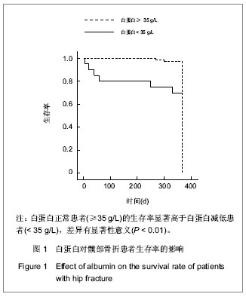
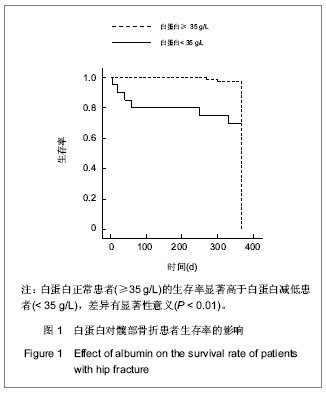
| [1] Wu LC, Chou MY, Liang CK, et al. Association of home care needs and functional recovery among community-dwelling elderly hip fracture patients. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2013;57: 383-388.[2] Smith T, Hameed Y, Cross J, et al. Assessment of people with cognitive impairment and hip fracture: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2013;57:117-126.[3] Chaudhry H, Devereaux PJ, Bhandari M. Cognitive Dysfunction in Hip Fracture Patients. Orthop Clin North Am. 2013;44:153-162.[4] Sandhu A, Sanders S, Geraci SA. Prognostic value of cardiac troponins in elderly patients with hip fracture-a systematic review. Osteoporosis Int. 2013;24:1145-1149.[5] Kieffer WKM, Rennie CS, Gandhe AJ. Preoperative albumin as a predictor of one-year mortality in patients with fractured neck of femur. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2013;95:26-28.[6] Geisler JP, Linnemeier GC, Thomas AJ, et al. Nutritional assessment using prealbumin as an objective criterion to determine whom should not undergo primary radical cytoreductive surgery for ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2007;106:128-131.[7] Acham H, Kikafunda JK. Hemoglobin status is the best nutritional variable that predicts achievement among schoolchildren in rural uganda. Ann Nutr Metab. 2009;55: 489-489.[8] Alvares da Silva CL, Lima-Costa MF, Araujo Firmo JO, et al. Hemoglobin level in older adults and the association with nutritional status and use of health services: the Bambui Project. Cad Saude Publica. 2012;28:2085-2094.[9] 陈万欣,张志民,邢丽,等.炎症及营养不良评分法在人工肾透析患者营养评估中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011, 15(31):5817-5821.[10] 王清华,袁芳,李强翔,等.持续性不卧床腹膜透析相关性腹膜炎: 3年108例次分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(18): 3389-3392.[11] Huelshoff A, Schricker T, Elgendy H, et al. Albumin synthesis in surgical patients. Nutrition. 2013;29:703-707.[12] 黄晓,莫冰峰,尹东,等.老年髋部骨折后死亡的相关影响因素分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(8):757-761.[13] Cooper C, Campion G, Melton LJ. Hip-fractures in the elderly-a worldwide projection. Osteoporosis Int. 1992;2: 285-289.[14] Auais M, Morin S, Nadeau L, et al. Changes in frailty-related characteristics of the hip fracture population and their implications for healthcare services: evidence from Quebec, Canada. Osteoporosis Int. 2013;24:2713-2724.[15] Wyers CE, Reijven PLM, Evers S, et al. Cost-effectiveness of nutritional intervention in elderly subjects after hip fracture. A randomized controlled trial. Osteoporosis Int. 2013;24: 151-162.[16] Uzoigwe CE, Burnand HGF, Cheesman CL, et al. Early and ultra-early surgery in hip fracture patients improves survival. Injury. 2013;44:726-729.[17] Della Rocca GJ, Crist BD. Hip Fracture Protocols What Have We Changed? Orthop Clin North Am. 2013;44:163-165.[18] Xu BB, Han L, Liu H, et al. Cardiovascular Disease and Hip Fracture among Older Inpatients in Beijing, China. Biomed Res Int. 2013.[19] Lumbers M, New SA, Gibson S, et al. Nutritional status in elderly female hip fracture patients: comparison with an age-matched home living group attending day centres. Br J Nutr. 2001;85:733-740.[20] Bonjour JP, Schurch MA, Rizzoli R. Nutritional aspects of hip fractures. Bone. 1996;18:S139-S144.[21] Eneroth M, Olsson UB, Thorngren KG. Insufficient fluid and energy intake in hospitalised patients with hip fracture. A prospective randomised study of 80 patients. Clin. Nutr. 2005; 24:297-303.[22] van Stijn MF, Korkic-Halilovic I, Bakker MS, et al. Preoperative Nutrition Status and Postoperative Outcome in Elderly General Surgery Patients: A Systematic Review. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2013;37:37-43.[23] Koval KJ, Maurer SG, Su ET, et al. The effects of nutritional status on outcome after hip fracture. J Orthop Trauma. 1999; 13:164-169.[24] O'Daly BJ, Walsh JC, Quinlan JF, et al. Serum albumin and total lymphocyte count as predictors of outcome in hip fractures. Clin Nutr. 2010;29:89-93.[25] Willems JM, de Craen AJ, Nelissen RG, et al. Haemoglobin predicts length of hospital stay after hip fracture surgery in older patients. Maturitas. 2012;72:225-228.[26] Poppas DP, Massicotte JM, Stewart RB, et al. Human albumin solder supplemented with TGF-beta(1) accelerates healing following laser welded wound closure. Lasers Surg Med. 1996; 19:360-368.[27] Koertzen M, Punjabi PP, Lockwood GG. Pre-operative serum albumin concentration as a predictor of mortality and morbidity following cardiac surgery. Perfusion Uk. 2013; 28:390-394.[28] Lee HP, Chang YY, Jean YH, et al. Importance of serum albumin level in the preoperative tests conducted in elderly patients with hip fracture. Injury. 2009;40:756-759.[29] Chai FY, Jiffre D. Preoperative Hypoalbuminemia is an Independent Risk Factor for the Development of Surgical Site Infection Following Gastrointestinal Surgery. Ann Surg. 2011; 254:665-665.[30] Lee EH, Chin JH, Choi DK, et al. Postoperative Hypoalbuminemia Is Associated With Outcome in Patients Undergoing Off-Pump Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2011;25:462-468.[31] Patterson BM, Cornell CN, Carbone B, et al. Protein Depletion And Metabolic Stress In Elderly Patients Who Have A Fracture Of The Hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992;74A: 251-260.[32] Pimlott BJ, Jones CA, Beaupre LA, et al. Prognostic impact of pre-operative albumin on short-term mortality and complications in patients with hip fracture. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2011;53:90-94.[33] Mizrahi EH, Fleissig Y, Arad M, et al. Admission albumin levels and functional outcome of elderly hip fracture patients: is it that important? Aging Clin Exp Res. 2007;19:284-289.[34] Bhaskar D, Parker MJ. Haematological indices as surrogate markers of factors affecting mortality after hip fracture. Injury. 2011;42:178-182.[35] Forse RA, Rompre C, Crosilla P, et al. Reliability of the total lymphocyte count as a parameter of nutrition. Can J Surg. 1985;28:216-219.[36] Puskarich CL, Nelson CL, Nusbickel FR, et al. The use of 2 nutritional indicators in identifying long-bone fracture patients who do and do not develop infections. J Orth Res. 1990;8: 799-803.[37] Rudiger A, Burckhardt OA, Harpes P, et al. The relative lymphocyte count on hospital admission is a risk factor for long-term mortality in patients with acute heart failure. Am J Emerg Med. 2006;24:451-454.[38] Kuwae N, Kopple JD, Kalantar-Zadeh K. A low lymphocyte percentage is a predictor of mortality and hospitalization in hemodialysis patients. Clin Nephrol. 2005;63:22-34.[39] Foster MR, Heppenstall RB, Friedenberg ZB, et al. A prospective assessment of nutritional status and complications in patients with fractures of the hip. J Orthop Trauma. 1990;4:49-57.[40] Nilssonehle H, Jagenburg R, Landahl S, et al. Decline of blood hemoglobin in the aged - a longitudinal-study of an urban swedish population from age 70 to 81. Br J Haematol. 1989;71:437-442.[41] Landi F, Russo A, Danese P, et al. Anemia status, hemoglobin concentration, and mortality in nursing home older residents. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2007;8:322-327.[42] Penninx B, Pahor M, Woodman RC, et al. Anemia in old age is associated with increased mortality and hospitalization. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2006;61:474-479.[43] Mosfeldt M, Pedersen OB, Riis T, et al. Value of routine blood tests for prediction of mortality risk in hip fracture patients. Acta Orthopaedica. 2012;83:31-35.[44] Gruson KI, Aharonoff GB, Egol KA, et al. The relationship between admission hemoglobin level and outcome after hip fracture. J Orthop Trauma. 2002;16:39-44.[45] Vochteloo AJ, van der Burg BL, Mertens B, et al. Outcome in hip fracture patients related to anemia at admission and allogeneic blood transfusion: an analysis of 1262 surgically treated patients. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011;12:262. |