Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (53): 9239-9244.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.53.023
Previous Articles Next Articles
Nucleus pulposus cell transplantation inhibits intervertebral disk degeneration
Wang Chun-sheng, Zhang Wei-bin
- Department of Soft Tissue Injury, Beiling Branch, General Hospital of Shenyang Military Region, Shenyang 110031, Liaoning Province, China
-
Revised:2013-11-13Online:2013-12-31Published:2013-12-31 -
Contact:Wang Chun-sheng★, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Soft Tissue Injury, Beiling Branch, General Hospital of Shenyang Military Region, Shenyang 110031, Liaoning Province, China ruige123@sina.com -
About author:Wang Chun-sheng★, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Soft Tissue Injury, Beiling Branch, General Hospital of Shenyang Military Region, Shenyang 110031, Liaoning Province, China ruige123@sina.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Chun-sheng, Zhang Wei-bin. Nucleus pulposus cell transplantation inhibits intervertebral disk degeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(53): 9239-9244.
share this article
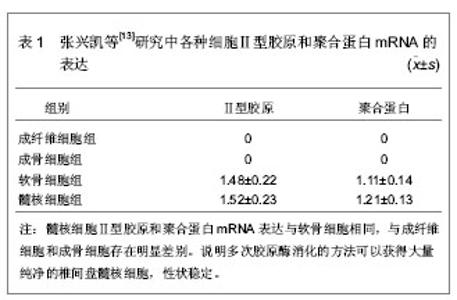
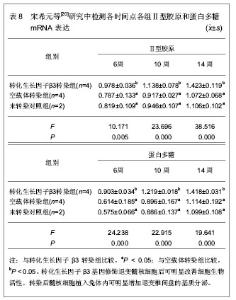
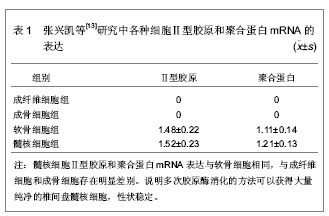
2.1 对髓核细胞分泌细胞外基质有促进作用的体外培养方法 从椎间盘退变移植细胞的选择方面来看,主要有自体软骨细胞、自体髓核细胞和自体骨髓基质干细胞,但只有髓核细胞是可行的,但髓核细胞由于某种原因获得的数量有限以及培养困难等,阻碍了研究的进程。近年来,关于改进髓核细胞培养方法的研究可以使细胞数量得到扩增。 2.1.1 多次胶原酶消化法培养髓核细胞 张兴凯 等[13]使用多次胶原酶消化的方法体外分离培养椎间盘髓核细胞,接种,传代,取第2代细胞,分别采用免疫细胞化学和反转录聚合酶链反应方法检测椎间盘髓核细胞特征性分泌物Ⅱ型胶原和聚合蛋白的分泌量及mRNA的表达,并与软骨细胞、成骨细胞及成纤维细胞进行比较,结果见表1。"
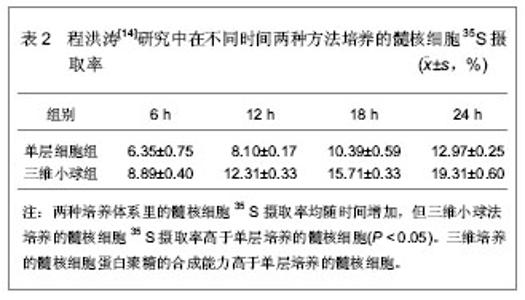
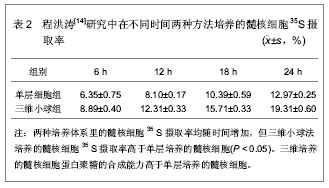
2.1.2 三维小球聚集培养髓核细胞 程洪涛[14]寻找合适的在体外培养髓核细胞的方法,获得质量和数量更良好的髓核细胞。采用胰酶+胶原酶联合消化法分离兔髓核细胞,分离所获细胞一部分用DMEM/F12混合培养基进行单层培养,其余的采用低速离心,使其形成小球形聚集,并在聚丙烯离心管中进行培养。三维小球聚集培养法是将髓核细胞悬液的细胞浓度调成 5×108 L-1,取1 mL细胞悬液加入15 mL聚丙烯离心管中,补充培养液至5 mL,用低温离心机以20×g离心力4 ℃离心5 min,使细胞聚集成团,放入CO2恒温细胞培养箱中,体积分数为5%的CO2在37 ℃恒温孵育,每2 d换液1次。两种方法在培养相同时间后,分别检测能够反映髓核细胞合成硫酸化蛋白聚糖能力的35S摄取率来比较两种培养体系里髓核细胞的合成代谢能力。在不同时间两种方法培养的髓核细胞35S摄取率,见表2。"
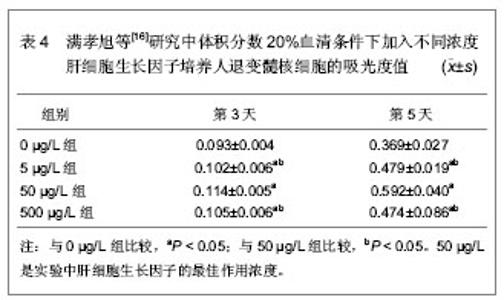
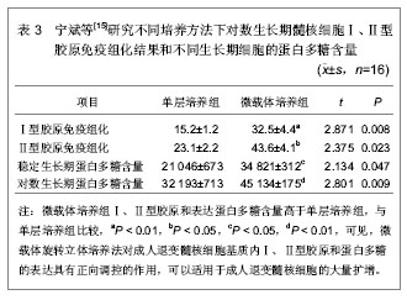
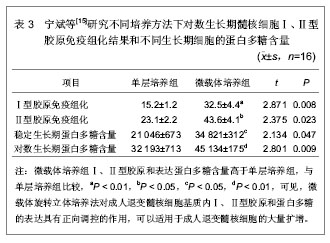
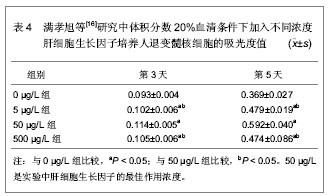
2.1.4 肝细胞生长因子对髓核细胞的作用 满孝旭等[16]研究肝细胞生长因子对体外培养人退变髓核细胞生物学活性的影响,应用免疫组织化学染色观察肝细胞生长因子受体在髓核细胞中的表达,并测不同浓度肝细胞生长因子的细胞生长曲线,筛选最佳的作用浓度。选取第3代髓核细胞,反转录聚合酶链反应检测Ⅱ型胶原、蛋白多糖、SOX9 mRNA表达。四唑盐比色法结果提示不同浓度肝细胞生长因子对体外培养的人退变髓核细胞均有明显的促增殖作用,与对照组相比差异均有显著性意义,肝细胞生长因子刺激后髓核细胞进入增殖期比例增加,同时促进髓核细胞Ⅱ型胶原、蛋白多糖、SOX9 mRNA表达量增加,可以促进细胞外基质表达。不同浓度肝细胞生长因子培养人退变髓核细胞的吸光度值结果,见表4。"
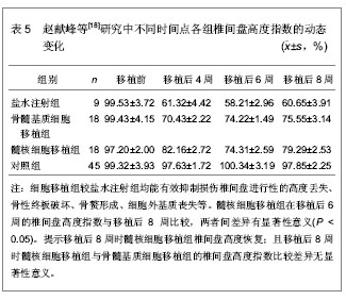
2.2 髓核细胞移植抑制椎间盘退变的实验研究 2.2.1 髓核细胞移植对受损椎间盘退变的影响 磁共振是目前公认的椎间盘退变动物模型的无损伤性影像学检查方法[17]。赵献峰等[18]比较髓核细胞移植和骨髓基质细胞移植对椎间盘退变的影响,采用原代细胞培养法获取并扩增髓核细胞及骨髓基质细胞,2岁龄新西兰白兔随机分为3组,盐水注射组3只,骨髓基质细胞移植组6只,髓核细胞移植组6只,在椎间盘进行髓核穿刺抽吸后分组注入盐水、骨髓基质细胞和髓核细胞,未处理的椎间盘作为对照组采集数据。通过测量椎间盘高度指数和磁共振影像结果来分析细胞移植对椎间盘损伤退变的影响。在移植后不同时间点各组椎间盘高度指数的动态变化,见表5。"
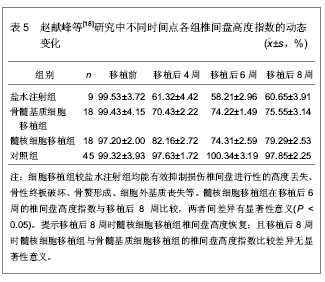
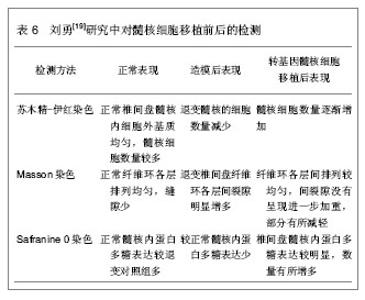
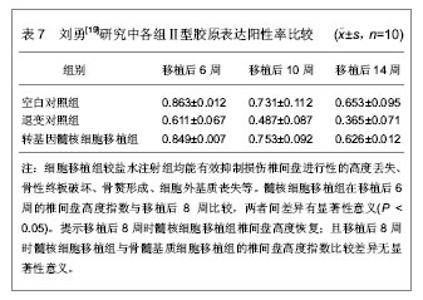
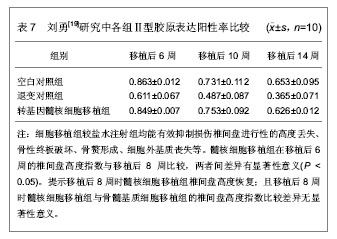
在不同时间点各组磁共振ST2WI数据显示,第8周时髓核细胞移植组T2信号强度(70.63±7.60)%高于骨髓基质细胞移植组(54.32±7.92)%,两组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。提示髓核细胞移植组细胞外基质的合成可能超过骨髓基质细胞移植组。可见,髓核细胞移植或骨髓基质细胞移植能够有效避免椎间盘损伤后发生的进行性退变过程。而且,在8周后髓核细胞移植组较骨髓基质细胞移植组显示出更强的基质合成能力。椎间盘高度及含水量出现恢复的迹象。外源性髓核细胞移植能够良好的适应受体椎间盘环境,并发挥相应的细胞外基质分泌功能。 2.2.2 髓核细胞移植促进退变椎间盘内蛋白多糖和Ⅱ型胶原的生物合成 刘勇[19]在微创经皮CT引导下穿刺椎间盘建立兔椎间盘退变模型,将60只新西兰大白兔分别用甲苯噻嗪注射液3 mg/kg、克他命注射液40 mg/kg肌肉注射麻醉后,兔取左侧卧位,腰背部正中及左侧穿刺区域备皮,以2.5%的碘伏消毒,选择椎间盘层面行CT扫描以穿刺造模,行腰椎间盘CT扫描,以定位穿刺椎间隙。兔左后方腰背部为进针点,消毒后在CT定位下,经皮以18G的穿刺针由左后方穿刺腰间盘。穿刺针尖接近纤维环时行CT扫描,调整穿刺角度及深度,缓缓进针,刺入髓核后再次CT扫描,以确定针尖位于髓核中央。 对兔椎间盘细胞进行培养,在体外转双基因,将腺相关病毒介导的结缔组织生长因子和基质金属蛋白酶组织抑制因子1双基因体外联合转染兔椎间盘髓核细胞后,再将转基因髓核细胞移植于退变兔腰椎间盘内,通过免疫组织化学和反转录聚合酶链反应以及35S整合法检测髓核细胞移植对椎间盘退变的影响,观察不同时期椎间盘信号、椎间高度、Ⅱ型胶原和蛋白多糖合成的变化。发现在体外转双基因腺相关病毒介导的结缔组织生长因子和基质金属蛋白酶组织抑制因子1髓核细胞移植可以延缓或逆转椎间盘的退变。研究中的几项检测结果发现,见表6。"

| [1] Karppinen J, Shen FH, Luk KD, et al. Management of degenerative disk disease and chronic low back pain. Orthop Clin North Am.2011;42(4):513-528.[2] Samartzis D, Cheung KM. Lumbar intervertebral disk degeneration. Orthop Clin North Am. 2011;42(4):xi-xii.[3] Adams MA, Roughley PJ.What is intervertebral disc degeneration, and what causes it? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(18):2151-2161.[4] Chung SA, Khan SN, Diwan AD. The molecular basis of intervertebral disk degeneration.Orthop Clin North Am. 2003;34(2):209-219.[5] Brisby H. Pathology and possible mechanisms of nervous system response to disc degeneration. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88 Suppl 2:68-71.[6] Bae WC, Masuda K. Emerging technologies for molecular therapy for intervertebral disk degeneration. Orthop Clin North Am. 2011;42(4):585-601.[7] 彭宝淦,施杞.退变椎间盘的组织病理学变化[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,1996,4(6):52-55.[8] 胡有谷.腰椎间盘突出症[M].第二版.北京:人民卫生出版社,1995: 118-136.[9] Inoue N, Espinoza Orías AA. Biomechanics of intervertebral disk degeneration. Orthop Clin North Am. 2011;42(4): 487-499.[10] Gan JC, Ducheyne P, Vresilovic EJ, et al. Intervertebral disc tissue engineering II: cultures of nucleus pulposus cells. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;(411):315-324.[11] 万方数据库.万方医学网[DB/OL].2013-09-21. https://med.wanfangdata.com.cn[12] Medline.Pubmed[DB/OL].2013-09-21.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/[13] 张兴凯,曹鹏,王君,等.多次胶原酶消化法培养小鼠椎间盘髓核细胞[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(28):5136-5140.[14] 程洪涛.兔髓核细胞的体外培养及髓核细胞移植抑制椎间盘退变的实验研究[D].江苏:东南大学,2004:1.[15] 宁斌,刘海飞,龚维明,等.成人退变髓核细胞微载体旋转立体培养对细胞外基质合成的影响[J].中华外科杂志,2013,51(5): 432-436.[16] 满孝旭,马迅,关晓明,等.肝细胞生长因子对体外培养的人退变髓核细胞生物学活性影响[J].中华临床医学杂志(电子版),2011, 5(24):7226-7231.[17] Gruber HE, Johnson T, Norton HJ, et al. The sand rat model for disc degeneration. Radiologic characterization of age-ralated changes:cross-sectional and prospective analyses. Spine.2002;27(3):230-234.[18] 赵献峰,刘浩,丰干均,等.髓核细胞与骨髓基质细胞移植对受损椎间盘退变的影响[J].四川大学学报(医学版),2009,40(3): 472-477.[19] 刘勇.转基因CTGF和TIMP1髓核细胞移植阻逆兔腰椎间盘退变的实验研究[D].山东:山东大学,2011:4-40.[20] 宋希元,彭圣智.TGF-β3修饰退变髓核细胞移植修复兔退变椎间盘的效果观察[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2012,26(7): 790-795.[21] 王月秋,陈伯华.骨髓间充质干细胞治疗椎间盘退变的研究进展[J].齐鲁医学杂志,2009,24(4):369-370,372.[22] Iwashina T, Mochida J, Sakai D, et al. Feasibility of using a human nucleus pulposus cell line as a cell source in cell transplantation therapy for intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(11):1177-1186.[23] Matsuzaki H, Wakabayashi K, Ishihara K, et al. Allografting intervertebral discs in dogs: a possible clinical application. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996;21(2):178-183.[24] Okuma M, Mochida J, Nishimura K, et al. Reinsertion of stimulated nucleus pulposus cells retards intervertebral disc degeneration:an in vitro and in vivo experimental study. J Orthop Res.2000;18(6):988-997.[25] Nomura T, Mochida J, Okuma M, et al. Nucleus pulposus allograft retards intervertebral disc degeneration.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(389):94-101.[26] Watanabe K, Mochida J, Nomura T, et al. Effect of reinsertion of activated nucleus pulposus on disc degeneration: an experimental study on various types of collagen in degenerative discs.Connect Tissue Res. 2003;44(2):104-108.[27] Ganey T, Libera J, Moos V, et al.Disc chondrocyte transplantation in a canine model: a treatment for degenerated or damaged intervertebral disc.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(23):2609-2620. [28] 于占革,杨威,温莹,等.兔不同节段椎间盘髓核细胞培养特性的比较[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2010,20(8):689-693.[29] 马凯歌,邵增务,王佰川,等.自噬参与压力诱导兔髓核细胞退变的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2013,30(2):354-357.[30] 陶海鹰,贺斌,卫爱林,等.羧甲基壳聚糖对体外培养大鼠椎间盘髓核细胞增殖、细胞周期及细胞外基质分泌的影响[J].中国实验外科杂志,2013,30(10):2165-2168. |
| [1] | Sun Xin, Jin Wen-jie, Shen Kang-ping, Liu Xing-zhen. Degeneration of injured intervertebral disk affected by anterior longitudinal ligament destruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(11): 1664-1668. |
| [2] | Zhu Ai-guo, Chen Yun, Zhang Feng, Zhu Jian-wei, Jin Guo-hua. Applied anatomy and clinical significance of three-dimensional reconstruction of the lumbosacal plexus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(53): 7946-7951. |
| [3] | Ding Mu-chen, Shi Zhi-cai, Lu Chun-wen, Wu Jin-hui, Wang Chao, Yuan Jia-bin, Zhou Zhen. Lumbosacral sagittal parameters measured by magnetic resonance in association to L5/S1 intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(48): 7245-7250. |
| [4] | Liu Ya-pu, Hou Xiu-wei, Wu Guang-liang, Xia Hong. Comparison of stress distribution of adjacent segments after artificial cervical disc replacement versus anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(44): 6541-6548. |
| [5] | Wang Jian-ji, Yang Long, Li Jing, Sun Qi, Zuo Wei-min, Ren Qi-feng, Sun Yu, Wu Zhan-yu, Zou Qiang, Ma Min-xian, Ye Chuan. Development and application of special-purpose grafter by femoral head decompression combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transplantation based on three-dimensional printing technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(44): 6636-6642. |
| [6] | Liu Ying-jie, Peng Jun, Liu Xiao-kang, Zhao Cheng, Yang Er-zhu, Xu Jian-guang. Experimental animal models of intervertebral fusion-induced adjacent segment degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(39): 5825-5833. |
| [7] | Hu Wei, Ma Xin-long, Yuan Jian-jun, Zhang Ren-zan, Peng Bing, Zhang Xue-li. Expression of interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-6 and cyclooxygenase 2 in cervical intervertebral disc of cervical spondylosis patients with different clinical symptoms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(35): 5270-5276. |
| [8] | Wan Sheng-yu1, Yang Bo2, Lin Xu1. Influences of BioFlex dynamic stabilization system fixation on the stress of adjacent segments of intervertebral disc at different decompression ranges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(35): 5203-5209. |
| [9] | Wang Xiao-ping, Lu Ming, Ma Pei, Chen Zhi-ming, Yuan Wei, Zhao Fu-jiang, Zhao Hao,Ren Dong-yun, Ma Hua-song, Wu Zhi-hong. Effects of simulated weightlessness on biomechanics of motion unit of rhesus monkey lumbar vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(26): 3843-3848. |
| [10] | Lv Pin-lei, Su Yue-han, Cao Yun, Wang Zheng. Treatment of osteoarthritis using colony-forming cells in stromal vascular fraction of adipose tissue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2149-2154. |
| [11] | Ruan Guang-ping, Yao Xiang, Liu Ju-fen, Wang Jin-xiang, Hu Yuan-yuan, Li Zi-an, Yang Jian-yong, Pang Rong-qing, Pan Xing-hua. Transplantation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2172-2178. |
| [12] | Jiang Yan-jie, Mao Cheng-gang, Ning Xian-feng, Li Rong, Li Zi-pu. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells via intramuscular injection influence the expression of cytokines related to dilated cardiomyopathy in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2179-2185. |
| [13] | Lai Qin, Yu Lian, Qiu Yong-rong, Chen Long-tian, Huang Jian-qing, Li Yu-min, Zhang Li, Wu Wei-hao, Wu Ai-yu, Luo Bi-hua, Tian Pan. Umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells transplantion for polymyositis/dermatomyositis: variation of Th cytokines [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2186-2191. |
| [14] |
Liu Yu-liang, Li Jun, He Yu-qin, Zhuo Feng, Wei Kai-bin.
Transplantation of human umbilical cord derived-mesenchymal stem cells by different ways for the treatment of spinal cord injury
|
| [15] | Zhao Xiao-jian, Lu Cai-ping, Chu Wei-wei, Zhang Ya-xiao, Zhang Bing, Zhen Qiang, Tan Guo-liang, Wang Ren-feng, Liu Jia-bao, Wu Lin. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for treatment of emphysema: intravenous versus intratracheal approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2211-2215. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||