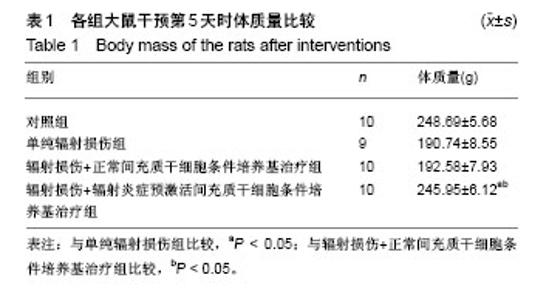
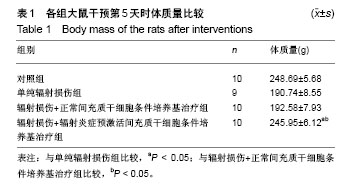
| [1] Citrin D, Cotrim AP, Hyodo F, et al. Radioprotectors and mitigators of radiation-induced normal tissue injury. Oncologist. 2010;15(4):360-371.[2] Martin E, Pointreau Y, Roche-Forestier S, et al. Normal tissue tolerance to external beam radiation therapy: small bowel. Cancer Radiother. 2010; 14(4-5):350-353.[3] Keating A. Mesenchymal stromal cells: new directions. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;10(6):709-716.[4] Sémont A, Mouiseddine M, François A, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells improve small intestinal integrity through regulation of endogenous epithelial cell homeostasis. Cell Death Differ. 2010;17(6):952-961.[5] Canavan JB, Scottà C, Vossenkämper A, et al. Developing in vitro expanded CD45RA+ regulatory T cells as an adoptive cell therapy for Crohn's disease. Gut. 2016;65(4):584-594.[6] Mao F, Wu Y, Tang X, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate inflammatory bowel disease through the regulation of 15-LOX-1 in macrophages. Biotechnol Lett. 2017;39(6):929-938.[7] Di Trapani M, Bassi G, Midolo M, et al. Differential and transferable modulatory effects of mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles on T, B and NK cell functions. Sci Rep. 2016;6:24120.[8] De Castro LL, Xisto DG, Kitoko JZ, et al. Human adipose tissue mesenchymal stromal cells and their extracellular vesicles act differentially on lung mechanics and inflammation in experimental allergic asthma. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):151.[9] Thorpe DW, Stringer AM, Gibson RJ. Chemotherapy-induced mucositis: the role of the gastrointestinal microbiome and toll-like receptors. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2013;238(1):1-6.[10] 刘婉薇,陈韵,郑跃,等. 炎症预激活骨髓间充质干细胞条件培养基修复小肠黏膜急性辐射损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(10):1544-1550.[11] Dalal J, Gandy K, Domen J. Role of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in Crohn's disease. Pediatr Res. 2012;71(4 Pt 2):445-451.[12] Zhao K, Lou R, Huang F, et al. Immunomodulation effects of mesenchymal stromal cells on acute graft-versus-host disease after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015;21(1):97-104.[13] Shrestha B, Coykendall K, Li Y, et al. Repair of injured spinal cord using biomaterial scaffolds and stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(4):91.[14] Gonzalez-Rey E, Anderson P, González MA, et al. Human adult stem cells derived from adipose tissue protect against experimental colitis and sepsis. Gut. 2009;58(7):929-939.[15] Fuenzalida P, Kurte M, Fernández-O'ryan C, et al. Toll-like receptor 3 pre-conditioning increases the therapeutic efficacy of umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells in a dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis model. Cytotherapy. 2016;18(5):630-641.[16] Chen Y, Song Y, Miao H, et al. Gene delivery with IFN-γ-expression plasmids enhances the therapeutic effects of MSCs on DSS-induced mouse colitis. Inflamm Res. 2015;64(9):671-681.[17] Raicevic G, Rouas R, Najar M, et al. Inflammation modifies the pattern and the function of Toll-like receptors expressed by human mesenchymal stromal cells. Hum Immunol. 2010;71(3):235-244.[18] Raicevic G, Rouas R, Najar M, et al. Inflammation modifies the pattern and the function of Toll-like receptors expressed by human mesenchymal stromal cells. Dev Growth Differ. 2014;56(3):233-244.[19] Le Blanc K, Mougiakakos D. Multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells and the innate immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012;12(5):383-396.[20] Liu L, Song H, Duan H, et al. TSG-6 secreted by human umbilical cord-MSCs attenuates severe burn-induced excessive inflammation via inhibiting activations of P38 and JNK signaling. Sci Rep. 2016;6:30121.[21] 郑跃,陈浩,沙卫红,等. 缺氧诱导骨髓间充质干细胞条件培养基体外修复辐射损伤小肠上皮细胞变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(45): 7230-7236.[22] Gao F, Chiu SM, Motan DA, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and immunomodulation: current status and future prospects. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7:e2062.[23] Burr SP, Dazzi F, Garden OA. Mesenchymal stromal cells and regulatory T cells: the Yin and Yang of peripheral tolerance. Immunol Cell Biol. 2013; 91(1):12-18.[24] Wang Y, Liu XP, Zhao ZB, et al. Expression of CD4+ forkhead box P3 (FOXP3)+ regulatory T cells in inflammatory bowel disease. J Dig Dis. 2011;12(4):286-294. |