Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (24): 4457-4464.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.24.013
Previous Articles Next Articles
Number of mast cells and expression of transforming growth factor beta 1 in the submandibular gland of diabetes mellitus rats
Zhu Jian-hua1, Tang Chun-ling1, Zhang Yan-qiu1, Liu Ji-guang2
- 1 Stomatology Hospital, Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154007, Heilongjiang Province, China
2 Postgraduate Department, Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154007, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Received:2012-10-28Revised:2012-12-14Online:2013-06-11Published:2013-06-11 -
Contact:Liu Ji-guang, M.D., Professor, Postgraduate Department, Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154007, Heilongjiang Province, China liujg5550@163.com -
About author:Zhu Jian-hua, Professor, Stomatology Hospital, Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154007, Heilongjiang Province, China zhu8622877@yahoo.com.cn -
Supported by:Scientific Research Funds of Jiamusi University, No. L2012-035*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhu Jian-hua, Tang Chun-ling, Zhang Yan-qiu, Liu Ji-guang. Number of mast cells and expression of transforming growth factor beta 1 in the submandibular gland of diabetes mellitus rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(24): 4457-4464.
share this article

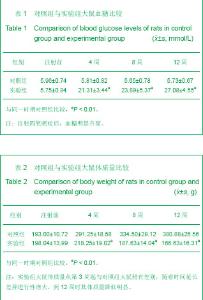
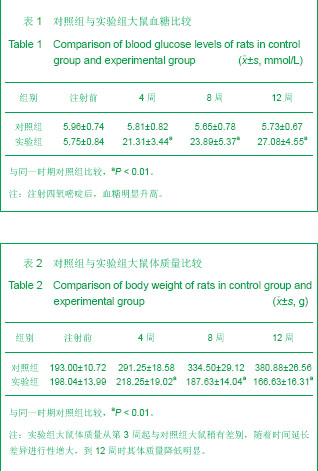
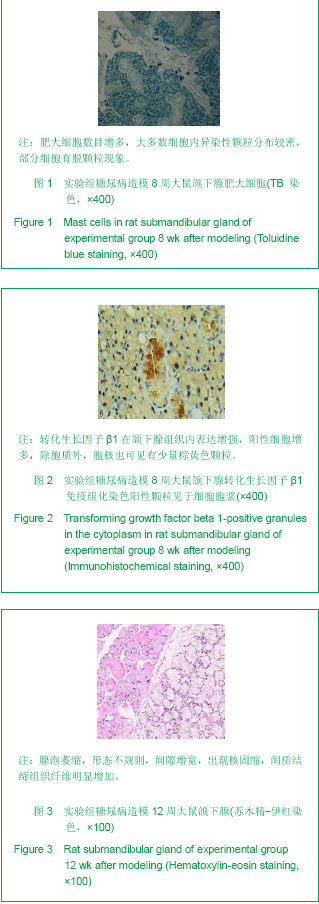
2.3 光镜观察形态学结果 造模4周时:实验组大鼠颌下腺导管及各种腺泡均呈不同程度的萎缩,间隙增宽;肥大细胞数目增多,大多数细胞内异染性颗粒分布较密,见少量的颗粒释放现象;转化生长因子β1在浆液性腺腺泡上皮和导管上皮细胞胞浆中有弥漫性棕黄色颗粒,间质成分中的血管上皮可见阳性表达。 造模8周时:实验组大鼠颌下腺导管及各种腺泡萎缩加重,间隙增宽显著,出现核固缩,颗粒曲管数目减少,细胞排列不整齐,浆液性腺泡趋于减少;肥大细胞数目增多,胞膜不清晰,大多数细胞内异染性颗粒分布较密,部分细胞有脱颗粒现象,见图1。转化生长因子β1在颌下腺组织内表达增强,阳性细胞增多,除胞质外,胞核也可见有少量棕黄色颗粒,见图2。 造模12周时:实验组大鼠颌下腺腺泡萎缩,形态不规则,间隙增宽,出现核固缩。导管数目明显减少,细胞排列不整齐,管腔变小,而间质结缔组织纤维及血管明显增加,见图3;肥大细胞数目显著增多,部分肥大细胞胞膜结构不清,颗粒涌出胞外,细胞形状不规则,有的细胞完全脱颗粒;转化生长因子β1的表达大多增至强阳性。"
| [1] Atkinson MA, Eisenbarth GS.Type 1 diabetes: new perspectives on disease pathogenesis and treatment. Lancet. 2001;358(9277):221-229.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=.Type%201%20diabetes%3A%20new%20perspectives%20on%20disease%20pathogenesis%20and%20treatment.%20Lancet.[2]Hao JM,Yang ZP. Xiandai Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi. 2001;15(5):373-374.郝京梅,杨宗萍. 2-型糖尿病病人唾液分泌功能与血糖状态间的关系[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2001,15(5):373-374.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=0&CurRec=1&recid=&filename=XDKY200105028&dbname=cjfd2001&DbCode=CJFQ&urlid=&yx=[3] Gresik EW, Hosoi K, Kurihara K,et al. The rodent granular convoluted tubule cell--an update. Eur J Morphol. 1996;34(3):221-224.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=The%20rodent%20granular%20convaluted%20tubule%20cell-an%20update[4] Amano O, Iseki S. Expression, localization and developmental regulation of insulin-like growth factor I mRNA in rat submandibular gland.Arch Oral Biol. 1993;38(8):671-677.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8215990[5] Amano O, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T, et al. Expression and localization of hepatocyte growth factor in rat submandibular gland. Growth Factors. 1994;10(2):145-151.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8068352[6] Mogi M, Matsuura S, Suzuki K, et al. Differential expression of transforming growth factor-alpha and epidermal growth factor during postnatal development of rat submandibular gland. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995;217(1):271-277.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Differential%20expression%20of%20transforming%20%20growth%20factor%20%20alpha%20and%20epidermal%20growth%20factor%20during%20postnatal%20development%20of%20rat%20submandibular%20gland[7] Amano O, Tsuji T, Nakamura T, et al. Expression of transforming growth factor beta 1 in the submandibular gland of the rat.J Histochem Cytochem. 1991;39(12):1707-1711.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Expression%20of%20transforming%20growth%20factor%20beta%201%20in%20the%20submandibular%20gland%20of%20the%20rat[8] Mahay S, Adeghate E, Lindley MZ, et al. Streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus alters the morphology, secretory function and acyl lipid contents in the isolated rat parotid salivary gland.Mol Cell Biochem. 2004;261(1-2):175-181.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Adeghate%20E%2CLindley%20MZ[9] Nicolau J, de Matos JA, de Souza DN, et al. Altered glycogen metabolism in the submandibular and parotid salivary glands of rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. J Oral Sci. 2005;47(2):111-116.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Altered%20glycogen%20metabolism%20in%20the%20submandibular%20and%20parotid%20salivary%20glands%20of%20rats%20with%20streptozotocin-induced%20diabetes.[10]Zhang N,Mu YZ. Zhonghua Laonian Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi. 2007;5(1):56-58.张娜,牟月照.糖尿病与口腔病损[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2007,5(1):56-58.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=0&CurRec=1&recid=&filename=ZHKQ200701028&dbname=cjfd2007&DbCode=CJFQ&urlid=&yx=[11]Wu XP,Jia XM,Wang SH,et al. Anhui Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2005;40(2):102-105.吴学平,贾雪梅,王盛花,等.链脲佐菌素糖尿病大鼠下颌下腺超微结构观察[J].安徽医科大学学报,2005,40(2):102-105.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=4&CurRec=1&recid=&filename=YIKE200502001&dbname=CJFD2005&DbCode=CJFQ&urlid=&yx=[12] Li WS,Sun QS. Linchuang Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi. 2006;22(3) :147-149.李维善,孙庆顺.实验性糖尿病大鼠颌下腺超微结构观察[J].临床口腔医学杂志, 2006, 22(3) :147-149.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=8&CurRec=1&recid=&filename=LCKY200603006&dbname=cjfd2006&DbCode=CJFQ&urlid=&yx=[13] Nogueira FN, Carvalho AM, Yamaguti PM,et al. Antioxidant parameters and lipid peroxidation in salivary glands of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.Clin Chim Acta. 2005;353(1-2):133-139.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Antioxidant%20parameters%20and%20lipid%20peroxidation%20in%20salivary%20glands%20of%20streptozotocin-induced%20diabetic%20rats[14] Gao HL,Liu FY,Xia ZL. Zhongguo Linchuang Kangfu. 2005;9(3):210-212.高红莉,刘方永,夏作理. 实验性糖尿病动物模型的理论研究与应用[J].中国临床康复,2005,9(3):210-212.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=12&CurRec=1&recid=&filename=XDKF200503106&dbname=CJFD2005&DbCode=CJFQ&urlid=&yx=[15] Uckaya G, Ozata M, Bayraktar Z, et al. Is leptin associated with diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care. 2000;23(3):371-376.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10868868[16]Zheng JM,Yin G,Yao GH,et al. Yixue Yanjiusheng Xuebao. 2012;25(6):622-627.郑敬民,尹广,姚根宏,等.肥大细胞在糖尿病肾病患者肾组织中的分布及相关性研究[J].医学研究生学报,2012,25(6):622-627.http://new.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail?id=PeriodicalPaper_yxyjsxb201206014[17]Zhang HY,Lin LY,Lin Q,et al. Jiangsu Yiyao. 2008;34(12):1262-1265.张慧云,林丽艳,林青,等.IL-12刺激肥大细胞分泌IL-4与ERK和AKT信号转导通路有关[J].江苏医药,2008,34(12):1262-1265.http://new.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail?id=PeriodicalPaper_jsyy200812029[18]Qin XJ,Yuan WL,Wang XK. Zhongguo Kouqiang Hemian Waike Zazhi. 2009;7(2):156-162.秦兴军,袁尉力,王绪凯.转化生长因子TGF-β在不同时期血管瘤中的表达与肥大细胞的相关性[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2009,7(2):156-162.http://new.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail?id=PeriodicalPaper_zgkqhmwkzz200902014[19]Zhang HY,Ma WJ, He SH. Hainan Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2010;16(12):1533-1535,1542.张慧云,马文静,何韶衡.TNF-α对肥大细胞IL-10、IL-12分泌和组胺释放的影响[J].海南医学院学报,2010,16(12):1533-1535,1542.http://new.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail?id=PeriodicalPaper_hainanyxyxb201012001 [20] Yang L,Li L,Chen GQ. Guoji Jianyan Yixue Zazhi. 2010;31(8):834-836.杨岚,李蕾,陈国千.肥大细胞功能和介质释放机制的研究进展[J].国际检验医学杂志,2010,31(8):834-836.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=16&CurRec=1&recid=&filename=GWSQ201008032&dbname=CJFD2010&DbCode=CJFQ&urlid=&yx=http://so.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/ViewHTML/PeriodicalPaper_gwyx-lcsw201008029.aspx[21] Yao HY,Li XF,Li SJ,et al. Dongwu Yixue Jinzhan. 2010;31(1):41-43.姚红艳,李秀富,李诗举,等.小鼠空肠肥大细胞组织化学及超微结构研究[J].动物医学进展,2010,31(1):41-43.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=20&CurRec=1&recid=&filename=DYJZ201001010&dbname=CJFD2010&DbCode=CJFQ&urlid=&yx=[22] Galli SJ, Maurer M, Lantz CS. Mast cells as sentinels of innate immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 1999;11(1):53-59.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Mast%20cells%20as%20sentinels%20of%20innate%20immunity.%20Curr%20Opin%20Immunol[23] Kang LN,Wang Y,Han XD,et al. Xibao Shengwuxue Zazhi. 2003;25(2):65-69.康丽娜,王勇,韩晓冬,等.肥大细胞活化及生存[J].细胞生物学杂志,2003,25(2):65-69.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=24&CurRec=2&recid=&filename=XBZZ200302000&dbname=CJFD2003&DbCode=CJFQ&urlid=&yx=[24] Xiao SH,Liu YY,Wei LH,et al. Shengli Kexue Jinzhan. 2011;42(2):104-107.肖淑华,刘阳阳,魏连海,等.肥大细胞的研究进展[J].生理科学进展,2011,42(2):104-107.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=28&CurRec=1&recid=&filename=SLKZ201102008&dbname=CJFD2011&DbCode=CJFQ&urlid=&yx=[25] Gilbert RE, Rumble JR, Cao Z, et al. Endothelin receptor antagonism ameliorates mast cell infiltration, vascular hypertrophy, and epidermal growth factor expression in experimental diabetes.Circ Res. 2000;86(2):158-165.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Endothelin%20%20Receptor%20Antagonism%20Ameliorates%20Mast%20Cell%20Infiltration%2C%20Vascular%20Hypertrophy%20and%20Epidermal%20Growth%20Factor%20Expression%20in%20Experimental%20Diabetes.[26]Wu XP,Jia XM,Wang SH,et al. Jiepouxue Yanjiu. 2006;28(2):103-105.吴学平,贾雪梅,王盛花,等.糖尿病大鼠下颌下腺内肥大细胞的形态学观察[J].解剖学研究,2006,28(2):103-105.http://new.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail?id=PeriodicalPaper_jpxyj200602007[27]Xiang M,Yin LH. Guowai Yixue:Shengli Bingli Kexue yu Linchuang Fence. 2004;24(3):251-253.向萌,殷莲华.肥大细胞与血管新生[J].国外医学:生理、病理科学与临床分册,2004,24(3):251-253.http://new.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail?id=PeriodicalPaper_gwyx-slblkxylcfc200403016[28] Liu XM,Zhu ZH,Deng AG,et al. Zhonghua Shenzhangbing Zazhi. 2003;19(5):286-291.刘雪梅,朱忠华,邓安国,等.肥大细胞与慢性肾小球肾炎肾间质损害的关系[J].中华肾脏病杂志,2003,19(5):286-291.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=32&CurRec=1&recid=&filename=ZHSZ200305007&dbname=CJFD2003&DbCode=CJFQ&urlid=&yx=[29] Lawrence DA. Latent-TGF-beta: an overview. Mol Cell Biochem. 2001;219(1-2):163-170.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Latent-%20TGF-%CE%B2%EF%BC%9AAn%20overview.%20Mol%20Cell%20Bioehem[30] Peng Y,Zhang XG,Wang YL,et al. Zhongguo Quanke Yixue. 2013;16(2):232-234.彭晔,张旭刚,王艳玲,等.转化生长因子-β1与恶性肿瘤关系的临床研究进展[J].中国全科医学,2013,16(2):232-234.http://new.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail?id=PeriodicalPaper_zgqkyx201302040[31] Li JN,Liu W,Li WM. Guoji Mianyixue Zazhi. 2011;34(3):230-233.李军娜,刘巍,李为民.转化生长因子-β在心脏重构中作用的研究进展[J].国际免疫学杂志,2011,34(3):230-233.http://new.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail?id=PeriodicalPaper_gwyx-myxfc201103017[32] Wang XJ,Duan GF,Li H,et al. Hebei Yiyao. 2010;32(23):3375-3377.王星冀,段贵芬,李宏,等.血清转化生长因子-β的研究进展[J].河北医药,2010,32(23):3375-3377.http://new.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail?id=PeriodicalPaper_hbyy201023064[33]Hu R,Huang JY,Chen XH,et al. Zhongguo Laonianxue Zazhi. 2009;29(12):1568-1569.胡蓉,黄俊云,陈晓红,等.慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者血清转化生长因子β1水平及意义[J].中国老年学杂志,2009,29(12):1568-1569.http://new.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail?id=PeriodicalPaper_zglnxzz200912051[34] Otsuka G, Agah R, Frutkin AD, et al.Transforming growth factor beta 1 induces neointima formation through plasminogen activator inhibitor-1-dependent pathways. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26(4):737-743.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16373605[35] Schena FP, Gesualdo L. Pathogenetic mechanisms of diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16 Suppl 1:S30-33.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15938030[36] Du JK,Wang CY,Gao FL,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2007;11(32): 6362-6365.杜金凯,王春艳,高福禄,等.转化生长因子 β1 和血管内皮生长因子在单基因遗传自然发病糖尿病小鼠颌下腺的表达[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(32): 6362-6365.http://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=36&CurRec=1&recid=&filename=XDKF200732015&dbname=cjfd2007&DbCode=CJFQ&urlid=&yx=[37] Azhar M, Schultz Jel J, Grupp I, et al.Transforming growth factor beta in cardiovascular development and function. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2003;14(5):391-407.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12948523[38] Rosenkranz S.TGF-beta1 and angiotensin networking in cardiac remodeling.Cardiovasc Res. 2004;63(3):423-432.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15276467[39] Persson F, Rossing P, Hovind P, et al. Irbesartan treatment reduces biomarkers of inflammatory activity in patients with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria: an IRMA 2 substudy. Diabetes. 2006;55(12):3550-3555.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Irbesartan%20Treatment%20Reduces%20Biomarkers%20of%20Inflammatory%20Activity%20in%20Patients%20With%20Type%202%20Diabetes%20and%20Microalbuminuria%3A%20An%20IRMA%202%20Substudy[40] Langham RG, Kelly DJ, Gow RM, et al.Transforming growth factor-beta in human diabetic nephropathy: effects of ACE inhibition. Diabetes Care. 2006;29(12):2670-2675.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Transforming%20Growth%20Factor-%7Bbeta%7D%20in%20Human%20Diabetic%20Nephropathy%3A%20Effects%20of%20ACE%20inhibition |
| [1] | Zhang Song, Zhang Tao, Yang Jian-wen, An Min, Tang Ben-sen. Efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid on blood loss in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus during total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(11): 1681-1687. |
| [2] | Song Qiao-qiao, Zhou Hui-liang, Zhen Hai-tao, Wang Na, Deng Jing, Wang Jin-xiang, Pan Xing-hua . Establishment and evaluation of a rhesus monkey model of experimental type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 6048-6053. |
| [3] | Sun Dong-lei, Li Ren-lan. Application of mobile health in the prevention and control of chronic disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 6074-6080. |
| [4] | Yuan Shu-fang, Hu Lan-ying, Jiang Tao, Sun Li-hua, Zheng Rong-jiong, Zhao Jin-yan, Zhang Yue-xin . Effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transplantation on the expression of CD163 and interleukin-10 in rats with acute hepatic liver failure [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 919-925. |
| [5] | Qu Xin, Wang Xin-chao, Han Lu, Zhang Hai-chao. Different sources of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of liver fibrosis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 926-931. |
| [6] | Liu Shu-rong, Yu Bin, Jiao Bao-ping, Liu Yong-feng. Impact of warm ischemia injury on mitochondrial morphology and function of rat donor liver after cardiac death [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(5): 681-686. |
| [7] | Wu Guang-wen, Ye Jin-xia, Zheng Chun-song, Chen Wen-lie, Liu Xian-xiang, Ye Hong-zhi . Effect of Tougu Xiaotong capsule on articular cartilage changes in rat models of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(49): 7924-7929. |
| [8] | Ren Cai-ling, Qi Jie, Zhang Jun. Aerobic exercise affects c-Src mRNA expression and c-Src activity in aortic vascular endothelial cells of spontaneous hypertensive rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(49): 7943-7947. |
| [9] | Yao Dan-dan, Ma Rui-xia, Zhai Li-hui, Li Zuo-lin, Li Zhen. Angiotensin II-transient receptor potential channel C6 signaling pathway mediates podocyte injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(46): 7447-7451. |
| [10] | Lan Jing, Yan Jin-yu, Xia Run-fu, Li Jian-feng. Cistanche deserticola plus bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for treating spinal cord injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(41): 6639-6644. |
| [11] | Feng Kai, Xu Yi-wei, Ye Fu-guang, Jiang Min, Chen Hu, Shi Bing-yi. Blood glucose recovery following allogenetic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with hematological diseases complicated with diabetes mellitus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(41): 6645-6648. |
| [12] | Wei Shu-yi, Yin Guo-qian, Han Zhi-qiang, Pan Xin-yuan, Lin Bo-jie. Natural hirudin hydrogel improves the survival rate of random pattern flaps [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(53): 9107-9112. |
| [13] | Feng Xiao-fang, Min Min, Zuo Fu-jie, Zhou Mei-sheng, Wang Li-ming. Conversion from tacrolimus to cyclosporine A improves new-onset diabetes mellitus after transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(53): 9176-9181. |
| [14] | Yao Guan-feng, Wang Xin-jia, Luo Bin, Wang Wei-dong, Zeng Ji-can. Combined therapy of implants internal fixation and Halo-vest external fixation for the treatment of subaxial cervical fracture-dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(35): 6351-6356. |
| [15] | Ma Yong-fu, Liu Yang, Guo Jun-tang, Zhang Tao, Liang Chao-yang. Degradable properties of biodegradable composite stents in the trachea [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(29): 5371-5378. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||