Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (52): 9011-9016.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.52.012
Previous Articles Next Articles
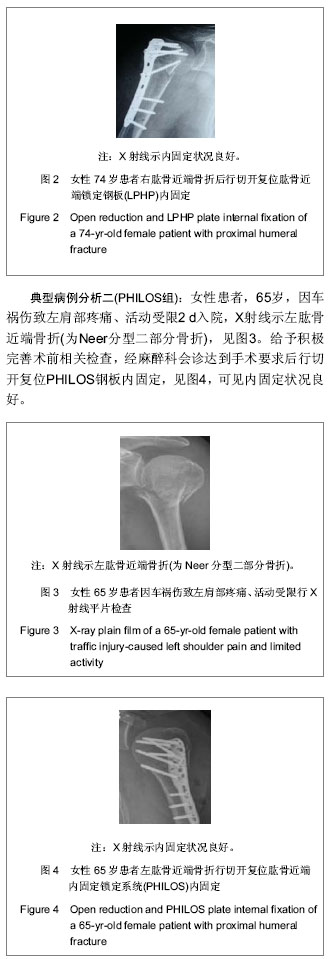
Two kinds of locking plate for treatment of proximal humerus fractures in the elderly
Chen Li, Zhao Di-qing, Yang Guang-zhong, Chen Gang
- Department of Reparative and Reconstructive Surgery, Orthopedics Center, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Revised:2013-09-03Online:2013-12-24Published:2013-12-24 -
Contact:Chen Gang, Ph.D., Associate chief physician, Department of Reparative and Reconstructive Surgery, Orthopedics Center, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Chen Li★, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Reparative and Reconstructive Surgery, Orthopedics Center, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China serenity1900@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Li, Zhao Di-qing, Yang Guang-zhong, Chen Gang. Two kinds of locking plate for treatment of proximal humerus fractures in the elderly[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(52): 9011-9016.
share this article
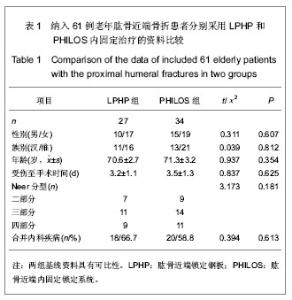
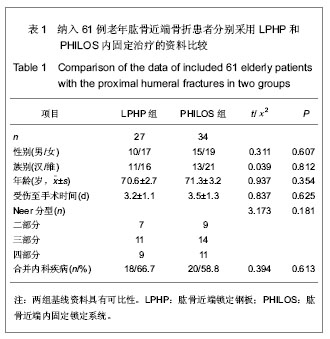
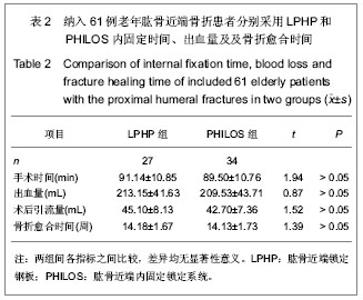
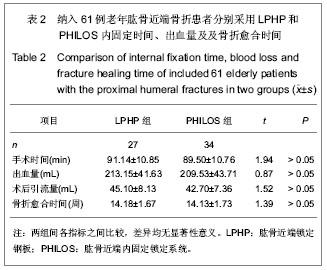
| [1] Kannus P, Palvanen M, Niemi S, et al. Rate of proxinlal humeral fractures in older Finnish women between 1970 and 2007. Bone.2009;44(4):656-659.[2] 张德光,刘福金,刘爱华.肱骨近端骨折锁定加压接骨板内固定治疗肱骨近端骨折[J].中华创伤杂志,2006,22(11):836-838.[3] Bjorkenheim JM, Pajarinen J, Savolainen V. Internal fixation of proximal humeral fractures with a locking compression plate: a retrospective evaluation of 72 patients followed for a minimum of 1 year. Acta Orthop Scand. 2004;75(6):741-745.[4] Neer CS 2nd. Displaced proximal humeral fractures. I. Classification and evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1970; 52(6):1077-1089.[5] Constant CR, Murley AH. A clinical method of functional assessment of the shoulder. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1987; (214):160-164 .[6] Norouzi M, Naderi MN, Komasi MH, et al. Clinical results of using the proximal humeral internal locking system plate for internal fixation of displacedproximal humeral fractures. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ).2012;41(5):E64-68.[7] 刘印文.手法闭合复位经皮微创固定治疗肱骨近端骨折[J].中国骨伤,2012,24(11):949-951.[8] Weinstein DM, Bratton DR, Ciccone WJ 2nd, et al. Locking plates improve torsional resistance in the stabilization of three-part proximal humeral fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006;15(2):239-243.[9] El-Sayed MM. Surgical management of complex humerus head fractures. Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2010;2(2):e14.[10] Wild JR, DeMers A, French R, et al. Functional outcomes for surgically treated 3- and 4-part proximal humerus fractures. Orthopedics. 2011;34(10):e629-633.[11] 熊进,施鸿飞,王守丰,等.应用内固定锁定系统治疗老年肱骨近端骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(20):1585-1587.[12] Gavaskar AS, Muthukumar S, Chowdary N. Biological osteosynthesis of complex proximal humerus fractures: surgical technique and results from a prospective single center trial. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2010;130(5):667-672.[13] Thanasas C, Kontakis G, Angoules A, et a1. Treatment of proximal humerus fractures with locking plates: a systematic review. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2009;18(6):837-844.[14] Ruchholtz S, Hauk C, Lewan U, et al. Minimally invasive polyaxial locking plate fixation of proximal humeral fractures: a prospective study. J Trauma. 2011;71(6):1737-1744.[15] 胡稷杰,金丹,魏宽海,等.肱骨近端锁定钢板或肱骨近端内锁定系统与其他内固定治疗肱骨近端骨折的Meta分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2012,14(12):1047-1054[16] 程兴东,孙强,曾逸文.高龄肱骨近端骨折患者的外科治疗[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2012,18(1):33-35.[17] Hettrich CM, Neviaser A, Beamer BS, et al. Locked plating of the proximal humerus using an endosteal implant. J Orthop Trauma. 2012;26(4):212-215.[18] 何小健,庄健,周凯华,等. 锁定接骨板治疗肱骨近端三、四部分骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(4):688-695.[19] 黄磊,李广旭,李波,等.PHILOS锁定加压接骨板与肱骨近端锁定加压接骨板治疗肱骨近端骨折[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(52):9861-9864 .[20] Faraj D, Kooistra BW, Vd Stappen WAH, et al. Results of 131 consecutive operated patients with a displaced proximal humerus fracture: an analysis with more than two years follow-up. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol.2011;21(1):7-12.[21] Konrad G, Hirschmüller A, Audige L, et al. Comparison of two different locking plates for two-, three- and four-part proximal humeral fractures--results of an international multicentre study. Int Orthop. 2012;36(5):1051-1058. [22] 方铭,孙贤杰,曹铨,等.锁定接骨板治疗老年肱骨近端骨折的近期疗效[J].临床骨科杂志,2012,15(4):400-401.[23] 张华,倪卫东,高仕长,等.锁定加压接骨板治疗肱骨近端骨折[J].中华创伤杂志,2008,24(7):527-530.[24] 付中国,邓磊,白露,等.肱骨近端骨折锁定接骨板治疗术后并发症分析[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2011,43(5):666-670.[25] 曾浪清,陈云丰,刘燕洁,等.内侧柱支撑重建在锁定钢板治疗成人肱骨近端骨折中的临床意义[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2012, 14(7): 561-565.[26] Baumgartner D, Nolan BM, Mathys R, et al. Review of fixation techniques for the four-part fractured proximal humerus in hemiarthroplasty. J Orthop Surg Res. 2011;6:36.[27] Lescheid J, Zdero R, Shah S, et al. The biomechanics of locked plating for repairing proximal humems fractures with or without medial cortical support.J Trauma.2010;69(5):1235- 1242.[28] Röderer G, Erhardt J, Kuster M, et al. Second generation locked plating of proximal humerus fractures--a prospective multicentre observational study. Int Orthop. 2011;35(3):425- 432.[29] 黄强,王满宜,荣国威.复杂肱骨近端骨折的手术治疗[J].中华骨科杂志,2005;25(3):159-164.[30] Spross C, Platz A, Rufibach K, et al. The PHILOS plate for proximal humeral fractures-Risk factors for complications at one year. J Trauma. 2012;72(3):783-792.[31] Wijgman AJ, Roolker W, Patt TW, et a1. Open reduction and internal fixation of three and four-part fractures of the proximal part of the humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Am .2002;84-A(11): 1919-1925.[32] Jost B, Spross C, Grehn H, et al. Locking plate fixation of fractures of the proximal humerus: analysis of complications, revision strategies and outcome. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013; 22(4):542-549. |
| [1] | Chen Qun-qun, Qiao Rong-qin, Duan Rui-qi, Hu Nian-hong, Li Zhao, Shao Min. Acu-Loc®2 volar distal radius bone plate system for repairing type C fracture of distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1025-1030. |
| [2] | Zhang Zhen-hui, Wang Qing-de, Mei Wei, Mao Ke-zheng, Zhu Yao-hui, Guo Run-dong, Jiang Wen-tao, Liu Pei-lin, Wang Zhong-wei. Transpedicular screw placement in the cervical vertebrae assisted by rapid prototyping individual navigation template [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 340-344. |
| [3] | Zou Wei, Xiao Jie, Long Hao, Zhang Yang, Wu Chen, Du Yu-hui, Feng Ming-xing, Zhou Chang-jun. Screw placement selection of minimally invasive percutaneous pedicle screw fixation for thoracolumbar fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 356-361. |
| [4] | Chen Lu-yao, Hu Shi-qiang, Wang Xiao-ping, Wu Wei-wei, Wei Zhan-tu, Huang Jian. Accuracy of digital orthopedic three-dimensional reconstruction for thoracolumbar pedicle screw placement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 373-377. |
| [5] | Du Shi-yao, Zhou Feng-jin, Ni Bin, Chen Bo, Chen Jin-shui. Finite-element analysis of a novel posterior atlantoaxial restricted non-fusion fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 383-389. |
| [6] | Liu Jun, Liao Su-ping. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of Kirschner nails and external fixation for Bennett fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 390-395. |
| [7] | Sheng Xiao-lei, Yuan Feng, Li Zhi-duo, Yang Yu-ming, Lu Hai-tao, Zhang Jun-wei. Comparison of the accuracy of lower cervical anterior transpedicular screws between three-dimensional printing assembly navigation template and free hand placement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 406-411. |
| [8] | Wu Min-hao, Sun Wen-chao, Yan Fei-fei, Xie Yuan-long, Hou Zhi-qiang, Feng Fan, Cai Lin . Treatment research and new progress of early-onset scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 433-439. |
| [9] | Wang Lei, Wang Feng-feng, Ma Yan-hui, Zhang Jie, Hu Fang, Ma Gai-ping, Liu Mei-mei, Ma Zhang-wen. Meta analysis of clinical outcome of intramedullary nails versus locking plates for two-part proximal humerus fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 478-484. |
| [10] | Hu Jun, Zhang De-qiang, Tang Xin. Postoperative quality of life of internal fixation versus hemiarthroplasty for femoral neck fractures in the elderly [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(19): 2953-2960. |
| [11] | Jiang Wei, Yuan Feng. Unilateral pedicle screw fixation combined with translaminar facet screw fixation versus bilateral pedicle screw fixation for lower lumbar degenerative diseases: a 2-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(19): 2973-2979. |
| [12] | Wang Xiu-ping, Sun Rui-bo, Liu You-wen, Zhang Ying, Jia Yu-dong, Yang Yu-xia, Wang Hui-chao. Femoral neck fractures fixed with intramedullary cannulated screws: factors for postoperative functional recovery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(19): 2999-3004. |
| [13] | Liu Gang, Zhang Lei, Wang Guo-you, Zhou Xin, Zhang Tao, Guan Tai-yuan, Guo Xiao-guang, Fu Shi-jie. Double-row suture anchors under arthroscopy for avulsion-type greater tuberosity fractures (Mutch type I) [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(19): 3005-3010. |
| [14] | Yang Min, Ma Xiang-yang, Yang Jin-cheng, Chen Shu-jin, Zou Xiao-bao. Biomechanical properties of a novel automatic anti-rotation posterior atlantoaxial internal fixation system: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(19): 3031-3037. |
| [15] | Qiu Hao, Lu Min-peng, Dong Jing, Zhang Zhong-zu, Chu Tong-wei, Wang Qun-bo, Quan Zheng-xue, Jiang Dian-ming. Subtotal corpectomy and reconstruction with titanium mesh cage implantation and pedicle screw fixation through posterior approach in treatment of thoracolumbar burst fracture or thoracolumbar fracture dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(53): 7932-7938. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||