Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (13): 2121-2126.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1687
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in lung diseases
Zhong Yulan, Gan Xin
- Department of Respiratory Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China
-
Revised:2019-01-11Online:2019-05-08Published:2019-05-08 -
Contact:Gan Xin, MD, Chief physician, Department of Respiratory Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China -
About author:Zhong Yulan, Master candidate, Physician, Department of Respiratory Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81660009 and 81260004 (both to GX); the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province, No. 20161ACB20012 (to GX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhong Yulan, Gan Xin. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in lung diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(13): 2121-2126.
share this article
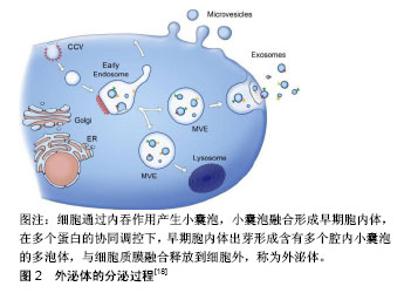
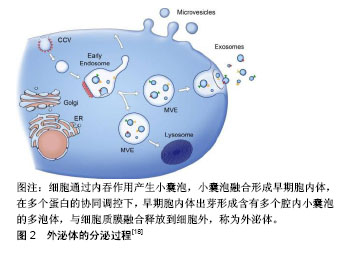
2.1 间充质干细胞源外泌体的生物学特性 间充质干细胞源外泌体的产生和其他细胞来源外泌体产生机制一致,都是通过胞内体途径,见图2,即内体膜内陷形成具有许多腔内囊泡的多泡体,腔内囊泡在与质膜融合后作为外泌体释放,因此外泌体是从内体衍生的唯一一类细胞外囊泡[16]。迄今为止,间充质干细胞被认为是分泌外泌体能力最强的细胞。通过传递细胞间的蛋白质、遗传物质和脂质等信息,外泌体已成为细胞间通讯的重要参与者[17]。外泌体是一种细胞外脂质囊泡,通常直径为40-100 nm,密度为1.10-1.18 g/mL,表达特异性膜蛋白,如CD9、CD63和CD81[18]。此外,外泌体含有内体相关蛋白(包括GTPase,RNARE,flotillin,Annexins),其中一些(包括TSG101和ALIX)对腔内囊泡的生物起源具有重要作用。由于外泌体的成分依赖于它们的细胞来源[18],间充质干细胞源外泌体有其自身的特点,除了外泌体的常见表面标志物,还表达特殊的膜结合蛋白,如CD73、CD44和CD29[19]。外泌体具有与质膜方向相同的双脂膜。当使用高效液相色谱法分离间充质干细胞衍生的条件培养基(MSC-CM)时,发现条件培养基含有一部分尺寸均匀的颗粒,其流体力学半径为55-65 nm。在电子显微镜下,这些颗粒的直径较小,为40-150 nm,这可能是由于样品制备过程中脱水造成的[20]。外泌体最独特的功能是与靶向受体细胞的特异性相互作用,这可能是细胞间通讯的基础,从各种细胞衍生的外泌体参与重要的生理和病理过程,如处置不需要的蛋白质、抗原呈递、遗传信息交换、免疫应答、组织修复和再生以及代谢,参与血管生成、炎症、肿瘤转移等,这些功能取决于外泌体中包含的组分,尤其是蛋白质和RNA。一些研究报道,外泌体含有调节受体细胞功能的miRNA[21],包裹在外泌体中的miRNA受到各种病理生理应激刺激和微环境的严格调控[22],这使得宿主细胞能够根据不同的功能需求和外部干预状态产生各种各样的miRNA。与外泌体中的miRNA一样,间充质干细胞源外泌体中的蛋白质具有调节疾病发病或组织修复和再生的潜力。到目前为止,间充质干细胞源外泌体中已经鉴定出超过一千种蛋白质[23]。间充质干细胞源外泌体也携带RNA载体,有研究发现间充质干细胞源外泌体中的RNA相对较短,当在琼脂糖或聚丙烯胺凝胶上观察时大多数RNA小于300个核苷酸(nts)[20]。然而,与其他外泌体不同的是,间充质干细胞源外泌体不表达18S和28S RNA,而人类平均mRNA是2 314个核苷酸,外泌体中的RNA通常太短而不能携带蛋白质编码信息。因此,间充质干细胞源外泌体的治疗效果越来越多的归因于miRNA在细胞间的转移。"

2.2 间充质干细胞源外泌体在慢性肺部疾病中的相关作用及其机制 2.2.1 间充质干细胞源外泌体在肺动脉高压中的作用 肺动脉高压的定义是平均肺动脉压力大于25 mm Hg,其特征在于远端肺动脉循环的血管重塑。在肺动脉高压中观察到的重塑包括肺血管内皮细胞增殖和凋亡抵抗、远端肺小动脉的肌肉化、细胞外基质蛋白的沉积和周围血管炎症[24-25]。这些病变导致外周小动脉缺失和闭塞性血管病变。随着疾病的进展,肺血管阻力增加,导致右心衰和死亡[26]。目前可用的治疗药物主要是针对肺循环具有一定程度选择性的血管舒张药物,而不是针对增殖性血管重塑。许多研究支持间充质干细胞源外泌体对细胞保护、抗炎作用,在动物模型中证明了对抗肺动脉高压的效果。Aliotta等[27]研究显示间充质干细胞源外泌体能够减弱野百合碱诱导肺动脉高压小鼠的右心室肥大和肺血管重塑,对间充质干细胞源外泌体的miRNA进行微阵列分析发现含有65个表达上调的miRNA,表明间充质干细胞源外泌体可能基于其miRNA调节肺动脉高压。miR-124在间充质干细胞源外泌体中表达增加,而miR-124下调有助于肺动脉高压中的肺血管重塑,推测间充质干细胞源外泌体处理后肺动脉高压小鼠肺血管重塑的逆转可能是由于miR-124表达的上调。Lee等[28]在低氧诱导的肺动脉高压小鼠中经静脉注入间充质干细胞源外泌体,发现其抑制了低氧引起的STAT3信号和miR-17家族的激活,并且增加了miR-204家族的表达,从而打破STAT3-miR-204-STAT3前馈环并将平衡转变为抗增殖状态,改善了肺动脉高压、右心室肥大和肺血管重塑。据报道,STAT3(由血管内皮生长因子或白细胞介素6激活)可直接调节肺动脉内皮细胞中miR-17/92微小RNA簇的转录,导致骨形态发生蛋白受体2水平降低[29]。骨形态发生蛋白受体2是转化生长因子β家族的表面受体之一,与骨形态发生蛋白结合后抑制血管平滑肌细胞增殖并导致其凋亡,骨形态发生蛋白受体2下调导致信号级联的显著变化,最终导致肺血管床重塑进而发展成肺动脉高压[30]。因此,间充质干细胞源外泌体为肺动脉高压提供了一个很有前景的治疗方法。 2.2.2 间充质干细胞源外泌体在肺癌中的作用 肺癌是全世界癌症相关最常见的死亡原因,每年约有1 800万人被确诊,并且有1 600万人因该疾病而死亡[31],在地区和种族差异上,5年生存率从4%-17%不等[32],近年来因肺癌筛查和个性化治疗(精准医学)的研究有了很大的提高。然而,肺癌的整体治愈率和生存率仍然很低[33],因此,迫切需要继续研究新的治疗策略以改善肺癌患者的预后。已有研究表明人脐带间充质干细胞培养基在肺癌细胞中起双重作用,一方面抑制细胞增殖和促进细胞凋亡,另一方面可以诱导上皮间质转化并促进肺癌细胞的迁移和侵袭,并且这种作用是人脐带间充质干细胞培养基中外泌体介导的[34]。转化生长因子β是上皮间质转化的主要诱导剂,可显著增强肿瘤的侵袭性和转移[35]。间充质干细胞培养基对肺癌细胞的上皮间质转化促进作用受到间充质干细胞中转化生长因子β1表达的影响,有研究者将转化生长因子βsiRNA转染到间充质干细胞中,然后从培养基中收集外泌体,观察其对A549肺癌细胞上皮间质转化、侵袭和迁移的影响,结果表明沉默间充质干细胞中的转化生长因子β1可以减弱A549细胞中间充质干细胞源外泌体诱导的上皮间质转化。免疫荧光染色也支持该结果,此外,划痕试验和transwell试验结果表明,沉默间充质干细胞中转化生长因子β1的表达可显著减弱间充质干细胞源外泌体对A549细胞迁移和侵袭的促进作用[34]。Huang等[36]研究发现间充质干细胞源外泌体通过携带血小板源性生长因子促进肺癌细胞的增殖、迁移和上皮间质转化,靶向PDGFD通路可能是调节间充质干细胞源外泌体与肺肿瘤细胞间相互作用的新型治疗策略。 2.2.3 间充质干细胞源外泌体在支气管肺发育不良中的作用 支气管肺发育不良,也称为婴儿期慢性肺病,是早产的一个主要并发症,其特点是肺泡和血管发育受限,肺功能受损,通常伴有严重的神经发育不良后遗症。重要的是,许多中度至重度支气管肺发育不良早产儿,甚至没有明显肺部疾病的婴儿在18-36岁时都表现为早发性肺气肿;此外,大约1/4的中度至重度支气管肺发育不良婴儿因炎症、血管细胞功能障碍和肺泡缺氧而发生肺动脉高压[37]。这些儿童中肺动脉高压的发生显著增加了死亡率,研究显示确诊肺动脉高压后2年死亡率为47%[38]。由于没有有效的治疗方法来预防或治疗发育性肺损伤,因此迫切需要新的治疗方法。大量的研究已经进行了以干细胞为基础的治疗方法来改善肺损伤。Willis等[39]从人间充质干细胞培养基中分离外泌体,将新生小鼠暴露于高氧(体积分数为75%O2)条件下,在出生后4 d用外泌体处理并在出生后7 d时返回室内空气,在出生后7,14,42 d时收集实验组和对照组的肺组织以评估肺参数。结果表明暴露在高氧下的小鼠表现出明显的肺泡简化、纤维化和肺血管重塑,经间充质干细胞源外泌体治疗后上述指标有效改善,同时肺功能也支持该结果。用qPCR验证细胞因子的mRNA表达,发现间充质干细胞源外泌体显著激活骨髓来源巨噬细胞,降低了肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6等mRNA水平,并且明显抑制了Retnla和Cd206的表达,提高了Arg1的表达,而肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6是巨噬细胞促炎性M1表型标志物;Arg1、Cd206通常与抗炎、促增殖相关,常被称为M2表型标志物,它们在高氧肺中失调,并被有效抑制。这表明间充质干细胞源外泌体通过调节巨噬细胞免疫表型,抑制促炎性M1表型,增强体内和体外抗炎M2表型而改善实验性支气管肺发育不良。Chaubey等[40]研究也证明在高氧诱导的支气管肺发育不良模型小鼠中,腹膜内给予间充质干细胞源外泌体也改善了肺部炎症、肺泡-毛细血管渗漏和其他形态学改变,并且这种作用是由于间充质干细胞源外泌体中存在TSG-6蛋白,TSG-6降低了支气管肺发育不良小鼠肺内促炎细胞因子白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β水平,随后作者用TSG-6siRNA转染间充质干细胞,并将分离的间充质干细胞源外泌体注射到支气管肺发育不良小鼠模型后消除了上述治疗效果,表明间充质干细胞源外泌体中TSG-6是重要的治疗分子。此外,Braun等[41]研究也显示间充质干细胞源外泌体可改善高氧诱导的肺损伤,间充质干细胞源外泌体中含有血管内皮生长因子并诱导血管生成、增强肺血管密度及减轻右心室肥大。以上结果均表明,对间充质干细胞源外泌体研究的不断深入可能是治疗支气管肺发育不良的新策略。 2.2.4 间充质干细胞源外泌体在急性肺损伤/急性呼吸窘迫综合征中的作用 急性肺损伤和急性呼吸窘迫综合征是重症患者急性呼吸衰竭的主要原因,可由内毒素、机械通气所诱导。急性肺损伤是一种复杂的临床综合征,包括急性炎症、微血管损伤、肺血管和上皮通透性增加,常导致急性呼吸衰竭,最终发生急性呼吸窘迫综合征。急性呼吸窘迫综合征主要表现为急性低氧血症(即PaO2/FiO2≤200 mm Hg)、双肺叶浸润及无左房高压[42],其病理特征在于肺泡屏障破坏和肺部炎症[43]。尽管急性呼吸窘迫综合征治疗取得了很大进展,但死亡率仍然很高(轻度为34.9%,中度为40.3%,严重为46.1%)[44]。急性肺损伤使用类似的诊断标准,但低氧血症较轻(PaO2/FiO2≤300 mm Hg)。最近,许多研究证明间充质干细胞为内毒素诱导的急性肺损伤提供一种新颖的治疗策略。间充质干细胞可以通过分泌生长因子、抗炎因子和各种可溶性因子来改善急性肺损伤[45]。外泌体是介导细胞旁分泌的重要物质,可以介导mRNA、miRNA和蛋白质到受体细胞,然后改变细胞功能。Li等[46]将缺血预处理的间充质干细胞或外泌体通过尾静脉注入内毒素诱导的急性肺损伤小鼠体内,与对照组相比,间充质干细胞源外泌体可降低急性肺损伤小鼠支气管肺泡灌洗液中白细胞和中性粒细胞水平,该研究比较了缺血预处理30,60,90 min后间充质干细胞对急性肺损伤模型的治疗效果,结果表明缺血预处理60 min后间充质干细胞的治疗效果最佳。Zhu等[47]发现来自间充质干细胞的外泌体可以治疗内毒素诱导的急性肺损伤,间充质干细胞通过外泌体携带的角质细胞生长因子发挥作用。Song等[48]用白细胞介素1β预处理人脐带间充质干细胞,与初始间充质干细胞相比,全身给予白细胞介素1β预处理的间充质干细胞可以更有效地改善小鼠脓毒症的症状并提高存活率,并且发现miR-146a被白细胞介素1β刺激之后明显上调并被包装到外泌体中,将该外泌体miR-146a转移至巨噬细胞,巨噬细胞极化至M2表型,从而减轻了肺水肿、炎性细胞浸润及出血。相反,用miR-146a抑制剂转染间充质干细胞部分地抵消了白细胞介素1β预处理的间充质干细胞来源外泌体的免疫调节作用。杨尧等[49]将人脐带间充质干细胞源外泌体经尾静脉注入急性肺损伤大鼠,发现可以减轻大鼠血清中炎症因子白细胞介素10、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β水平,并且这种作用是由于间充质干细胞来源外泌体抑制丝裂原活化蛋白激酶磷酸化所致。 综上所述,间充质干细胞源外泌体可作为肺部疾病的治疗靶点,具体详见表1[29-32,36-38,41-43,48-51]。"

| [1] Saeed H, Ahsan M, Saleem Z, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) as skeletal therapeutics - an update. J Biomed Sci. 2016;23:41.[2] Xu L, Huang S, Hou Y, et al. Sox11-modified mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) accelerate bone fracture healing: Sox11 regulates differentiation and migration of MSCs. FASEB J. 2015;29(4): 1143-1152.[3] Zhang Y, Cai W, Huang Q, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate bacteria-induced liver injury in mice by inducing regulatory dendritic cells. Hepatology. 2014;59(2):671-682.[4] Monsel A, Zhu YG, Gennai S, et al. Therapeutic Effects of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell-derived Microvesicles in Severe Pneumonia in Mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015;192(3): 324-336.[5] Mackenzie TC, Flake AW. Human mesenchymal stem cells persist, demonstrate site-specific multipotential differentiation, and are present in sites of wound healing and tissue regeneration after transplantation into fetal sheep. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2001;27(3): 601-604.[6] Satoh H, Kishi K, Tanaka T, et al. Transplanted mesenchymal stem cells are effective for skin regeneration in acute cutaneous wounds. Cell Transplant. 2004;13(4):405-412.[7] Gupta N, Su X, Popov B, et al. Intrapulmonary delivery of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improves survival and attenuates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in mice. J Immunol. 2007;179(3):1855-1863.[8] Copland IB, Lord-Dufour S, Cuerquis J, et al. Improved autograft survival of mesenchymal stromal cells by plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 inhibition. Stem Cells. 2009;27(2):467-477.[9] Katsha AM, Ohkouchi S, Xin H, et al. Paracrine factors of multipotent stromal cells ameliorate lung injury in an elastase -induced emphysema model. Mol Ther. 2011;19(1):196-203.[10] Vizoso FJ, Eiro N, Cid S, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome: Toward Cell-Free Therapeutic Strategies in Regenerative Medicine. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(9): E1852.[11] Iso Y, Spees JL, Serrano C, et al. Multipotent human stromal cells improve cardiac function after myocardial infarction in mice without long-term engraftment. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;354(3): 700-706.[12] Kinnaird T, Stabile E, Burnett MS, et al. Local delivery of marrow- derived stromal cells augments collateral perfusion through paracrine mechanisms. Circulation. 2004;109(12):1543-1549.[13] Giebel B, Kordelas L, Börger V. Clinical potential of mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Stem Cell Investig. 2017;4:84.[14] Bruno S, Grange C, Deregibus MC, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles protect against acute tubular injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;20(5):1053-1067.[15] Lai RC, Arslan F, Lee MM, et al. Exosome secreted by MSC reduces myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. 2010; 4(3):214-222.[16] Lai RC, Yeo RW, Lim SK. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015;40:82-88.[17] Bang C, Thum T. Exosomes: new players in cell-cell communication. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012;44(11):2060-2064.[18] Raposo G, Stoorvogel W. Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol. 2013;200(4):373-383.[19] Yu B, Zhang X, Li X. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(3):4142-4157.[20] Chen TS, Lai RC, Lee MM, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell secretes microparticles enriched in pre-microRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010; 38(1):215-224.[21] Bang C, Batkai S, Dangwal S, et al. Cardiac fibroblast-derived microRNA passenger strand-enriched exosomes mediate cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. J Clin Invest. 2014;124(5):2136-2146.[22] Jelonek K, Widlak P, Pietrowska M. The Influence of Ionizing Radiation on Exosome Composition, Secretion and Intercellular Communication. Protein Pept Lett. 2016;23(7):656-663.[23] Lai RC, Tan SS, Teh BJ, et al. Proteolytic Potential of the MSC Exosome Proteome: Implications for an Exosome-Mediated Delivery of Therapeutic Proteasome. Int J Proteomics. 2012;2012:971907.[24] Rabinovitch M, Guignabert C, Humbert M, et al. Inflammation and immunity in the pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circ Res. 2014;115(1):165-175.[25] Mathew R. Pathogenesis of pulmonary hypertension: a case for caveolin-1 and cell membrane integrity. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014;306(1):H15-25.[26] Thompson AAR, Lawrie A. Targeting Vascular Remodeling to Treat Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Trends Mol Med. 2017;23(1): 31-45.[27] Aliotta JM, Pereira M, Wen S, et al. Exosomes induce and reverse monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in mice. Cardiovasc Res. 2016;110(3):319-330.[28] Lee C, Mitsialis SA, Aslam M, et al. Exosomes mediate the cytoprotective action of mesenchymal stromal cells on hypoxia- induced pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. 2012;126(22): 2601-2611.[29] Brock M, Trenkmann M, Gay RE, et al. Interleukin-6 modulates the expression of the bone morphogenic protein receptor type II through a novel STAT3-microRNA cluster 17/92 pathway. Circ Res. 2009;104(10): 1184-1191.[30] Takahashi H, Goto N, Kojima Y, et al. Downregulation of type II bone morphogenetic protein receptor in hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2006;290(3):L450-458.[31] Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012 .Int J Cancer. 2015;136(5):E359-386.[32] Torre LA, Siegel RL, Jemal A. Lung Cancer Statistics. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;893:1-19.[33] Herbst RS, Morgensztern D, Boshoff C. The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature. 2018;553(7689):446-454.[34] Zhao X, Wu X, Qian M, et al. Knockdown of TGF-β1 expression in human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reverts their exosome-mediated EMT promoting effect on lung cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2018; 428:34-44.[35] Heldin CH, Vanlandewijck M, Moustakas A. Regulation of EMT by TGFβ in cancer. FEBS Lett. 2012;586(14):1959-1970.[36] Huang F, Yao Y, Wu J, et al. Effect of mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes carrying PDGFD on lung cancer. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology.2017;10(1):224-232.[37] Del Cerro MJ, Sabaté Rotés A, Cartón A, et al. Pulmonary hypertension in bronchopulmonary dysplasia: clinical findings, cardiovascular anomalies and outcomes. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2014;49(1):49-59.[38] Khemani E, McElhinney DB, Rhein L, et al. Pulmonary artery hypertension in formerly premature infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia: clinical features and outcomes in the surfactant era. Pediatrics. 2007;120(6):1260-1269.[39] Willis GR, Fernandez-Gonzalez A, Anastas J, et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Exosomes Ameliorate Experimental Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Restore Lung Function through Macrophage Immunomodulation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;197(1):104-116.[40] Chaubey S, Thueson S, Ponnalagu D, et al. Early gestational mesenchymal stem cell secretome attenuates experimental bronchopulmonary dysplasia in part via exosome-associated factor TSG-6. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):173.[41] Braun RK, Chetty C, Balasubramaniam V, et al. Intraperitoneal injection of MSC-derived exosomes prevent experimental bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;503(4):2653-2658.[42] ARDS Definition Task Force, Ranieri VM, Rubenfeld GD, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin Definition. JAMA. 2012;307(23): 2526-2533.[43] Simonson OE, Mougiakakos D, Heldring N, et al. In Vivo Effects of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Two Patients With Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(6): 845.[44] Bellani G, Laffey JG, Pham T, et al. Epidemiology, Patterns of Care, and Mortality for Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Intensive Care Units in 50 Countries. JAMA. 2016;315(8):788-800.[45] Horie S, Laffey JG. Recent insights: mesenchymal stromal/stem cell therapy for acute respiratory distress syndrome. F1000Res. 2016;5: 1532.[46] Li L, Jin S, Zhang Y. Ischemic preconditioning potentiates the protective effect of mesenchymal stem cells on endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in mice through secretion of exosome. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(3): 3825-3832.[47] Zhu YG, Feng XM, Abbott J, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell microvesicles for treatment of Escherichia coli endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in mice. Stem Cells. 2014;32(1):116-125.[48] Song Y, Dou H, Li X, et al. Exosomal miR-146a Contributes to the Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy of Interleukin-1β-Primed Mesenchymal Stem Cells Against Sepsis. Stem Cells. 2017;35(5): 1208-1221.[49] 杨尧,朱耀斌,李志强,等. 间充质干细胞外泌体对大鼠急性肺损伤的保护作用[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2017,31(7):628-631. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [6] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [8] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [9] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [10] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [12] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [13] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [14] | Zhao Min, Feng Liuxiang, Chen Yao, Gu Xia, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Exosomes as a disease marker under hypoxic conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1104-1108. |
| [15] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||