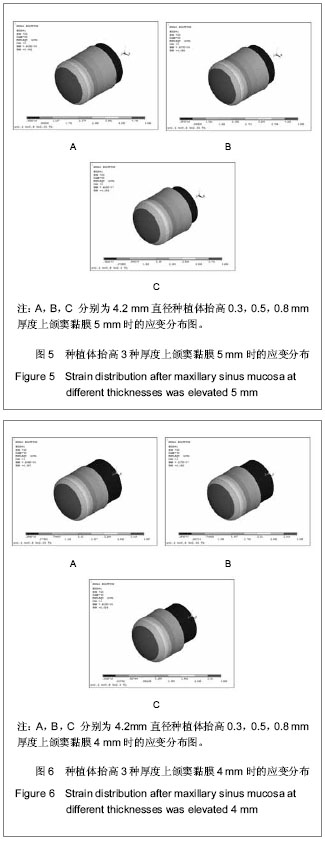
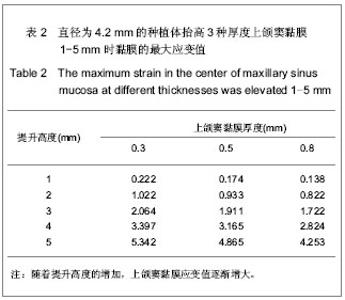
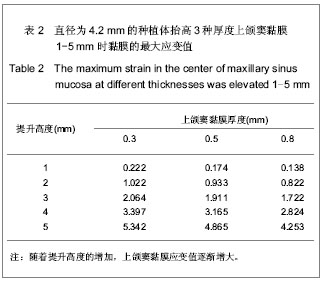
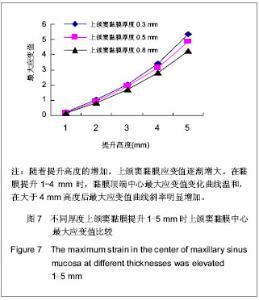
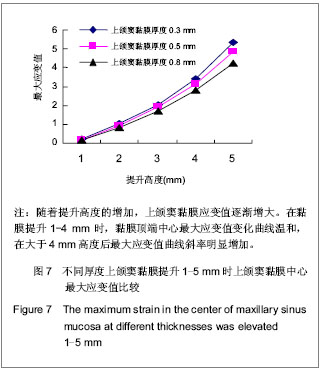
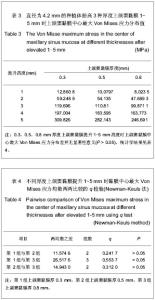
| [1] Berengo M,Sivolella S,Majzoub Z, et al.Endoscopic evaluation of the bone-added osteotome sinus floor elevation procedure. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004;33(2):189-194. [2] Del Fabbro M, Testori T, Francetti L, et al.Systematic review of survival rates for implants placed in the grafted maxillary sinus.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent.2004;24(6): 565-577.[3] Leblebicioglu B,Ersanli S,Karabuda C, et al.Radiographic evaluation of dental implants placed using an osteotome technique.J Periodontol.2005;76(3):385-390.[4] 李晓东,裴仲秋,杨小竺.闭合式上颌窦底提升同期牙种植体植入术疗效研究[J].重庆医学,2007,36(4):314-315.[5] 赵保东,李宁毅,许家森,等.经牙槽嵴顶入路的上颌窦提升植骨及同期种植体植入术[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2003,38(4): 251-253.[6] McDermott NE,Chuang SK,Woo VV, et al. Maxillary sinus augmentation as a risk factor for implant failure.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2006;21(3):366-374.[7] Degidi M,Daprile G,Piattelli A, et al. Evaluation of factors influencing resonance frequency analysis values,at insertion surgery,of implants placed in sinus-augmented and nongrafted sites.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.2007; 9(3): 144-149.[8] Barone A, Santini S, Sbordone L, et al.A clinical study of the outcomes and complications associated with maxillary sinus augmentation.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2006;21(1): 81-85. [9] 朱卓立,宫苹,焦锡葳.上颌窦提升术与上颌窦炎相关性研究现状[J].国外医学:口腔医学分册,2004,31(6):467-469.[10] van den Bergh JP, ten Bruggenkate CM, Disch FJ, et al. Anatomical aspects of sinus floor elevations.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2000;11(3):256-65.[11] 蒋峰,张雄.上颌窦底壁分嵴的研究进展[J].中国口腔种植学杂志, 2010,15(1):48-50.[12] Morgensen C, Tos M. Quantitative Histology Of the maxillary sinus.Rhinology.1977;15(3):129-40[13] Ardekian L, Oved-Peleg E, Mactei EE, et al. The clinical significance of sinus membrane perforation during augmentation of the maxillary sinus. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006;64(2):277-282.[14] Hernández-Alfaro F, Torradeflot MM, Marti C.Prevalence and management of Schneiderian membrane perforations during sinus-lift procedures.Clin Oral Implants Res.2008;19(1): 91-98.[15] Garbacea A,Lozada JL,Church CA, et al. The incidence of maxillary sinus membrane perforation during endoscopically assessed crestal sinus floor elevation: a pilot study.J Oral Implantol. 2012;38(4):345-359. [16] Ding X,Zhu XH,Wang HM, et al. Effect of sinus Membrane perforation on the survival of implants placed in combination with osteotome sinus floor elevation.J Craniofac Surg. 2013; 24(2):102-104.[17] Becker ST, Terheyden H, Steinriede A, et al.Prospective observation of 41 perforations of the Schneiderian membrane during sinus floor elevation.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2008; 19(12):1285-1289. [18] Wallace SS, Mazor Z, Froum SJ, et al. Schneiderian membrane perforation rate during sinus elevation using piezosurgery: clinical results of 100 consecutive cases.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent.2007;27(5):413-419.[19] Aimetti M, Massei G, Morra M, et al.Correlation between gingival phenotype and Schneiderian membrane thickness. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2008;23(6):1128-1132.[20] Yilmaz HG, Tözüm TF.Are gingival phenotype,residual ridge height,and membrane thickness critical for the perforation of maxillary sinus? J Periodontol.2012;83(4):420-425.[21] Pommer B,Unger E,Sütö D, et al. Mechanical properties of the Schneiderian membrane in vitro.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009;20(6):633-637.[22] 简波,宋应亮,李德华,等.含多个种植体的无牙下颌骨三维有限元模型的建立[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2008,18(10):552-555.[23] 冯伟,周新聪,严新平,等.接触问题实体建模及有限元法仿真实现[J].武汉理工大学学报,2004,26(6):52-55.[24] 郑诚功.骨科生物力学研究的发展与现状[J].医用生物力学,2007, 22(4):326-327. [25] Koca OL, Eskitascioglu G, Usumez A. Three-dimensional finite-element analysis of functional stresses in different bone locations produced by implants placed in the maxillary posterior region of the sinus floor. J Prosthet Dent. 2005; 93(1):38-44.[26] 薄斌,周树夏,张明,等.颌面部撞击伤的生物力学研究[J].中华创伤杂志,2001,17(2):80-82.[27] 黄宇文.有限元分析在口腔生物力学中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(13):2423-2426.[28] 胡建军,周延民,王志彪,等.不同载荷下天然牙一种植牙联合桥基牙应力分布[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2001,6(1):17-19.[29] Stegaroiu R, Watanabe N, Tanaka M, et al. Peri-implant stress analysis in simulation models with or without trabecular bone structure. Int J Prosthodont.2006;19(1):40-42.[30] 李长义,荆洪阳.下颌后牙固定义齿连接体受力的三维有限元分析[J].天津医科大学学报,2002,8(1):90-91.[31] Lin CL, Chang SH, Chang WJ, et al. Factorial analysis of variables influencing mechanical characteristics of a single tooth implant placed in the maxilla using finite element analysis and the statistics-based Taguchi method. Eur J Oral Sci.2007;115(5):408-416.[32] 李美华,王伟,董丽华,等.用三维有限元方法对单端固定桥进行应力分析[J].口腔医学纵横杂志,2000,16(3):197-199.[33] Fanuscu MI, Vu HV, Poncelet B.Implant biomechanics in grafted sinus: a finite element analysis. J Oral Implantol. 2004; 30(2):59-68.[34] 孙艳霞,鲍旭东,蒋春涛.软组织建模中的有限元模型[J].生物医学工程研究,2004,23(3):137-140.[35] 张林,顾晓明,王莹,等.正颌外科软组织形态有限元分析系统的建立与应用[J].中华整形外科杂志,2003,19(3):207-210.[36] Geramy A, Faghihi S. Secondary trauma from occlusion: three dimensional analysis using the finite element method. Quintessence Int.2004;35(10):835-843.[37] Toms SR,Dakin GJ,Lemons JE. Quasi-linear viscoelastic behavior of the human periodontal ligament. J Biom.2002; 35(10):1411-1415.[38] 魏志刚,汤文成,严斌,等.基于有限元法的牙周膜本构模型研究[J].工程力学,2009,26(10):211-216.[39] 卢红飞,艾虹,麦志辉,等.牙齿牙周矫治装置三合一三维有限元模型的建立[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(22):4010- 4013. [40] 赵玺,米丛波,居曼江•买买提,等.牙周膜牵张成骨术快速移动尖牙的三维有限元模型建立[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(22):4014-4017.[41] 林苑云,郑美华,韦佩伶,等.冠外固位体义齿基牙牙周组织应力分布的三维有限元分析[J]. 广东牙病防治,2012,20(3):130-133. |