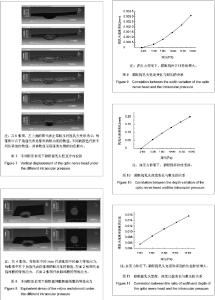
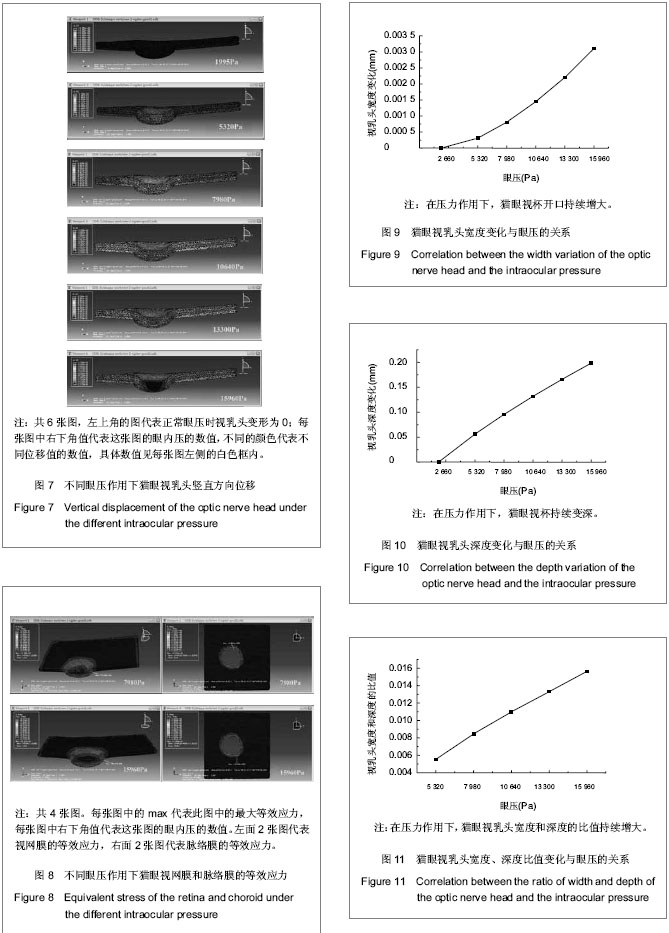
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
Shape variation of optic nerve head by mechanical analysis using three-dimensional finite element model
Qi Xin-zheng, Wei Chao, Yang Jia-yan, Mu Jing, Zhang Kun-ya, Liu Zhi-cheng, Qian Xiu-qing
- School of Biomedical Engineering, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100069, China
-
Revised:2013-11-09Online:2013-12-10Published:2013-12-10 -
Contact:Qian Xiu-qing, Ph.D., Associate professor, School of Biomedical Engineering, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100069, China qianxq@ccmu.edu.cne -
About author:Qi Xin-zheng, School of Biomedical Engineering, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100069, China Qi.xinzheng@163.com -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 11102123*, 31070840*; Scientific General Program of Beijing Municipal Education Commission, No. KM201110025009*; Funding Program for Academic Human Resources Development in Institutions of Higher Learning Under the Jurisdiction of Beijing Municipality of China, No. PHR201008398*, PHR201110506*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Qi Xin-zheng, Wei Chao, Yang Jia-yan, Mu Jing, Zhang Kun-ya, Liu Zhi-cheng, Qian Xiu-qing. Shape variation of optic nerve head by mechanical analysis using three-dimensional finite element model[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.50.015.
share this article
| [1] Quigley HA, Addicks EM, Green WR, et al. Optic nerve damage in human glaucoma. II: The site of injury and susceptibility to damage. Arch Ophthalmol.1981;99(4): 635-649.[2] 季宝玲, 游逸安, 方爱武, 等. OCT测量视网膜神经纤维层和黄斑厚度在青光眼早期诊断中的意义[J]. 眼视光学杂志,2008, 10(1): 54-58.[3] 胡赛静, 邱翎. 正常眼与原发性开角型青光眼的OCT视盘参数分析的对比研究[J]. 临床眼科杂志, 2007, 15(1):26-28.[4] 戴惟葭, 边俊杰, 杨惠青, 等. 急性闭角型青光眼视网膜神经纤维层改变的一年动态观察[J]. 眼科, 2010, 19(5): 331-335.[5] Sigal IA, Flanagan JG, Tertinegg I, et al. Modeling individual-specific human optic nerve head biomechanics. Part II: influence of material properties. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2009;8:99-109.[6] Yang H, Downs JC, Sigal IA, et al. Deformation of the normal monkey optic nerve head connective tissue after acute IOP elevation within 3-D histomorphometric reconstructions. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009;50:5785-5799.[7] 杨翎, 袁志兰, 占慧琴. FD-OCT测量视盘周围视网膜神经纤维层和视神经乳头参数在青光眼早期诊断中的意义[J]. 南京医科大学学报:自然科学版, 2010,30(7): 1026-1030.[8] 杨新光, 刘钊, 于敬妮, 等. 原发性青光眼早期视盘参数与视野缺损的关系[J]. 临床眼科杂志, 2009, 17(4):295-299.[9] 徐亮, 夏翠然, 杨桦, 等. 正常人不同类型视乳头及早期青光眼患者视乳头形态学研究[J]. 中华眼科杂志, 2002, 38(6): 325-328.[10] Quigley HA, Addicks EM. Quantitative studies of retinal nerve fiber layer defects. Arch Ophthalmol. 1982;100: 807-814.[11] Quigley HA, Addicks EM. Regional differences in the stucture of the laminal cribeosa and their relation to glaucomatous optic nerve damage. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981;99: 137-143.[12] He DQ, Ren ZQ. A biomathematical model for pressure- dependent lamina cribrosa behavior. J Biomech. 1999; 32: 579-584.[13] Belleza AJ, Hart RT, Burgoyne CF. The optic nerve head as a biomechanical structure: initial finite element modeling. Invest OphthalmolVis Sci. 2000;41(10): 2991-3000.[14] Yang H, Downs JC, Bellezza A, et al. 3-D histomorphometry of the normal and early glaucomatous monkey optic nerve head: prelaminar neural tissues and cupping. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007;48:5068-5084.[15] Sigal IA, Flinagan JG, Ethier CR. Finite element modeling of optic nerve head. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004;45(12): 4378- 4387.[16] Sigal IA, Flinagan JG, Tertinegg I, et al. Reconstruction of human nerve heads for finite element modeling. Tech Health Care. 2005;13: 313 -329.[17] Sigal IA, Flanagan JG, Tertinegg I, et al. 3D morphometry of the human optic nerve head. Exp Eye Res. 2010;90:70-80.[18] Roberts MD, Grau V, Grimm J, et al. Remodeling of the connective tissue microarchitecture of the lamina cribrosa in early experimental glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009; 50(2): 681-690.[19] Roberts MD, Liang Y, Sigal IA, et al. Correlation between Local Stress and Strain and Lamina Cribrosa Connective Tissue Volume Fraction in Normal Monkey Eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010;51(1):295-307.[20] Sigal IA. An applet to estimate the IOP-induced stress and strain within the optic nerve head. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52(8): 5497-5506.[21] Sigal IA, Yang H, Roberts MD, et al. IOP-induced lamina cribrosa displacement and scleral canal expansion: an analysis of factor interactions using parameterized eye-specific models. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011; 52(3):1896-1907.[22] Norman RE, Flanagan JG, Sigal IA, et al. Finite element modeling of the human sclera: Influence on optic nerve head biomechanics and connections with glaucoma. Exp Eye Res. 2011;93: 4-12.[23] Chen TC, Cense B, Miller JW, et al. Histologic correlation of in vivo optical coherence tomography images of the human retina. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006;141:1165-1168.[24] Toth CA, Birngruber R, Boppart SA, et al. Argon laser retinal lesions evaluated in vivo by optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol. 1997;123:188-198.[25] Toth CA, Narayan DG, Boppart SA, et al. A comparison of retinal morphology viewed by optical coherence tomography and by light microscopy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1997;115: 1425-1428.[26] Strouthidis NG, Fortune B, Yang H, et al. longitudinal change detected by spectral domain optical coherence tomography in the optic nerve head and peripapillary retina in experimental glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52(3): 1206-1219.[27] Yang H, Qi J, Hardin C, et al. Spectral-domain optical coherence tomography enhanced depth imaging of the normal and glaucomatous nonhuman primate optic nerve head. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53: 394-405.[28] Reis AS, Sharpe GP, Yang H, et al. Optic disc margin anatomy in patients with glaucoma and normal controls with spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology. 2012;119:738-747.[29] Inoue R, Hangai M, Kotera Y, et al. Three-dimensional high-speed optical coherence tomography imaging of lamina cribrosa in glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 2009;116: 214-222.[30] Ruggeri M, Wehbe H, Jiao S, et al. In vivo three-dimensional high-resolution imaging of rodent retina with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007;48:1808-1814.[31] Abbott CJ, McBrien NA, Grunert U, et al. Relationship of the optical coherence tomography signal to underlying retinal histology in the tree shrew (Tupaia belangeri). Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009;50:414-423[32] Qiu JF, Qian XQ, Cui QQ, et al. Three-Dimensional Reconstruction and Finite Element Modeling Analysis of the Rabbit Optic Nerve Head in Acute High Intraocular Pressure. Jap J Appl Phys. 2012;51(6): 067001.[33] Chen K, Rowley AP, Weiland JD. Elastic properties of porcine ocular posterior soft tissues. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010; 93(2):634-645.[34] Del Priore LV. Stiffness of retinal and choroidal tissue: a surface wrinkling analysis of epiretinal membranes and choroidal folds. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006;142(3):435-440.[35] 钱勇, 刘菊, 段文静, 等. 频域OCT检测青光眼视乳头及黄斑区容积改变的初步研究[J]. 临床眼科杂志, 2011,19(3): 200-203.[36] Maruko I, Iida T, Sugano Y, et al. Subfoveal retinal and choroidal thickness after verteporfin photodynamic therapy for polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 2011; 151(4):594-603.[37] Park HY, Jeon SH, Park CK. Enhanced depth imaging detects lamina cribrosa thickness differences in normal tension glaucoma and primary open-angle glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 2012;119: 10-20.[38] Park SC, De Moraes CG, Teng CC, et al. Enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography of deep optic nerve complex structures in glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 2012;119: 3-9.[39] 张昆亚, 殷莹, 张伟, 等. 利用连通器原理设计体内加压及眼球体积监测装置观测兔眼球蠕变特性[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009, 43(13): 8499- 8502.[40] 王兰, 梁远波, 王宁利, 等.原发性开角型和闭角型青光眼眼压降低前后视盘改变和筛板顺应性的对比研究[J]. 眼科, 2009, 18(4): 264-269. |
| [1] | Liu Jie, Fan Ruoxun, Gao Jiazi, Zeng Sheng, Liu Jun. Mechanical responses of the degenerated lumbar spines with different degrees at low frequency vibration generated by vehicle driving using finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1371-1377. |
| [2] | Wang Yiya, Zhang Han, Lan Hai. Digital evaluation of finite element model for percutaneous kyphoplasty with bone cement injection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1378-1383. |
| [3] | Liu Yan, Ge Hongqing, Guan Hua, Chen Wenzhi. Finite element analysis of different fixation methods for poor medial column support proximal humeral fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1384-1389. |
| [4] |
Zhang Cong, Zhao Yan, Du Xiaoyu, Du Xinrui, Pang Tingjuan, Fu Yining, Zhang Hao, Zhang Buzhou, Li Xiaohe, Wang Lidong.
Biomechanical analysis of the lumbar spine and pelvis in adolescent
idiopathic scoliosis with lumbar major curve |
| [5] | Wang Hong, Wu Quan, Tang Geng, Zhang Gong. Design and clinical application of personalized antibiotic cement spacer of knee joint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(6): 821-826. |
| [6] | Wang Xiaohui, Wang Kun, Hu Zhiyong, Tian Hongliang. Design of the prosthetic socket and the finite element analysis of the interfacial stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(6): 862-868. |
| [7] | Luan Shuangyu, Zeng Liang, Chen Bin, Tian Wei, Yan Nan, Chen Xi, Zhang Shuo, Wang Zhengdong. Effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on microglial activation after optic nerve injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 3937-3942. |
| [8] | Ji Haihong, Dong Qiang. Finite element analysis of different fixation methods for mandibular defects reconstructing with fibula flaps [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(24): 3821-3827. |
| [9] | Li Zhongxian, Ji Yucheng, Weng Yujie, Ning Pengfei. Mongolian osteopathy in the treatment of ulna-radius fractures: finite element analysis of mechanical principle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(21): 3293-3298. |
| [10] | Wu Zheng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan, Sun Rong, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Liu Tao, Ou Hua. Effect of meniscus injury on the biomechanical properties of knee joint under gait cycle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(21): 3299-3303. |
| [11] | Liu Fushenghua, Xu Jian, Zhao Bingcheng, Wei Gehan, Qin Wenbao. Three-dimensional finite element biomechanical analysis of stage II adult acquired flatfoot deformity after medial column stabilization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(18): 2805-2810. |
| [12] | Ling Guanhan, Li Yongbin, Pan Xuewen, Lin Hengfeng, He Ke, Li Yuanchun, Lu Baiyu, Chen Changlin. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of fibula implantation for China-Japan Friendship Hospital type osteonecrosis of femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(18): 2817-2822. |
| [13] | Annikaer•Aniwaer, Palidaimu•Tuerti, Adili•Maimutimin, Zhang Fan, Niruti•Tuerxun. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of different implant prostheses in maxillary anterior teeth region under different occlusal relationships [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(16): 2531-2536. |
| [14] |
Wang Xiao, Tan Guoqing, Xue Haipeng, Xu Zhanwang.
Finite element analysis of lumbar interbody fusion combined
with adjacent-segment semi-rigid fixation |
| [15] | Jiang Qiang, Ding Yu, Liu Jinyu, Cao Shiqi, Lu Zhengcao. Finite element simulation and biomechanical analysis of fully endoscopic precisely laminectomy decompression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(12): 1891-1896. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||