Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (51): 8827-8833.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.51.008
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of internal fixation with simvastatin coating on healing of rat osteoporotic fractures at late period
Xi Guang-wei1, Wang Xue-ling1, Gong Lin1, Meng Xian-min1, Zhang Jun-shan2, Tian Fa-ming2
- 1 Aerospace Center Hospital, Beijing 100049, China; 2 Hebei United University, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China
-
Online:2013-12-17Published:2013-12-17 -
Contact:Tian Fa-ming, M.D., Lecturer, Hebei United University, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China tfm9911316202@163.com -
About author:Xi Guang-wei★, Master, Physician, Aerospace Center Hospital, Beijing 100049, China Xiguangwei2013@163.com -
Supported by:the Scientific Research and Development Instruction Plan of Tangshan City, No. 13130281Z*; the Major Laboratory Subject of Tangshan City, No. 12150226B*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xi Guang-wei, Wang Xue-ling, Gong Lin, Meng Xian-min, Zhang Jun-shan, Tian Fa-ming. Effects of internal fixation with simvastatin coating on healing of rat osteoporotic fractures at late period[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(51): 8827-8833.
share this article

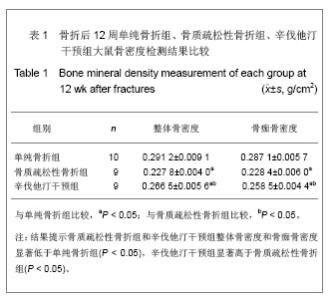
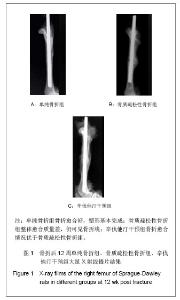
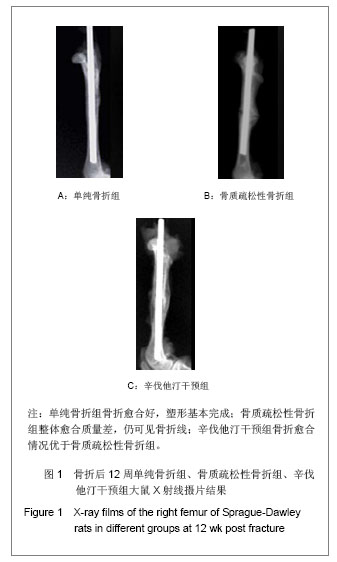
如图1所示,大鼠离体股骨干X射线摄片,观察骨痂的完整性和骨折的愈合情况发现,各组内固定克氏针均无松动和移位,无畸形愈合及成角。单纯骨折组骨折两端对位、对线良好,骨痂与骨皮质密度接近相同并相互连接,塑形基本完成;骨质疏松性骨折组整体愈合质量差,骨痂密度浅淡,部分标本仍见模糊的骨折线;辛伐他汀干预组骨折线消失,骨痂填满骨缺损,骨膜反应深。 X射线评分单纯骨折组(5.20±0.42)分、辛伐他汀干预组(3.95±0.52)分,显著高于骨质疏松性骨折组(2.53± 0.46)分,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 2.5 骨痂组织形态学观察 苏木精-伊红染色结果显示单纯骨折组骨性骨痂转换完成,可见板层骨形成,使骨折部位形成坚强的骨性连接;骨质疏松性骨折组愈合进程延迟,骨痂不成熟,重塑未完成;辛伐他汀干预组较骨质疏松性骨折组小梁骨形成多,粗细均匀一致,排列规则,提示骨折愈合过程较骨质疏松性骨折组加快,见图2。"

| [1]Mundy G, Garrett R, Harris S, et al. Stimulation of bone formation in vitro and in rodents by statins. Science. 1999; 286(5446): 1946-1949.[2]Oxlund H, Andreassen TT. Simvastatin treatment partially ovariectomy- induced bone loss while increasing cortical bone formation. Bone. 2004;34(4): 609-618.[3]Pauly S, Luttosch F, Morawski M, et al. simvastatin locally applied from biodegradable coating of osteosynthetic implants in improves fracture healing coparable to BMP-2 application. Bone. 2009;45(3): 505-511.[4]张俊山, 田发明, 康玉川, 等.高生物涂层局部应用辛伐他汀对骨质疏松大鼠骨折愈合的影响[J].第三军医大学学报, 2013, 53(12): 1274-1278.[5]Saville PD. Changes in skeletal mass and fragility with castration in the rat: a model of osteoporosis. J Am Geriatr Soc.1969;17(2):155-166.[6]田发明, 张柳, 骆阳, 等.仙灵骨葆对骨质疏松性骨折骨痂血管形成的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011, 15(32): 5913-5917.[7]田发明,张柳,骆阳,等.辛伐他汀对大鼠骨质疏松性骨折愈合的影响[J].中国药学杂志,2012,47(21):1719-1723.[8]崔永锋,王琦,张毅,等.杜仲对兔骨折愈合影响的X线影像学研究[J].中药新药与临床药理,2003,14(3):163-165.[9]Boeloni JN, Ocarino NM, Goes AM, et al. Comparative study of osteogenic differentiation potential of mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow and adipose tissue of osteoporotic female rats. Connect Tissue Res. 2013. [Epub ahead of print][10]Smith BJ, Bu SY, Wang Y, et al.A comparative study of the bone metabolic response to dried plum supplementation and PTH treatment in adult, osteopenic ovariectomized rat. Bone. 2013. [Epub ahead of print][11]Zhao H, Li X, Li N, et al. Long-term resveratrol treatment prevents ovariectomy-induced osteopenia in rats without hyperplastic effects on the uterus. Br J Nutr. 2013:1-11. [12]Zhao B, Wang Q, Tao T, et al. The in vitro and in vivo treatment effects of overexpressed lentiviral vector-mediated human BMP2 gene in the femoral bone marrow stromal cells of osteoporotic rats. Int J Mol Med. 2013;32(6):1355-1365.[13]Zhang LZ, Xin JL, Zhang XP, et al. The anti-osteoporotic effect of velvet antler polypeptides from Cervus elaphus Linnaeus in ovariectomized rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013; 150(1):181-186.[14]Nikolaou VS, Efstathopoulos N, Kontakis G, et al. The influence of osteoporosis in femoral fracture healing time. Injury. 2009;40(6):663-668. [15]Kubo T, Shiga T, Hashimoto J,et al. Osteoporosis influences the late period of fracture healing in a rat model prepared by ovariectomy and low calcium diet. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.1999; 68(5-6):197-202.[16]Wang JW, Li W, Xu SW, et al.osteoporosis influences the middle and late periods of fracture healing in a rat osteoporotic model. Chin J Traumatology. 2005; 8(2): 111-116.[17]乔林, 徐克惠, 刘宏伟, 等.去势对雌性大鼠骨折愈合影响的实验研究[J].四川大学学报:医学版,2005,36(1):108-111.[18]Hao YJ, Zhang G, Wang YS, et al.Changes of microstructure and mineralized tissue in the middle and late phase of osteoporotic fracture healing in rats.Bone.2007;41(4): 631-638.[19]Tarantino U, Cerocchi I, Scialdoni A, et al. Bone healing and osteoporosis. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2011;23(2s):62-64.[20]Cao Y, Mori S, Mashiba T, et al. estrogen and alendronate affect the processes of fracture repair differently in ovariectomized rats. J Bone Miner Res. 2002; 17 (12): 2237-2246.[21]Manabe T, Mori S, Mashiba T, et al. Eel calcitonin (elcatonin) suppressed callus remodeling but did not interfere with fracture healing in the femoral fracture model of cynomolgus monkeys. J Bone Miner Metab. 2009; 27(3): 295-302.[22]Rejnmark L, Olsen ML, Johnsen SP, et al. Hip fracture risk in statin users--a population-based Danish case-control study. Osteoporos Int.2004; 15(6): 452-458. [23]Nguyen ND, Wang CY, Eisman JA, et al. On the association between statin and fracture: a Bayesian consideration. Bone. 2007; 40(4):813-820.[24]Nichols R, Hopman WM, Morton AR, et al. Statins are associated with a reduced risk of bone fracture in hemodialysis (HD) patients, Hemodial Int. 2008;12(2): 275- 279.[25]Helin-Salmivaara A, Korhonen MJ, Lehenkari P, et al. Statins and hip fracture prevention--a population based cohort study in women. PLoS One. 2012;7(10): e48095.[26]Ray WA, Daugherty JR, Griffin MR.Lipid-lowering agents and the risk of hip fracture in a Medicaid population. Inj Prev. 2002; 8(4):276-279.[27]LaCroix AZ, Cauley JA, Pettinger M, et al. Statin use, clinical fracture, and bone density in postmenopausal women: results from the Women's Health Initiative Observational Study,Ann Intern Med. 2003;139(2):97-104.[28]Rizzo M, Rini GB. Statins, fracture risk, and bone remodeling: what is true? Am J Med Sci. 2006; 332(2):55-60.[29]Hatzigeorgiou C, Jackson JL. Hydroxymethylglutaryl- coenzyme A reductase inhibitors and osteoporosis: a meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int. 2005;16(8): 990-998.[30]Uzzan B, Cohen R, Nicolas P, et al. Effects of statins on bone mineral density: a meta-analysis of clinical studies. Bone. 2007; 40(6):1581-1587.[31]田发明, 张柳, 孟亚强, 等.辛伐他汀对大鼠骨量及骨髓基质干细胞增殖、分化的影响[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2007, 13(8): 580-585.[32]Van Staa TP,Wegman S,de Vres F,et al.Use of statins and risk of fractures. JAMA. 2001;285(14):1850-1855.[33]Von Stechow D, Fish S, Yahalom D, et al. Does simvastatin stimulate bone formation in vivo?BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2003; 4: 8.[34]Ozec I, Kilic E, Gumus C, et al. Effect of local simvastatin application on mandibular defects. J Craniofac Surg. 2007; 18(3):546-550. [35]Ayukawa Y, Okamura A, Koyano K. Simvastatin promotes osteogenesis around titanium implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2004; 15(3):346-350.[36]Skoglund B, Aspenberg P. Locally applied Simvastatin improves fracture healing in mice.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2007; 8:98.[37]Wang JW, Xu SW, Yang DS, et al. Locally applied simvastatin promotes fracture healing in ovariectomized rat. Osteoporos Int. 2007; 18(12):1641-1650.[38]Nyan M, Hao J, Miyahara T, et al. Accelerated and Enhanced Bone Formation on Novel Simvastatin-Loaded Porous Titanium Oxide Surfaces. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2013. [Epub ahead of print][39]Chou J, Ito T, Bishop D, et al. Controlled Release of Simvastatin from Biomimetic β-TCP Drug Delivery System. PLoS One. 2013; 8(1): e54676. [40]Qi Y, Zhao T, Yan W, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell sheet transplantation combined with locally released simvastatin enhances bone formation in a rat tibia osteotomy model. Cytotherapy. 2013;15(1):44-56. [41]Schmitt JM, Hwang K, Winn SR, et al. Bone morphogenetic proteins: an update on basic biology and clinical relevance. J Orthop Res. 1999;17(2):269-278.[42]Kempen DH, Kruyt MC, Lu L, et al. Effect of autologous bone marrow stromal cell seeding and bone morphogenetic protein-2 delivery on ectopic bone formation in a microsphere/poly(propylene fumarate) composite. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009; 15(3):587-594.[43]Mbalaviele G, Sheikh S, Stains JP, et al. Beta-catenin and BMP-2 synergize to promote osteoblast differentiation and new bone formation. J Cell Biochem. 2005; 94(2): 403-418. |
| [1] | Li Xiaoqun, Xu Kaihang, Ji Fang. Corylin inhibits osteoclastogenesis and attenuates postmenopausal osteoporosis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(在线): 4-. |
| [2] | Zhong Yuanming, Luo Man, Tang Fubo, Tang Cheng. Relationship between a linear black signal area of STIR image in MRI of osteoporotic thoracolumbar fracture and the size of external force [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1400-1404. |
| [3] | Xu Shaoce, Wang Shiyao, Zhou Jianwei, Pan Yixin, Wang Yuliang. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 regulation and mechanism in callus formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1083-1088. |
| [4] | Liu Zhendong, Qin Sihe. Four-dimensional space events of fracture healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(6): 903-910. |
| [5] | Liu Qun, Sun Dongdong, Gao Lilan, He Zhijiang, Sun Minglin. Risk factors for fractures secondary to percutaneous kyphoplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(6): 976-984. |
| [6] | Cao Guolong, Tian Faming, Liu Jiayin. Lovastatin combined with insulin effects on fracture healing in rat models of bilateral ovariectomized type 2 diabetic mellitus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 673-681. |
| [7] | Yu Peiyuan, Zhang Zhida, Liang Lichang, Yang Zhidong, Huang Jinjing, Peng Jiancheng, Liang Ziyang, He Jiahui, Zhao Wenhua, Yu Fuyong, Chen Guifeng, Liang De, Jiang Xiaobing . Difference in the effect of metformin on bone strength of lumbar vertebrae and hind limbs in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 657-661. |
| [8] | Luo Peijie, Yuan Kai, Li Daxing, Zhang Shuncong, Guo Huizhi, Tang Yongchao, Zhou Tengpeng, Guo Danqing, Li Yongxian, Mo Guoye. Comparison of the short-segment and long-segment cement-augmented pedicle screw fixation for osteoporotic thoracolumbar fracture: a finite element study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 342-347. |
| [9] | Yang Shun, Chen Keyi, Cheng Yabo, Xiang Wang, Zhang Jing, Gu Hongji, Chi Haotian. Wrist arthroscopy-assisted titanium internal fixator for the treatment of complex distal radius fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 366-371. |
| [10] | Liu Ruizhen, Wang Wangren, Hao Chen, Liang Dongmu, Guan Haishan. Effect of bone cement distribution on adjacent vertebral body fracture after unilateral percutaneous vertebroplasty for single segment osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(28): 4498-4504. |
| [11] | Xie Hui, Chen Haopeng, Wang Benjie, Fu Weimin, Zhao Dewei. Effect of different distribution types of bone cement after percutaneous kyphoplasty on osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures at different sites [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(28): 4505-4510. |
| [12] | Yao Shunhan, Wei Huacheng, Qin Jiagang, Liao Liang. Mogroside V stimulates osteoblast proliferation and differentiation by promoting LncRNA TUG1 expression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4129-4134. |
| [13] |
Li Shaoshuo, Gu Yidan, Shao Yang, Yin Heng, Wang Jianwei.
Visualization analysis of CiteSpace knowledge maps regarding prevention and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4224-4230. |
| [14] |
Dong Xiling, Zhang Xiaoming, Liu Tongbin.
Recombinant human parathyroid hormone (1-34): pro-osteogenic action and application in oral field [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4231-4236. |
| [15] |
Ye Yunjin, Li Jianyang, Ge Jirong, Xu Huijuan, Chen Sainan, Xie Lihua, Li Li.
Combination of hip geometry mechanics and fracture risk assessment tool to predict fracture risk in middle-aged and elderly women [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4101-4105. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||