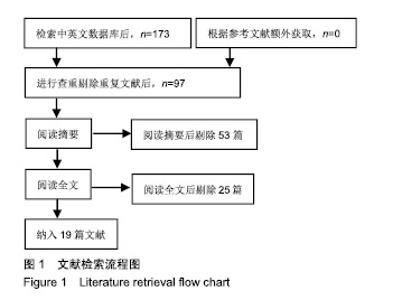
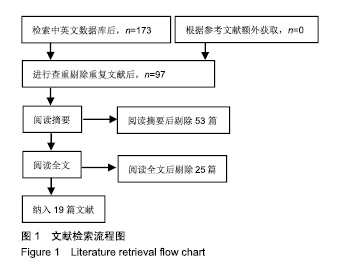
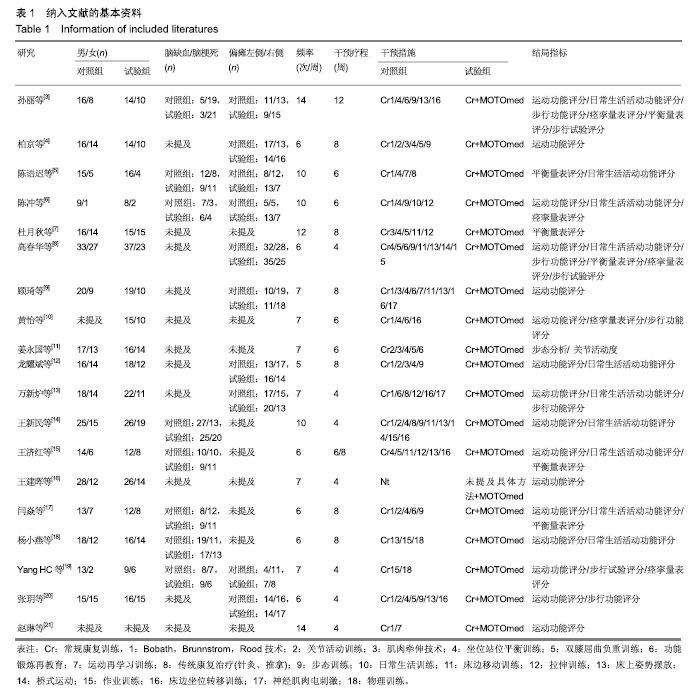
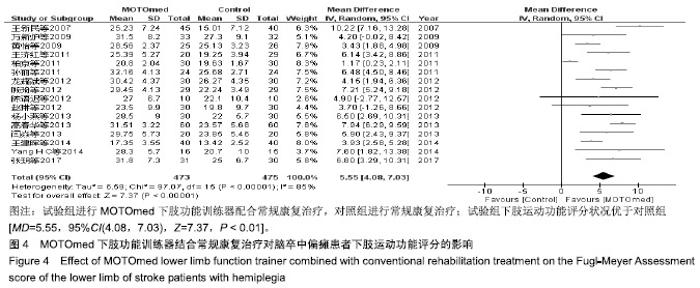
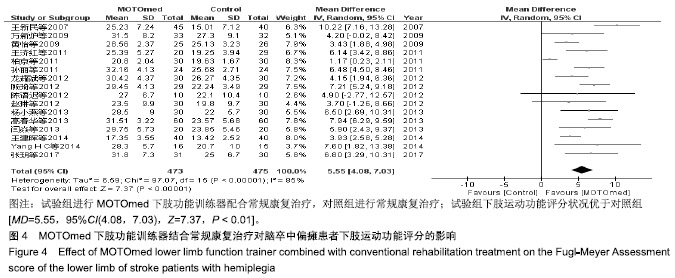
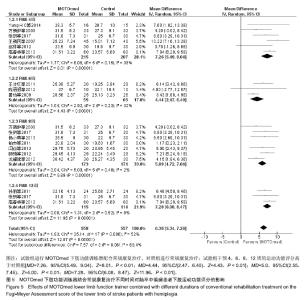
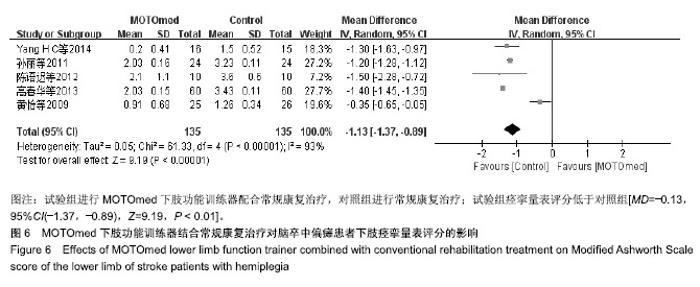
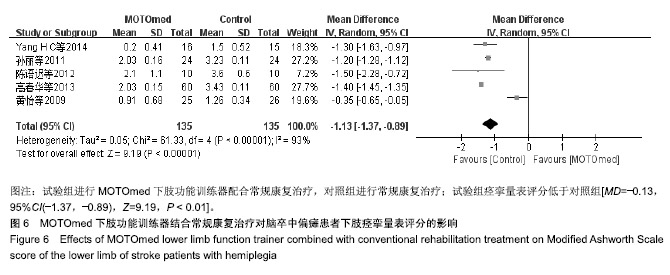
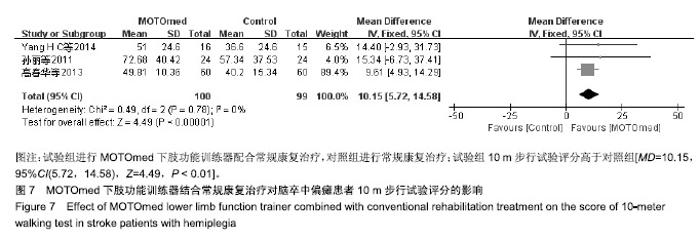
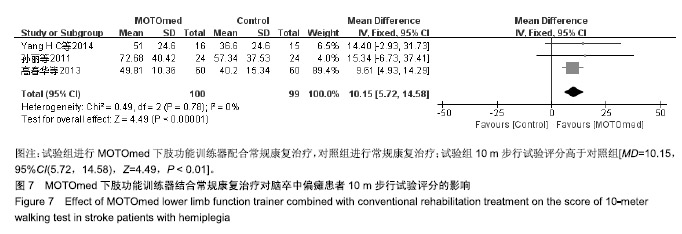
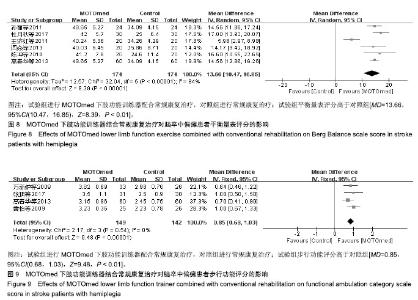
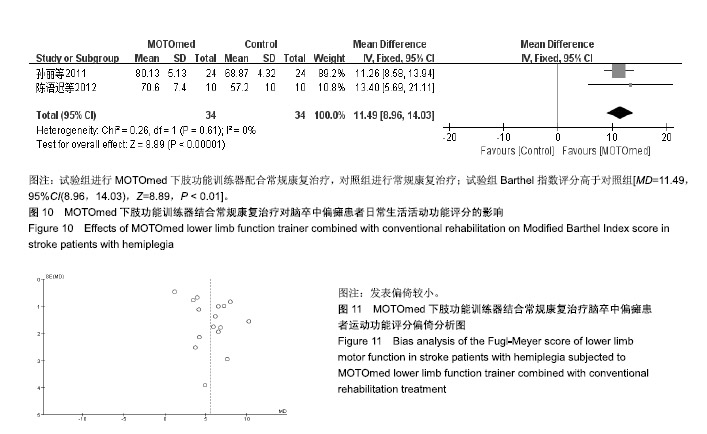
| [1]燕铁斌,许云影,李常威.功能性电刺激改善急性脑卒中患者肢体功能的随机对照研究[J].中华医学杂志,2006,86(37):2627-2631.[2]张娜,唐巧萍,熊友红.靳三针结合MOTOmed智能运动训练对痉挛型脑瘫患儿下肢功能的影响[J].中国针灸,2014,34(7):657-660.[3]孙丽,谢瑛.MOTOmed智能运动训练系统对脑卒中偏瘫患者下肢功能恢复的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志,2011,26(10):977-979.[4]柏京,杨卫新.MOTOmed智能运动训练系统对脑卒中偏瘫患者下肢功能及站立稳定性的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志, 2011,26(8): 734-737.[5]陈语迟,孙全义,张春柳,等.MOTOmed智能运动训练系统对高龄脑卒中偏瘫患者下肢日常生活活动能力的影响[J].按摩与康复医学, 2012,3(6):3-4.[6]陈冲,高晓平,冯小军. MOTOmed智能运动训练系统训练对脑卒中偏瘫患者平衡功能及日常生活活动能力的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2010,32(7):510-512.[7]杜月秋,李伟,李雪红,等.智能运动训练系统对脑出血偏瘫患者平衡功能的影响[J].中国农村卫生, 2017(16):73-73.[8]高春华,徐乐义,黄杰,等. MOTOmed智能运动训练系统对脑卒中偏瘫患者平衡及下肢运动功能的影响[J].中国康复理论与实践, 2013, 25(8):725-728.[9]顾琦,田湉,张芳芳.MOTOmed智能运动训练系统对脑出血偏瘫患者下肢运动功能的影响[J].南通大学学报(医学版), 2012,32(6): 563-564.[10]黄怡,潘翠环,万新炉,等.重复性下肢训练对脑梗死患者下肢功能改善的作用[J].中国康复,2009, 24(3):167-168.[11]姜永国,冯重睿,张新斐.对脑卒中所致偏瘫患者进行MOTOmed运动训练的效果探究[J].当代医药论丛,2017,15(10):95-96.[12]龙耀斌.MOTOmed智能运动训练系统对脑卒中偏瘫患者步态改善的作用[J].中国康复,2012, 27(5):363-364.[13]万新炉,高春华,叶正茂,等.MOTOmed训练系统对脑梗死偏瘫患者下肢运动功能的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志, 2009,31(7): 503-504.[14]王新民,李霞,刘志美,等. 急性脑卒中后偏瘫患者应用MOTOmed智能运动系统综合康复训练疗效观察[C]//中华医学会第九次全国物理医学与康复学学术会议论文集, 2007,11(7):33-35.[15]王济红,张玉明,张明. 早期卧位踏车训练对亚急性期脑卒中患者功能预后的影响[J].中国伤残医学,2011,19(1):128-129.[16]王建晖.运动训练对早期脑梗死偏瘫患者下肢功能的影响[J].中国康复,2014,29(5):355-355.[17]闫焱,孔艳茹.MOTOmed运动训练对脑卒中偏瘫患者下肢功能的改善[J].中国冶金工业医学杂志,2013,30(4):486-487.[18]杨小燕,李云,李妙玲,等.MOTOmed康复训练仪对脑卒中偏瘫患者运动功能及日常生活活动能力的影响[J]. 南昌大学学报(医学版), 2013,53(3):55-57.[19]Yang HC,Lee CL,Lin R,et al.Effect of biofeedback cycling training on functional recovery and walking ability of lower extremity in patients with stroke.Kaohsiung J Med Sci.2014;30(1):35-42.[20]张玥,王轶钊,侯玮佳,等.早期介入下肢重复性训练对脑梗死患者下肢运动功能及步行能力的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志, 2017,32(11): 1285-1287.[21]赵琳,徐国崇,郑颖杰.MOTOMED智能运动训练系统对脑卒中患者步行能力的影响[J].辽宁医学杂志,2012, 26(2):82-83.[22]刘承梅.MOTOmed训练对脊髓损伤患者功能独立性评定的影响[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2011, 14(10):14-15.[23]李先锋,黄文越.早期康复训练对脑卒中患者肢体功能恢复的影响[J].神经损伤与功能重建,2008, 3(1):64-64.[24]季力,崔晓.丰富环境对脑神经可塑性的影响[J].神经病学与神经康复学杂志,2013,10(2):99-101.[25]王丽娜,张彩侠,高晶,等.MOTOmed 虚拟情景训练系统在痉挛型脑瘫患儿康复治疗中的应用[J].山东医药, 2015,55(2):35-36.[26]张军,邱智,潘冠文,等.MOTOmed智能运动训练对脑卒中偏瘫患者步行能力的影响[J].实用临床医学, 2014, 15(3):5-7.[27]吴李娜,黄鹰,温屯清.动态康复依从性干预对脑卒中康复积极性及康复效果的影响[J].当代医学, 2018,24(5):121-123. |