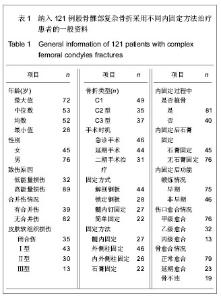
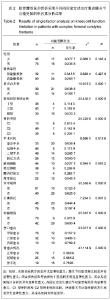
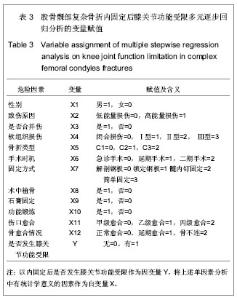
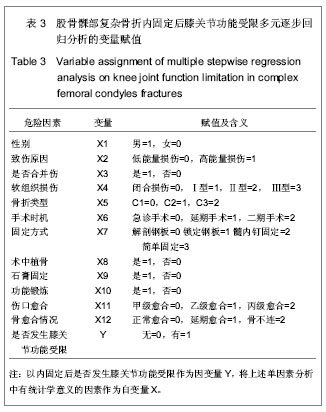
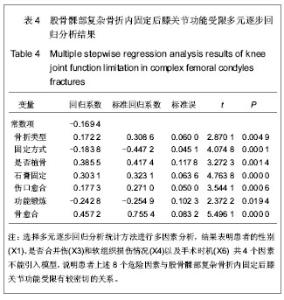
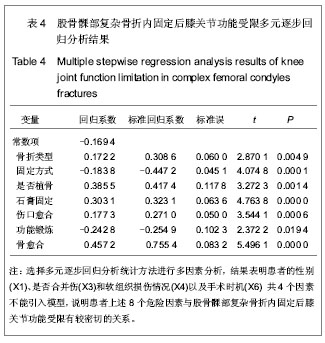
| [1] 杨海峰,黄俊伍,张春林,等.不同内固定物治疗胫骨平台后内侧骨折的生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(26):4826- 4832.[2] 郭斌,靳方运,陈成礼,等.内外组合式固定治疗股骨髁部复杂骨折[J].中国骨伤,2003,9(25):564-565.[3] 沈文东,范为民.股骨髁部不稳定骨折四种内固定方法的生物力学[J].南京医科大学学报,2005,25(11):789.[4] Merchan EC, Maestu PR,Blanco RP. Blade-plating of closed displaced supracondylar fractures of the distal femur with the AO system.J Trauma.1992;32(2):174-178.[5] 王明鑫,熊敏,刘德昌,等.光辅助X射线体表定位在骨科植入物内固定中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(13): 2375-2382.[6] Heiney JP, Battula S, O'Connor JA, et al. Distal femoral fixation: a biomechanical comparison of retrograde nail, retrograde intramedullary nail, and prototype locking retrograde nail. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2012;27(7): 692-696.[7] 盛朝辉,刘汉娇,庞瑞明,等.AO解剖钢板内固定治疗股骨髁间骨折疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2007,22(1):55-56.[8] 江振华,赵卫东,樊仕才,等.改良“叉”形钢板固定股骨髁部C1型骨折的生物力学评价[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2003,21(5): 498-500.[9] 张洪涛,刘康,陈尔东,等.锁定钢板治疗股骨远端C型骨折129 例[J].实用医学杂志,2010,26(15):2764-2766. [10] 张轩轩,隆腾飞,张丕军,等.交锁髓内钉与微创经皮钢板治疗成人胫骨中下段骨折的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(22): 4107-4114.[11] 黄智,云维,邹重文,等.股骨髁部骨折的手术治疗[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2009,11(7):640-641.[12] 陈海涛. 股骨逆行交锁髓内钉植入固定治疗股骨髁部复杂骨折[J].右江民族医学院学报,2002,24(3):367-367.[13] Sen RK, Gul A, Aggarwal S, et al. Comminuted refracture of the distal femur and condyles in patients with an intramedullary nail: a report of 5 cases. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2005;13(3):290-295.[14] Kim YS, Choi HH, Cho YN, et al. Numerical Investigations of Interactions between the Knee-Thigh-Hip Complex with Vehicle Interior Structures. Stapp Car Crash J. 2005;49: 85-115. [15] Henriksen M, Hunter DJ, Dam EB, et al. Is increased joint loading detrimental to obese patients with knee osteoarthritis? A secondary data analysis from a randomized trial. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013. [16] Catagni MA, Ottaviani G, Maggioni M. Treatment strategies for complex fractures of the tibial plateau with external circular fixation and limited internal fixation. J Trauma. 2007;63(5): 1043-1053.[17] 钟贵彬,侯春林,张伟,等.微创内固定系统治疗骨折失误原因分析及对策(附3例报告) [J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2007,22(2): 164-165.[18] 包国玉,郝廷,王兴国,等.双钢板内固定治疗股骨髁间C型骨折的临床疗效分析[J].中国医药导报,2011,8(24):39-41.[19] 姚永成,王友华,张正洲,等.内外侧双侧钢板内固定治疗复杂股骨髁间骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2010,25(1):51-52.[20] Heiney JP, Barnett MD, Vrabec GA, et al. Distal femoral fixation: a biomechanical comparison of trigen retrograde intramedullary (i.m.) nail, dynamic condylar screw (DCS), and locking compression plate (LCP) condylar plate. J Trauma. 2009;66(2):443-449. [21] 徐萃香,刘一,李长胜.当前骨折内固定治疗中的几个基本问题[J].中华骨科杂志,1996,16(4):204-207.[22] Piscitelli P, Iolascon G, Innocenti M, et al. Painful prosthesis: approaching the patient with persistent pain following total hip and knee arthroplasty. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab. 2013; 10(2):97-110. [23] Pei Y, Kim Y, Obinata G, et al. Robot-aided motion planning for knee joint rehabilitation with two robot-manipulators. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2013;2013:2495-2498. [24] Bretin P, O'Loughlin PF, Suero EM, et al. Influence of femoral malrotation on knee joint alignment and intra-articular contract pressures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(8): 1115- 1120. [25] Chang CY, Rupp JD, Reed MP, et al. Predicting the effects of muscle activation on knee, thigh, and hip injuries in frontal crashes using a finite-element model with muscle forces from subject testing and musculoskeletal modeling. Stapp Car Crash J. 2009;53:291-328. |