Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (53): 9251-9260.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.53.025
Meta analysis of 2-μm laser in the treatment of non-muscle-invasive bladder tumor
Yu Jie1, Wang Yu-jie1, Liu Yu2, Ma Qi3, Zhang Li-dong1
- 1Department of Urology Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China;
2Evidence-Based Medicine Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 3Department of Functional Experiment Center, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Revised:2013-11-19Online:2013-12-31Published:2013-12-31 -
Contact:Zhang Li-dong, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Chief physician, Department of Urology Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China 2375783665@qq.com -
About author:Yu Jie★, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Urology Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China 1316510267@qq.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yu Jie, Wang Yu-jie, Liu Yu, Ma Qi, Zhang Li-dong. Meta analysis of 2-μm laser in the treatment of non-muscle-invasive bladder tumor[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(53): 9251-9260.
share this article
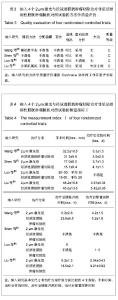
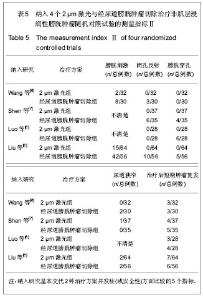
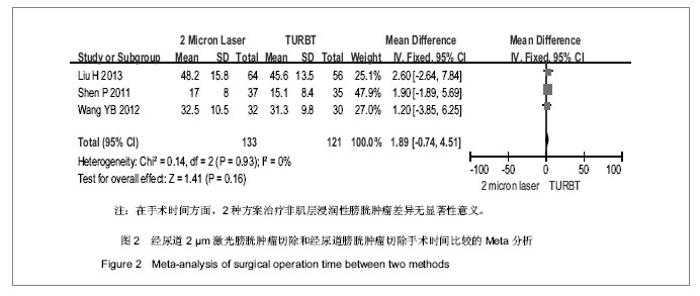
2.2 方法学质量评价 所纳入4个随机对照研究的诊断标准、纳入排除标准明确,研究对象基线资料可比。只有2个研究交代分组方法,其中1个研究交代随机方法采用随机数字表法分组[11],另外1个研究随机方法采用计算机随机分组[8]。 全部研究分配隐藏不清楚,只有1个研究交代未使用盲法[8],大部分盲法不清。 评定全部纳入研究质量等级均为C级。见表3。纳入研究测量指标见表4,5。 2.3 Meta分析结果 2.3.1 手术时间 纳入4个研究中只有3个研究比较了2种治疗方案的手术时间[8,10-11]。 Meta分析前对纳入研究结果进行异质性检验,各项研究结果间有统计学异质性(χ²=0.14,P=0.93>0.1,I2=0),故采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析,结果:加权均数差的合并效应量MD=1.89,MD合并95%CI[-0.74,4.51],置信区间包含0,合并效应量检验,Z=1.41 P=0.16。 故认为经尿道2 μm激光膀胱肿瘤切除与经尿道膀胱肿瘤切除治疗非肌层浸润性膀胱肿瘤的手术时间差异无显著性意义,见图2。"

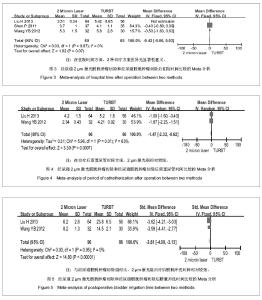
2.3.2 治疗后住院时间 纳入4个研究中只有3个研究比较了2种方案治疗后的住院时间[5-6,8],其中Liu等[5]研究认为经尿道2 μm激光膀胱肿瘤切除与经尿道膀胱肿瘤切除治疗非肌层浸润性膀胱肿瘤后住院时间差异有显著性意义,而余下2个研究则认为差异无显著性意义[7-8]。Meta分析前对纳入研究结果进行异质性检验,各项研究结果间有明显有统计学异质性,I2=95%,分析异质性产生原因可能为不同研究间差异存在显著性,考虑剔除纳入研究中SD差异显著者,再次对纳入研究结果进行异质性检验(χ2=0.03,P=0.87>0.1,I2=0%),研究结果间无明显统计学异质性,故采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析,结果:加权均数差的合并效应量MD=-0.42,MD合并95%CI[-0.86,0.03],置信区间包含0,合并效应量检验,Z=1.82,P=0.07。故认为经尿道2 μm激光膀胱肿瘤切除与经尿道膀胱肿瘤切除治疗非肌层浸润性膀胱肿瘤后住院时间差异无显著性意义,见图3。 2.3.3 治疗后留置尿管时间 纳入研究中只有2个研究比较了治疗后留置尿管时间[5,8]。2个研究间有明显统计学异质性(χ²=5.96,P=0.01 < 0.1,I2=83%),故采用随机效应模型进行Meta分析,结果:加权均数差的合并效应量MD=-1.47,MD合并95%CI[-2.32,-0.62],置信区间不包含0,合并效应量检验,Z=3.39,P=0.000 7。故认为经尿道2 μm激光膀胱肿瘤切除与经尿道膀胱肿瘤切除治疗非肌层浸润性膀胱肿瘤后留置尿管时间差异有显著性意义,经尿道2 μm激光膀胱肿瘤切除后留置尿管时间相对较短,见图4。 2.3.4 治疗后膀胱冲洗时间 纳入研究中只有Liu等[5]、Wang等[8]研究比较2种方案治疗后膀胱冲洗时间,均认为2 μm激光组治疗后膀胱冲洗时间短于经尿道膀胱肿瘤切除组。考虑到各研究SD差异较大改用相对效应指标SMD行Meta分析,Meta分析前对纳入研究结果进行异质性检验,各项研究结果间无明显统计学异质性(χ2= 0.00,P=0.95>0.1,I2=0),故采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析,结果:合并效应量SMD=-3.61,SMD合并95%CI[-4.09,-3.13],置信区间不包含0,合并效应量检验,Z=14.80,P < 0.000 01。故认为经尿道2 μm激光膀胱肿瘤切除与经尿道膀胱肿瘤切除治疗非肌层浸润性膀胱肿瘤后膀胱冲洗时间差异有显著性意义,经尿道2 μm激光膀胱肿瘤切除后膀胱冲洗时间相对较短,见图5。"

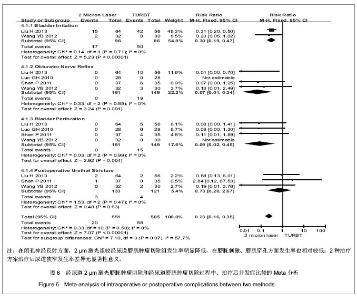
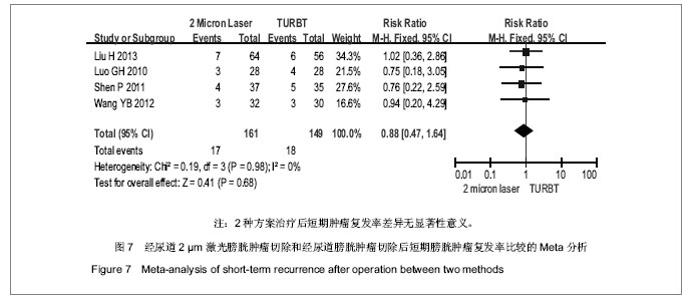
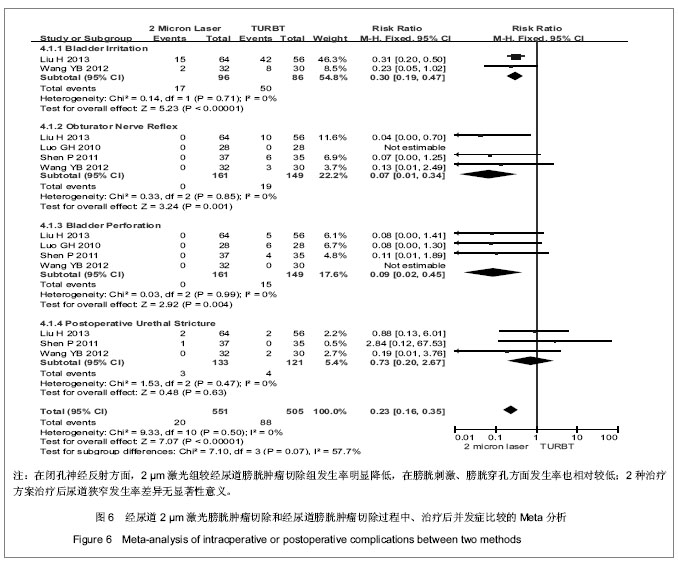
2.3.5 治疗过程中、治疗后并发症 膀胱刺激:纳入研究中有2个研究比较膀胱刺激发生率[5,8]。Meta分析前对纳入研究结果进行异质性检验,各项研究结果间无明显统计学异质性(χ²=0.14,P=0.71>0.1,I2=0%),故采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析,结果:合并效应量RR=0.30,RR合并95%CI[0.19,0.47],置信区间不包含1,合并效应量检验,Z=5.23,P < 0.000 01。故认为经尿道2 μm激光膀胱肿瘤切除与经尿道膀胱肿瘤切除治疗非肌层浸润性膀胱肿瘤膀胱刺激发生率差异有显著性意义,前者膀胱刺激发生的风险仅为后者的30%,见图6。 闭孔神经反射:纳入4个研究全部比较术中闭孔神经反射发生率。4个研究间无明显统计学异质性(χ2= 0.33,P=0.85 > 0.1,I2=0%),故采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析,结果:合并效应量RR=0.07,RR合并95%CI[0.01,0.34],置信区间不包含1,合并效应量检验,Z=3.24,P=0.001。故认为经尿道2 μm激光膀胱肿瘤切除与经尿道膀胱肿瘤切除治疗非肌层浸润性膀胱肿瘤术中闭孔神经反射发生率差异有显著性意义,2 μm激光组较经尿道膀胱肿瘤切除组闭孔神经反射发生率低;与经尿道膀胱肿瘤切除组比较,2 μm激光组将闭孔神经反射发生风险降低至7%,见图6。 膀胱穿孔:纳入4个研究中均比较治疗后膀胱穿孔发生率。Meta分析前对纳入研究结果进行异质性检验,各项研究结果间无明显统计学异质性(χ2=0.03,P=0.99>0.1,I2=0%),故采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析,结果:合并效应量RR=0.09,RR合并95%CI[0.02,0.45],置信区间不包含1,合并效应量检验,Z=2.92,P=0.004。故认为经尿道2 μm激光膀胱肿瘤切除与经尿道膀胱肿瘤切除治疗非肌层浸润性膀胱肿瘤后膀胱穿孔发生率差异有显著性意义;与经尿道膀胱肿瘤切除组比较,2 μm激光组降低了91%膀胱穿孔发生风险,见图6。 尿道狭窄:纳入研究中只有3个研究比较了治疗后尿道狭窄发生率[5,7-8]。Meta分析前对纳入研究结果进行异质性检验,各项研究结果间无明显统计学异质性(χ2= 1.53,P=0.47>0.1,I2=0%),故采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析,结果:合并效应量RR=0.73,RR合并95%CI[0.20,2.67],置信区间包含1,合并效应量检验,Z=0.48,P=0.63。故认为经尿道2 μm激光膀胱肿瘤切除与经尿道膀胱肿瘤切除治疗非肌层浸润性膀胱肿瘤尿道狭窄发生率差异无显著性意义,见图6。 2.3.6 治疗后短期膀胱肿瘤复发率 纳入4个研究均比较了2种治疗方案治疗后短期(3-12个月)随访期间膀胱肿瘤复发率,4个研究认为经尿道2 μm激光膀胱肿瘤切除与经尿道膀胱肿瘤切除治疗非肌层浸润性膀胱肿瘤后短期膀胱肿瘤复发率差异无显著性意义。Meta分析前对纳入研究结果进行异质性检验,各项研究结果无明显统计学异质性(χ2=0.19,P=0.98>0.1,I2=0%),故采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析,结果:合并效应量RR=0.88,RR合并95%CI[0.47,1.64],置信区间包含1,合并效应量检验,Z=0.41,P=0.68。故认为经尿道2 μm激光膀胱肿瘤切除与经尿道膀胱肿瘤切除治疗非肌层浸润性膀胱肿瘤后短期膀胱肿瘤复发率差异无显著性意义,见图7。"
| [1] 那彦群,叶章群,孙光.中国泌尿外科疾病诊断治疗指南[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2011: 17-29.[2] Parsons RL, Campbell JL, Thomley MW, et al. The effect of the laser of dog bladders : a preliminary report . J Urol. 1966; 95(5):716-717.[3] 余小敏.激光技术在良性前列腺增生手术的应用及发展[J].激光技术,2011,35(5):718-720.[4] Herrmann TR, Liatsikos EN, Nagele U, et al. EAU guidelines on laser technologies. Eur Urol. 2012;61(4):783-795.[5] Liu H,Wu J. Comparison of the safety and efficacy of conventional monopolar 2-micron laser transurethral resection in the management of multiple nonmuscle-invasive bladder cancer. J Int Med Res. 2013;41(4):984-992.[6] 罗光恒,刘军. 2 微米激光治疗非肌层浸润性膀胱肿瘤的疗效分析[J].现代泌尿生殖肿瘤杂志,2010,2(3):145-147.[7] 沈鹏,欧彤文,许建军,等.经尿道2μm激光与电切治疗浅表性膀胱肿瘤的临床疗效比较[J].现代泌尿外科杂志,2011,16(5): 417-421.[8] 王毓斌,吕永安,邵晋凯,等. 2μm激光膀胱肿瘤切除术与经尿道膀胱肿瘤电切术治疗非肌层浸润性膀胱肿瘤的疗效比较[J].肿瘤研究与临床,2012,24(5):321-323. [9] Divrik RT, Yildirim U, Zorlu F, et al. The effect of repeat transurethral resection on recurrence and progression rates in patients with T1 tumors of the bladder who received intravesical mitomyin: a prospective, randomized , clinical trial . J Urol. 2006;175(5):1641-1644.[10] 张心如,谷保军,谢弘,等.2 μm激光与TURBt治疗非肌层浸润性膀胱肿瘤的对照研究[J].临床泌尿外科杂志,2010,25(6): 408-411.[11] 贾永中,罗敏,肖序仁,等.绿激光和Revolix 2 微米激光治疗浅表性膀胱肿瘤的比较研究[J].中国微创外科杂志,2009,9(7): 623-625. [12] Zhu Y, Jiang X, Zhang J, et al. safety and efficacy of holmium laser resection for primary non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer versus transurethral electroresection: single-center experience.Urology. 2008;72(3):608-612.[13] 薛松,夏术阶.激光治疗浅表性膀胱肿瘤现状及进展[J].中华泌尿外科杂志,2010,31(2):138-139.[14] Wendt-Nordahl G, Huckele S,Honeck P, et al. systematic evaluation of a recently introduced 2-micron continuous wave thulium laser for vaporesection of the prostate. J Endourol. 2008;22(5):1041-1045.[15] Fu WJ, Hong BF, Yang Y, et al. Vaporesection for managing benign prostatic hyperplasia using a 2μm continuous wave laser : a prospective trial with 1-year follow up. BJU Int. 2009; 103(3):352-356.[16] Fried NM, Murray KE. High-Power thulium fiber laser ablation of urinary tissues at 1.94 micrometers. J Endourol. 2005;19(1): 25-31.[17] Xia SJ, Zhuo J, Sun XW, et al. Thulium laser versus standard transurethral resection of the prostate :a randomized prospective trial. Eur Urol. 2008;53(2):382-389.[18] Poulakis V, Dahm P, Witzsch U, et al. Transurethral electrovaporization VS transurethral resection for symptomatic prostatic obstruction: a meta-analysis. BJU Int.2004;94(1):89-95.[19] 夏术阶. 2μm外科激光治疗系统在泌尿外科的应用[J].临床泌尿外科杂志,2009,24(10):725-727.[20] EL-sherif AF, King TA. Soft and hard tissue ablation with short-pulse high peak power and continuous thulium-silica fiber laser. Lasers Med Sci. 2003;18(3):139-147.[21] 刘余庆,卢剑,肖春雷,等. 2 μm连续波激光与经尿道膀胱肿瘤切除术治疗非肌层浸润性膀胱癌的比较研究[J].中国微创外科杂志,2013,13(1):23-28.[22] Kramer MW, Bach T, Wolters M, et al. Current evidence for transurethral laser therapy of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. World J Urol. 2011;29(4):433-442.[23] Liu H, Xue S, Ruan Y, et al.2-micron continuous wave laser treatment for multiple non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer with intravesical instillation of epirubicin. Lasers Surg Med. 2011;43(1):15-20.[24] 高旭,任善成,孙颖浩.软性膀胱镜下铥激光切除治疗非肌层浸润性膀胱癌18例分析[J].中华腔镜泌尿外科杂志:电子版,2007,1(2):90-92.[25] 郭应禄,周利群,主译.坎贝尔•沃尔什. 泌尿外科学[M]. 9版. 北京:北京大学医学出版社,2009: 2539-2599.[26] Zhong C,Guo SW,Tang YQ, et al. Clinical observation on 2 micron laser for non-muscle-invasive bladder tumor: single-center experience .World J Urol. 2010;28(2):157-161. |
| [1] | Lu Yanqin, Yi Fang, Ju Wei, Li Wenjie, Lei Lei. Reparation of femoral defects with a Ca-P coated magnesium alloy scaffold carrying sustained release microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(2): 232-238. |
| [2] | Wang Xiao-ming, Duan Hao, Xia Bin, Wei Jian-min. Feasibility of lateral-position pedicle screw placement via combined anterior-posterior approaches in spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(39): 6333-6338. |
| [3] | Liu Yan-cheng, Xia Qun, Hu Yong-cheng, Zhang Ji-dong, Bai Jian-qiang, Ji Ning, Zhang Kuan. Evaluation of gait characteristics of cervical spondylotic myelopathy patients by a portable gait analyzer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(11): 1774-1779. |
| [4] | Zhang Meng-yuan, Chen Ke-yi, La Xiao-lin, Deekshya Shrestha. A meta-analysis of clinical efficacy of fresh embryo transfer versus frozen embryo transfer in in vitro fertilization cycles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(53): 9245-9250. |
| [5] | Yang Tuo, Gao Shu-guang, Luo Wei, Li Yu-sheng, Xiong Yi-lin, Sun Jin-peng, Lei guang-hua. Analgesia after arthroscopic surgery: Randomly controlled Meta-analysis on intra-articular injection of bupivacaine placebo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(35): 6306-6313. |
| [6] | Wang Lu, Jian Jie, Lu Hui-fang. Efficiency of resin infiltration versus fluride varnish for treatment of post-orthodontic white spot lesions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(29): 5303-5308. |
| [7] | Ding Ming-xiang, Lin Shao-hua, Li Liang-ming, Hou Bo, Liang Chao-feng, Gong Jin, . Biocompatibility of an acellular brain tissue scaffold with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(14): 2495-2500. |
| [8] | Zhou Yan, Piao Jin-hua, Jin Lian-hua, Yang Si-rui. null [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(1): 112-117. |
| [9] | Liu Ji-chun, Hu Hong-tao, Xu Guo-hua, Jiang Yu-quan, Xu Ning, Ye Xiao-jian. A modified method of isolating and culturing human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2012, 16(45): 8394-8397. |
| [10] | Chen Yun-fei1, Wang Yi2, Yang Hong-ji3. null [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2012, 16(5): 899-·902. |
| [11] | Wang Cheng-wei1, Li Hong-lin1, Zhao Bo1, Li Lu-bing1, Pa Er Ha Ti1, Wang Xue1, Zheng Hui1, A Man1, Yu Jian-hua2. Evaluation of meniscus injury by magnetic resonance imaging: A documentary analysis based on Science Citation Index from 2001 to 2010 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2012, 16(4): 571-580. |
| [12] | Bai Chuan-yi1, Ning Ning1, Ling Wei2, Tian Zhen-xing2, Dang Xiao-qian1, Wang Kun-zheng1. null [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2012, 16(4): 585-588. |
| [13] | Zhou Zhong-xiao, Wei Xi-lin, Yao Jian-ru, Zhang Jian, Bian Gang, Li Jin-hui. Evaluation of biological hemostatic dressings and gauzes in surgical wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2010, 14(51): 9635-9638. |
| [14] | Zhang Kun, Jiang Yi, Lü Li-zhi, Zhang Xiao-jin, Yang Fang, Chen Yong-biao, Cai Qiu-cheng, Pan Fan. Orthotopic liver transplantation for primary hepatic cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2010, 14(44): 8357-8360. |
| [15] | Tian Bao-xiang, Fan Hua, Liu Feng-bin, Wei Chun-lin . Biological property and clinical application of tissue engineered skin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2010, 14(2): 337-340. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||