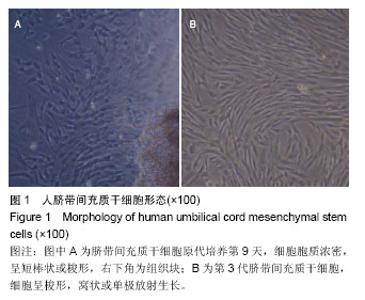
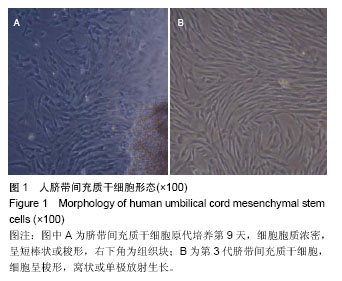
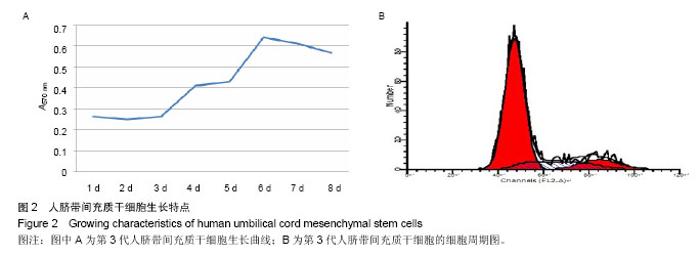
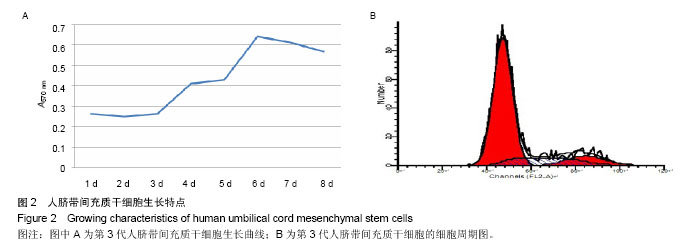
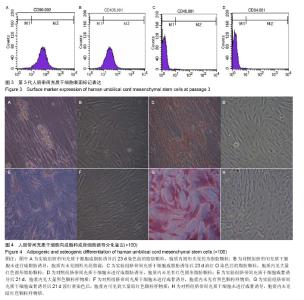
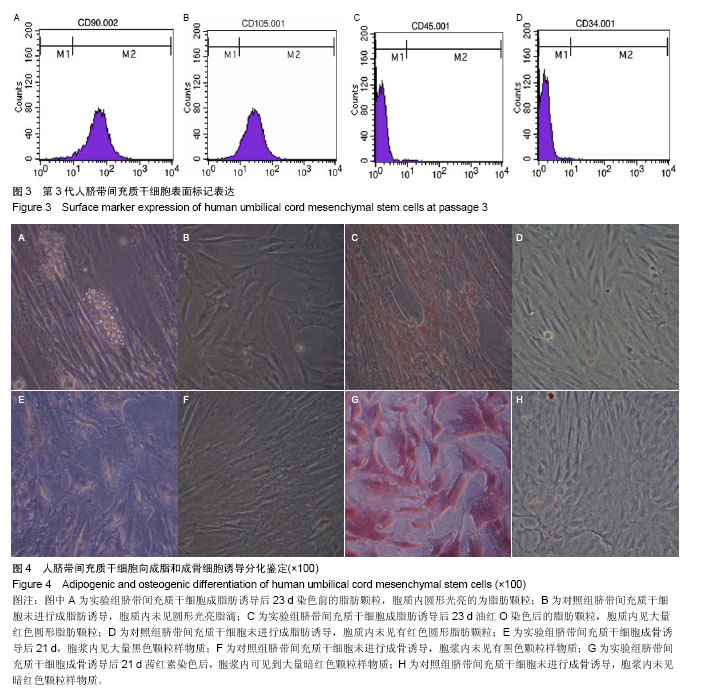
| [1] Doorn J, Moll G, Le Blanc K,et al.Therapeutic applications of mesenchymal stromal cells: paracrine effects and potential improvements.Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2012;18(2):101-115.
[2] Vidal MA, Lopez MJ.Adipogenic differentiation of adult equine mesenchymal stromal cells.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;702: 61-75.
[3] Delorme B, Ringe J, Pontikoglou C,et al.Specific lineage-priming of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells provides the molecular framework for their plasticity.Stem Cells. 2009;27(5):1142-1151.
[4] Scheideler M, Elabd C, Zaragosi LE,et al.Comparative transcriptomics of human multipotent stem cells during adipogenesis and osteoblastogenesis.BMC Genomics. 2008;9:340.
[5] Mueller MB, Blunk T, Appel B,et al.Insulin is essential for in vitro chondrogenesis of mesenchymal progenitor cells and influences chondrogenesis in a dose-dependent manner.Int Orthop. 2013;37(1):153-158.
[6] Rogers I, Casper RF.Umbilical cord blood stem cells.Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2004;18(6):893-908.
[7] Hanson SE, Gutowski KA, Hematti P.Clinical applications of mesenchymal stem cells in soft tissue augmentation.Aesthet Surg J. 2010;30(6):838-842.
[8] Chen Y, Shao JZ, Xiang LX,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells: a promising candidate in regenerative medicine.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008;40(5):815-820.
[9] Mi Z, Bhattacharya SD, Kim VM,et al.Osteopontin promotes CCL5-mesenchymal stromal cell-mediated breast cancer metastasis.Carcinogenesis. 2011;32(4):477-487.
[10] Mueller MB, Fischer M, Zellner J, et al.Hypertrophy in mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenesis: effect of TGF-beta isoforms and chondrogenic conditioning.Cells Tissues Organs. 2010;192(3):158-166.
[11] Levi B, Wan DC, Glotzbach JP,et al.CD105 protein depletion enhances human adipose-derived stromal cell osteogenesis through reduction of transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) signaling.J Biol Chem. 2011;286(45):39497-39509.
[12] Nurden AT.Platelets, inflammation and tissue regeneration. Thromb Haemost. 2011;105 Suppl 1:S13-33.
[13] Mitchell KE, Weiss ML, Mitchell BM,et al.Matrix cells from Wharton's jelly form neurons and glia.Stem Cells. 2003;21(1): 50-60.
[14] Troyer DL, Weiss ML.Wharton's jelly-derived cells are a primitive stromal cell population.Stem Cells. 2008;26(3):591-599.
[15] Kestendjieva S, Kyurkchiev D, Tsvetkova G,et al.Characterization of mesenchymal stem cells isolated from the human umbilical cord.Cell Biol Int. 2008;32(7):724-732.
[16] Secco M, Zucconi E, Vieira NM,et al.Multipotent stem cells from umbilical cord: cord is richer than blood!Stem Cells. 2008 Jan;26(1):146-150.
[17] Reger RL, Tucker AH, Wolfe MR.Differentiation and characterization of human MSCs.Methods Mol Biol. 2008; 449:93-107.
[18] Cassatella MA, Mosna F, Micheletti A,et al.Toll-like receptor-3-activated human mesenchymal stromal cells significantly prolong the survival and function of neutrophils. Stem Cells. 2011;29(6):1001-1011.
[19] Weiss ML, Medicetty S, Bledsoe AR,et al.Human umbilical cord matrix stem cells: preliminary characterization and effect of transplantation in a rodent model of Parkinson's disease. Stem Cells. 2006;24(3):781-792.
[20] Cirri P, Chiarugi P.Cancer-associated-fibroblasts and tumour cells: a diabolic liaison driving cancer progression.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012;31(1-2):195-208.
[21] Weiss S, Hennig T, Bock R,et al.Impact of growth factors and PTHrP on early and late chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells.J Cell Physiol. 2010;223(1):84-93.
[22] Weiss ML, Medicetty S, Bledsoe AR,et al.Human umbilical cord matrix stem cells: preliminary characterization and effect of transplantation in a rodent model of Parkinson's disease. Stem Cells. 2006;24(3):781-792.
[23] Conconi MT, Burra P, Di Liddo R,et al.CD105(+) cells from Wharton's jelly show in vitro and in vivo myogenic differentiative potential.Int J Mol Med. 2006;18(6):1089-1096.
[24] Jung KH, Song SU, Yi T,et al.Human bone marrow-derived clonal mesenchymal stem cells inhibit inflammation and reduce acute pancreatitis in rats.Gastroenterology. 2011; 140(3): 998-1008. |