Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells undergoing hypoxic preconditioning can differentiate into vascular endothelial-like cells
Hao Xiao-juan1, Zhu Lü-yun2
- 1Graduate School of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China; 2Department of Endocrinology, Bethune International Peace Hospital, Shijiazhuang 050082, Hebei Province, China
-
Revised:2013-08-06Online:2013-11-05Published:2013-11-05 -
Contact:Zhu Lü-yun, M.D., Professor, Department of Endocrinology, Bethune International Peace Hospital, Shijiazhuang 050082, Hebei Province, China zzllyy2008@yahoo.com.cn -
About author:Hao Xiao-juan★, Master, Physician, Graduate School of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China crazygirl1314@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hao Xiao-juan, Zhu Lü-yun. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells undergoing hypoxic preconditioning can differentiate into vascular endothelial-like cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.45.008.
share this article

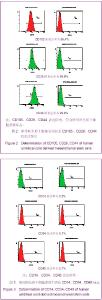
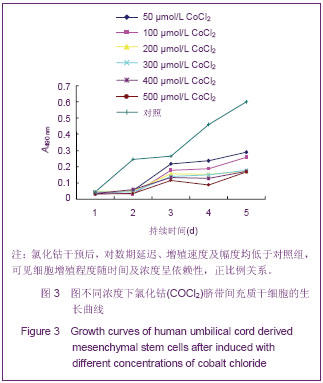
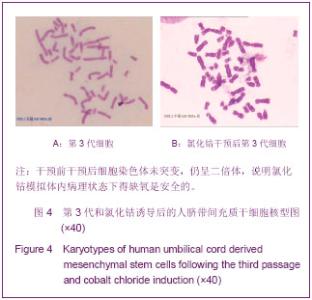
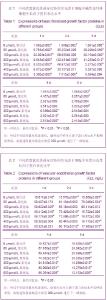
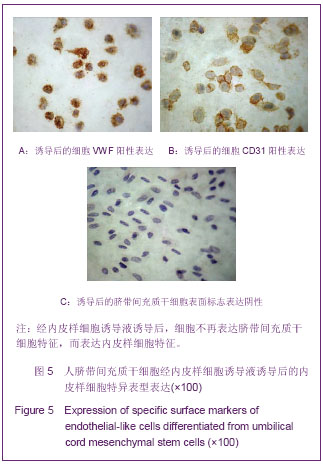
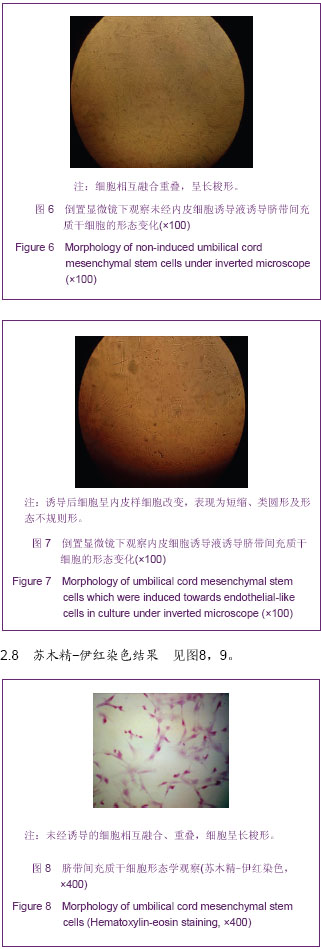
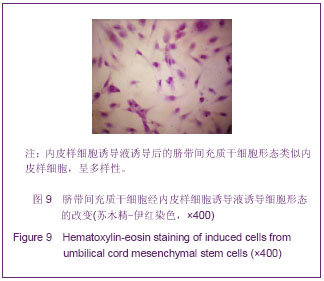
2.7 诱导后的内皮样细胞形态 诱导起初各组细胞增殖程度一致,1周后单纯脐带间充质干细胞组细胞明显增殖,细胞相互融合、重叠,细胞呈长梭形;脐带间充质干细胞+氯化钴诱导3 d组细胞增殖程度稍低于单纯脐带间充质干细胞组,细胞同样呈长梭形;脐带间充质干细胞+氯化钴组与单纯脐带间充质干细胞组细胞增殖明显减低,较诱导前无明显改变,见图6。 随着时间延长,单纯脐带间充质干细胞组和脐带间充质干细胞+氯化钴诱导3 d组增殖程度逐渐减低,细胞呈多角形及长梭形;脐带间充质干细胞+氯化钴组增殖程度大于单纯脐带间充质干细胞组和脐带间充质干细胞+氯化钴诱导3 d组,细胞形态近似圆形;对照组增殖减少最明显,细胞形态无明显改变;于第5周,前3组细胞形态均呈短缩、类圆形及形态不规则形,见图7。对照组形态较前无明显变化。"

| [1] 吕璐璐,宋永平,魏旭东,等.人脐带和骨髓源间充质干细胞生物学特征的对比研究[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2008,16(1): 140-146. [2] Wexler SA, Donaldson C, Denning-Kendall P, et al.Adult bone marrow is a rich source of human mesenchymal stem cells but umbilical cord and mobilized adult blood are not. Br J Haematol.2003;121(2):368-374. [3] Secco M, Zucconi E, Vieira NM, et al.Multipotent stem cells from umbilical cord: cord is richer than blood. Stem Cells. 2008;26(1):146-150. [4] Oswald J, Boxberger S, Jorgensen B, et al.Mesenchymal stem cells can be differentiated into endothelial cells in vitro.Stem Cells.2004;22(3):377-384. [5] 邵琴,王长谦,何奔,等.脐血外周血内皮祖细胞成内皮细胞的体外比较研究[J].临床心血管杂志,2006,6(6):346-350. [6] 朱斌,王云雅,张志勇,等.大鼠内皮祖细胞的分离、培养与定向诱导分化.[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2009,18(6):608-611. [7] Ghosh G, Subramanian IV, Adhikari N, et al. Hypoxia-induced microRNA-424 expression in human endothelial cells regulates HIF-α isoforms and promotes angiogenesis. Clin Invest. 2010;120(11):4141-4154. [8] Rev S, Semenza GL. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1-dependent mechanisms of vascularization and vascular remodelling. Cardiovasc Res. 2010;86(2):236-242. [9] Kim KS, Rajagopal V, Gonsalves C, et al. A novel role of hypoxia-inducible factor in cobalt chloride- and hypoxia-mediated expression of IL-8 chemokine in human endothelial cells. J Immunol. 2006;177(10);7211-7224. [10] 刘晓娟,惠延年,郭斌,等.缺氧下外源性血管内皮生长因子对体外大鼠Müller细胞的影响[J].国际眼科杂志, 2007,7(2):395- 399. [11] 许樟荣,敬华.糖尿病足国际临床指南[M].北京:人民军医出版社, 2003:6-45. [12] Nawaz A, Saboury B, Basu S, et al. Relation between popliteal-tibial artery atherosclerosis and global glycolytic metabolism in the affected diabetic foot: a pilot study using quantitative FDG-PET. Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2012;102(3): 240-246. [13] Mehta NN, Toriqian DA, Gelfand JM, et al. Quantification of atherosclerotic plaque activity and vascular inflammation using [18-F] fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (FDG-PET/CT). J Vis Exp. 2012;(63): 3777-3791. [14] Li L, Yu H, Zhu J,et al. The combination of carotid and lower extremity ultrasonography increases the detection of atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetes Complications. 2012;26(1):23-28. [15] Kirana S, Stratmann B, Prante C, et al. Autologous stem cell therapy in the treatment of limb ischaemia induced chronic tissue ulcers of diabetic foot patients. Clin Pract. 2012;66(4): 384-393. [16] 朱旅云,王广宇,马利成,等.脐血单个核细胞移植治疗糖尿病足23例[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(1):175-178. [17] 侯跃龙,李彤,严晓晔,等.缺氧预处理对脐带间充质干细胞bFGF分泌的影响[J].解放军医学杂志,2010,35(3):297-300. [18] Ardyanto TD, Osaki M, Tokuyasu N, et al . Cocl2-induced HIF-1 alpha expression correlates with proliferation and apoptosis in MKN-1 cells: a possible role for the P13K/Akt path way. Int Jm Oncol.2006;29(3):549-555. [19] Balaiya S, Khetpal V, Chalam KV. Hypoxia initiates sirtuin1-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor activation in choroidal endothelial cells through hypoxia inducible factor-2α. Mol Vis. 2012;18(17):114-120. [20] Fujita H,Koshida K,Keller ET, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 promotes prostate cancer progression. Prostate. 2002;53(3): 232-240. [21] Hu X,Ys SP ,Fraser JL,et al.Transplantation of hypoxia-preconditione mesenchymal stem cells improve infracted heart function via enhanced survival of implanted cells and angiogenesis.Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.2008; 135(4): 799-808. [22] Haider KH,Kim HW,Ashraf M. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in stem cell preconditioning: mechanistic role of hypoxia-related micro-RNAs. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2009; 138(1):257. [23] Zhao Y, Cai SX. Isolation, culture and differentiation into endothelial-like cells from rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2010;26(1):60-65. [24] Lai WH, Ho JC, Chan YC, et al. Attenuation of hind-limb ischemia in mice with endothelial-like cells derived from different sources of human stem cells. PLoS One. 2013; 8(3):57876. [25] Portalska J, Dean Chamberlain M,Lo C, et al . Collagen modules for in situ delivery of mesenchymal stromal cell-derived endothelial cells for improved angiogenesis. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2013;17 (10):1738. [26] Vishnubalaji R, Manikandan M, Al-Nbaheen M, et al, In vitro differentiation of human skin-derived multipotent stromal cells into putative endothelial-like cells. BMC Dev Biol. 2012;12:7. [27] Marchal JA, Picon M,Bueno C, et al . Purification and long-term expansion of multipotent endothelial-like cells with potential cardiovascular regeneration. Stem Cells Dev. 2012, 21(4):562-574. [28] Yan D, Wang X, Li D, et al. Macrophages overexpressing VEGF, transdifferentiate into endothelial-like cells in vitro and in vivo. Biotechnol Lett. 2011;33(9):1751-1758. [29] Berger S, Dyugovskaya L, Polyakov A,et al, Short-term fibronectin treatment induces endothelial-like and angiogenic properties in monocyte-derived immature dendritic cells: involvement of intracellular VEGF and MAPK regulation. Eur J Cell Biol. 2012;91(8):640-653. [30] Comsa S, Ciuculescu F, Henschler R, et al. MCF7-MSC co-culture assay: approach to assess the co-operation between MCF-7s and MSCs in tumor-induced angiogenesis. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2011;52(3):1071-1076. [31] Oskowitz A, McFerrin H, Gutschow M,et al. Serum-deprived human multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) are highly angiogenic. Stem Cell Res. 2011;6(3):215-225. [32] 陈旭春,程颖,杨蕾,等.三维及二维培养大鼠胰腺导管来源干细胞的体外对比实验研究[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2012,19(7): 722-726. |
| [1] |
Zheng Haijun, Jin Hui, Cui Hongling, Zhu Yakun, Zeng Hui, Han Fengjie, Qiu Cuiting, Liu Jing.
Safety of drug-coated balloon versus drug-eluting stents in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated by coronary artery small vessel disease in older adult patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(28): 4573-4579. |
| [2] | Peng Ya, Qin Yu, Yi Hongcheng, Gu Chunsong, Li Lili. Cytotoxicity assessment of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-cuttlebone composite scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 3943-3946. |
| [3] | Lu Pengcheng, Chen Xianghe, Yang Kang, Yu Huilin, Liu Bo. Mechanism by which autophagy-mediated exercise improves bone metabolic disorder in type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(20): 3256-3262. |
| [4] | Fu Yunyu, Qiu Xiaotang, Yang Wenkui, Mo Shian, Wu Xiaocui, Wu Yingping. Berberine alleviates ischemia/reperfusion injury in type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(2): 230-235. |
| [5] | Zhang Shuangyuan, Li Wenjin, Zhu Li, Wang Yu, Wei Zhoudan, Zhao Jiaoyang, Chen Yanan. Meta-analysis of dental implantation success rate in diabetic patients with 6% < glycated hemoglobin level < 8% [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(16): 2620-2624. |
| [6] | Zhang Wenjiang1, 2, Yi Jian3, Jia Ping1, Chen Bowei1, Wang Yong2, Liu Baiyan1. Genotype identification and model application of apolipoprotein E knockout mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(7): 1103-1108. |
| [7] | Li Bopeng, Chen Shuchun, Tang Yong, Ren Luping. Alpha-lipoic acid increases circulating endothelial progenitor cells in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(5): 803-808. |
| [8] | Liang Min1, Wang Hainiu2, Huang Peng2, Zhu Weihua2, Li Shunchang1 . Systematic review and meta-analysis of effect of resistance exercise on glucose and lipid metabolism disorder in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(35): 5718-5726. |
| [9] | Zhao Min, Chen Yao, Li Xuguang, Li Wenhua. Protein acetylation in hypoxic environment: research advance and the existing problems [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(34): 5570-5576. |
| [10] | Cao Jingli1, 2, Marina S. Ferguson3, Sun Jie3, Zhang Dong1, Liu Li1, Li Zirui1, Wang Yajie1, Sui Binbin1, Shen Mi1, Gao Peiyi1, 4, Thomas S. Hatsukami3, Zhao Xihai5, Yuan Chun1, 3, 5. An en bloc paraffin embedding method for serial sectioning of carotid atherosclerotic plaque [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(31): 5041-5045. |
| [11] | Yang Na1, Bao Pingping2, Lei Tao2. Adiponectin levels in plasma and periodontal tissue of mouse models of diabetic periodontitis treated by adiponectin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(23): 3692-3697. |
| [12] | Sun Zhizhong1, Jiang Yanjun1, Ji Shuliang1, Shi Chushuo1, Zhang Tian1, Zhou Xiaoqi1, Yang Zhihua1, Chen Yuexuan1, Luo Chuanjin2. Role of baicalin in the treatment of mouse models of atherosclerosis and the underlying mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(19): 3037-3043. |
| [13] | Jin Shanhu, Hu Yazhe. Effect of early different intensities of exercise on the modelling rate and blood glucose level of rats with late-stage type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(19): 3092-3096. |
| [14] | Zhang Xu1, Chen Wangsheng2, Feng Jian3, Zhang Mengjiao1, Jiang Wenjie1, Liang Xuemei1. Protective effect of Ginkgolide B against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cardiomyocyte injury and its underlying mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(19): 3097-3101. |
| [15] | Chen Yili1, Lao Yonghua2, Zhang Shaoqun1, Wu Baofeng3, Li Yikai1 . Hydrodynamic model of carotid artery atherosclerosis: hemodynamic changes of carotid atherosclerotic plaques under cervical rotatory manipulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2403-2308. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||