promote the therapeutical effects of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on acute myocardial infarction[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(19): 3017-3022.
share this article
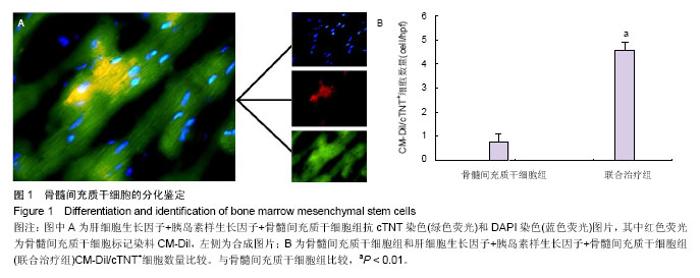
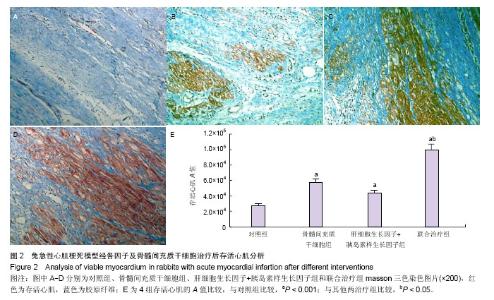
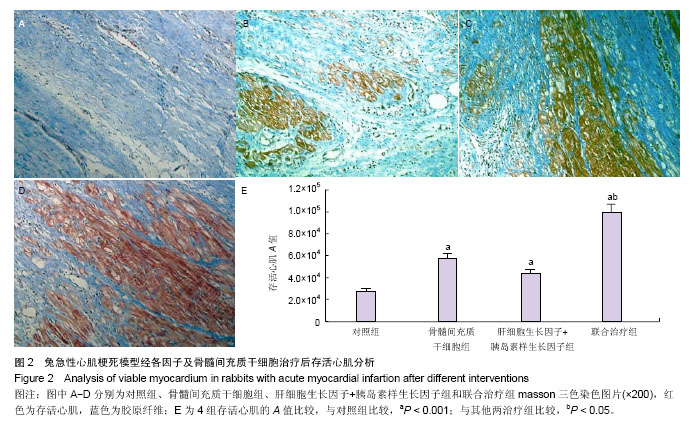
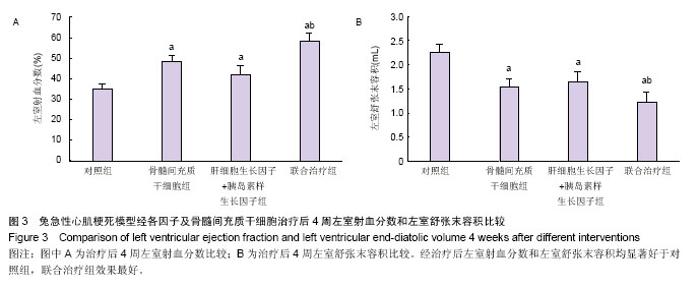
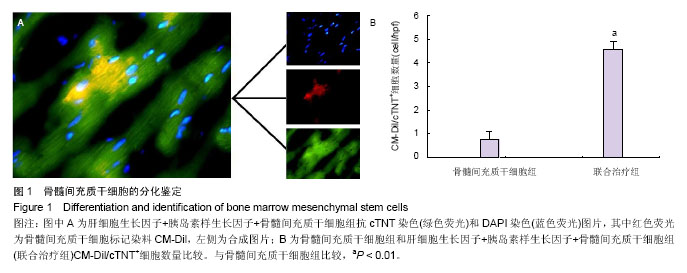
2.1 实验动物数量分析 共纳入31只实验动物,3只因左前降支结扎后发生心室颤动死亡,未进入实验分组;局部注射过程中无恶性心律失常及血流动力学紊乱事件。 2.2 干细胞分化鉴定 4周后的免疫荧光染色发现,在骨髓间充质干细胞组中只有少量的CM-Dil/cTNT+细胞(0.8±0.3)个/高倍视野,而在联合治疗组中这些细胞明显增多(4.6±0.3)个/高倍视野(P < 0.001,图1),提示移植的骨髓间充质干细胞心肌细胞样分化明显增加。 心肌存活评价:4周后,骨髓间充质干细胞组存活心肌面积A值为57 651±4 621、肝细胞生长因子+胰岛素样生长因子组存活心肌面积A值为43 790±4 339、联合治疗组存活心肌面积A值为99 319±7 518,均明显高于对照组 27 716±2 293(P < 0.05,图2)。且联合治疗组明显高于其他两治疗组(P < 0.001)。 心功能结果:4周后,骨髓间充质干细胞组左室射血分数为(48±3)%,肝细胞生长因子+胰岛素样生长因子组为(42±4)%,明显高于对照组(35±2)%(P < 0.05,图3A)。而联合治疗组(58±4)%明显高于其他两治疗组(P < 0.01)。在全部4组中,联合治疗组左室舒张末容积改善最为明显为(1.23±0.19) mL(P < 0.05),与对照组(2.24±0.18) mL相比,骨髓间充质干细胞组(1.52±0.17) mL和肝细胞生长因子+胰岛素样生长因子组(1.66±0.16) mL亦有明显改善(P < 0.01),差异有显著性意义(图3B)。"
| [1] 刘玉清,王瑶,周丽珍,等. 干细胞移植在心肌梗死中的应用研究进展[J].泸州医学院学报,2013,36(6):644-647. [2] 刘满江,胡雪松. 心肌梗死的干细胞移植治疗新进展[J].中国医学文摘:内科学,2006,27(4):308-310. [3] 马群兴,李彤,赵越,等.脐带间充质干细胞与脐血CD34+细胞联合移植治疗心肌梗死[J].中华胸心血管外科杂志,2014, 30(2): 82-85. [4] 赵媛媛,曹文明,马洁,等.构建大鼠急性心肌梗死模型并初步探讨人脐带间充质干细胞的修复作用[J].临床检验杂志,2013,31(12): 919-922. [5] 陈各才,岳爱环,阮中宝,等. 间充质干细胞治疗心肌梗死研究进展[J]. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2014,15(1):98-99. [6] 沈利水,屈百鸣. 骨髓间充质干细胞修复心肌损伤的研究进展[J]. 心脏杂志,2013,24(5):620-622. [7] Liechty KW, MacKenzie TC, Shaaban AF, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells engraft and demonstrate site-specific differentiation after in utero transplantation in sheep. Nat Med.2000;6(11):1282-1286. [8] Li Y, Hiroi Y, Ngoy S, et al. Notch1 in bone marrow-derived cells mediates cardiac repair after myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2011;123(8):866-876. [9] Balsam LB,Wagers AJ, Christensen JL, Kofidis T, Weissman IL, Robbins RC. Haematopoietic stem cells adopt mature haematopoietic fates in ischaemic myocardium. Nature. 2004; 428(6983):668-673. [10] Nygren JM, Jovinge S, Breitbach M, et al. Bone marrow-derived hematopoietic cells generate cardiomyocytes at a low frequency through cell fusion, but not transdifferentiation. Nat Med. 2004;10(5):494-501. [11] Scherschel JA, Soonpaa MH, Srour EF, et al. Adult bone marrow–derived cells do not acquire functional attributes of cardiomyocytes when transplanted into peri-infarct myocardium. Mol Ther. 2008;16:1129-1137. [12] Lunde K, Solheim S, Aakhus S, et al. Intracoronary injection of mononuclear bone marrow cells in acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1199-209. [13] Murry CE, Soonpaa MH, Reinecke H, et al. Haematopoietic stem cells do not transdifferentiate into cardiac myocytes in myocardial infarcts. Nature 2004;428(6983):664-668. [14] Potapova IA, Brink PR, Cohen IS, et al. Culturing of human mesenchymal stem cells as three-dimensional aggregates induces functional expression of CXCR4 that regulates adhesion to endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(19): 13100-13107. [15] Zhang GW, Liu XC, Li-Ling J, et al. Mechanisms of the protective effects of BMSCs promoted by TMDR with heparinized bFGF-incorporated stent in pig model of acute myocardial ischemia. J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15(5):1075-1086. [16] 王欢,邓丽群,王亚利,等.骨髓间充质干细胞通过旁分泌作用治疗大鼠心肌梗死[J].中华移植杂志(电子版),2013,7(2):27-30. [17] 徐信群,王泉兰,应国秋,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植对心肌梗死大鼠损伤心肌的修复效果[J].南昌大学学报:医学版,2013, 53(6):1-4,21. [18] 赵勇,哈小琴,张秋珊.肝细胞生长因子对冠心病患者外周血内皮祖细胞迁移、粘附功能的影响[J].标记免疫分析与临床, 2013, 20(5):281-284. [19] 王钟情,李爱丽.胰岛素生长因子-1在缺血性脑血管病中的研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志,2013,33(14):3529-3531. [20] Ellison GM, Torella D, Dellegrottaglie S, et al. Endogenous cardiac stem cell activation by insulin-like growth factor-1/hepatocyte growth factor intracoronary injection fosters survival and regeneration of the infarcted pig heart. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;58(9):977-986. [21] Li Z, Gu TX, Zhang YH. Hepatocyte growth factor combined with insulin like growth factor-1 improves expression of GATA-4 in mesenchymal stem cells cocultured with cardiomyocytes. Chin Med J (Engl).2008;121(4):336-340. [22] Xia CS, Zuo AJ, Wang CY, et al. Isolation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells using density gradient centrifugation and adherence screening methods. Minerva Med. 2013;104(5):519-525. [23] Qu Z, Xu H, Tian Y, et al. Atorvastatin improves microenvironment to enhance the beneficial effects of BMSCs therapy in a rabbit model of acute myocardial infarction. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013;32(2):380-399. [24] Yuan SH, Gao CB, Yin CU, et al. Recombinant adeno-associated virus BMP-4/7 fusion gene confers ossification activity in rabbit bone marrow stromal cells. Genet Mol Res. 2012;11(3):3105-3114. [25] Zhang GW, Wen T, Gu TX, et al. Transmyocardial drilling revascularization combined with heparinized bFGF-incorporating stent activates resident cardiac stem cells via SDF-1/CXCR4 axis. Exp Cell Res. 2012;318(4): 391-399. [26] Yang J, Xia J, He Y, et al. MSCs transplantation with application of G-CSF reduces apoptosis or increases VEGF in rabbit model of myocardial infarction. Cytotechnology. 2013. [Epub ahead of print] [27] Zhang YH, Zhang GW, Gu TX, et al. Exogenous basic fibroblast growth factor promotes cardiac stem cell-mediated myocardial regeneration after miniswine acute myocardial infarction. Coron Artery Dis. 2011;22(4):279-285. [28] Li T, Ma Q, Ning M, et al. Cotransplantation of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells and umbilical cord blood-derived CD34<sup>+</sup> cells in a rabbit model of myocardial infarction. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014; 387(1-2):91-100. [29] Song MB, Yu XJ, Zhu GX, et al. Transfection of HGF gene en- hances endothelial progenitor cell(EPC) function and improves EPC transplant efficiency for balloon-induced arterial injury in hyperchol- esterolemic rats. Vascul Pharmaco1. 2009;51(2-3):205-213. [30] 杨虹,邓成国,柯奇周,等. 胰岛素样生长因子1基因转染胚胎干细胞诱导分化的心肌细胞移植治疗心肌梗死[J]. 解剖学杂志, 2012, 35(4):444-447. [31] Stehlik J, Edwards LB, Kucheryavaya AY, et al. The Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: twenty-seventh official adult heart transplant report--2010. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2010;29(10):1089- 1039. [32] Karciauskaite D, Grybauskiene R, Grybauskas P, et al. Brain na- triuretic peptide and other cardiac markers in predicting left ven tricular remodeling in patients with the first myocardial infarction. Medicina. 2004;40(10):949-956. [33] 李卓,谷天祥,张玉海.同种异体骨髓间充质干细胞单独及联合生长因子移植对兔梗死心肌心功能的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(19):3781-3784. [34] Huang XP, Sun Z, Miyagi Y, et al. Differentiation of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells induces immunogenicity and limits their long-term benefits for myocardial repair. Circulation. 2010;122(23):2419-2429. [35] Kim JS, Hwang HY, Cho KR, et al. Intramyocardial transfer of hepatocyte growth factor as an adjunct to CABG: phase I clinical study. Gene Ther. 2013;20(7):717-722. [36] Blumenthal B, Poppe A, Golsong P, et al. Functional regeneration of ischemic myocardium by transplanted cells overexpressing stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1): intramyocardial injection versus scaffold-based application. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011;40(4):e135-141. [37] Kuku?a K, Chojnowska L, D?browski M, et al. Intramyocardial plasmid-encoding human vascular endothelial growth factor A165/basic fibroblast growth factor therapy using percutaneous transcatheter approach in patients with refractory coronary artery disease (VIF-CAD).Am Heart J. 2011;161(3):581-589. [38] Li Y, Takemura G, Kosai K, et al. Postinfarction treatment with an adenoviral vector expressing hepatocyte growth factor relieves chronic left ventricular remodeling and dysfunction in mice. Circulation. 2003;107:2499-2506. [39] Wang PP, Xie DY, Liang XJ, et al. HGF and direct mesenchymal stem cells contact synergize to inhibit hepatic stellate cells activation through TLR4/NF-kB pathway. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43408. [40] Ha XQ, Lü TD, Hui L, et al. Effects of mesenchymal stem cells transfected with human hepatocyte growth factor gene on healing of burn wounds.Chin J Traumatol. 2010;13(6): 349-355. [41] Sun S, Chen G, Xu M, et al. Differentiation and Migration of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Transplanted through the Spleen in Rats with Portal Hypertension. PLoS One. 2013; 8(12):e83523. [42] Mangi AA, Noiseux N, Kong D, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells modified with Akt prevent remodeling and restore performance of infarcted hearts. Nat Med. 2003;9:1195-1201. [43] Muraski JA, Rota M, Misao Y, et al. Pim-1 regulates cardiomyocyte survival downstream of Akt. Nat Med. 2007;13: 1467-1475. [44] Nelson DM, Hashizume R, Yoshizumi T, et al. Intramyocardial injection of a synthetic hydrogel with delivery of bFGF and IGF1 in a rat model of ischemic cardiomyopathy. Biomacromolecules. 2014;15(1):1-11. [45] Ibarra C, Vicencio JM, Estrada M, et al. Local control of nuclear calcium signaling in cardiac myocytes by perinuclear microdomains of sarcolemmal insulin-like growth factor 1 receptors.Circ Res. 2013;112(2):236-245. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [4] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [5] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [6] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [7] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [8] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [9] | Li Shanshan, Guo Xiaoxiao, You Ran, Yang Xiufen, Zhao Lu, Chen Xi, Wang Yanling. Photoreceptor cell replacement therapy for retinal degeneration diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [10] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [11] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [12] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [13] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [14] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [15] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||