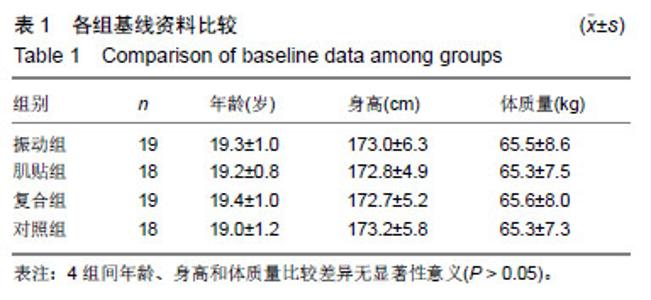
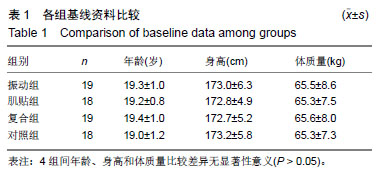
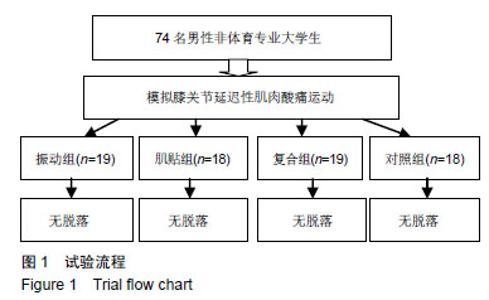
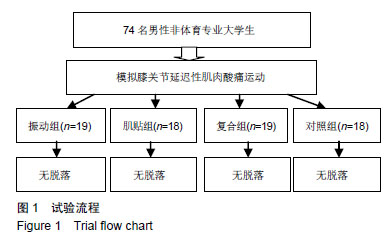
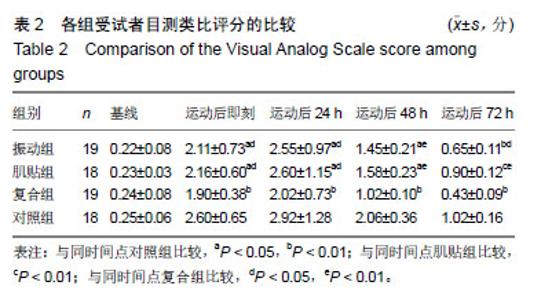
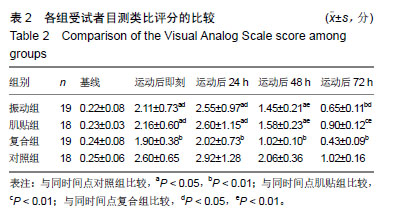
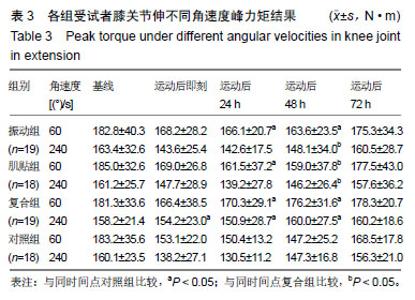
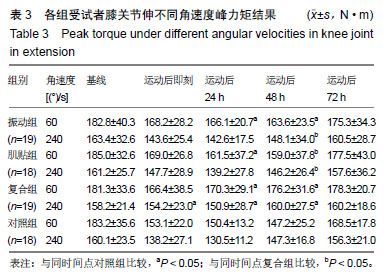
| [1]Mizumura K,Taguchi T.Delayed onset muscle soreness: Involvement of neurotrophic factors.J Physiol Sci.2016;66(1):43-52.[2]Selmi O,Ouerghi N,Khalifa WB,et al.Influence of Stress, Fatigue, Sleep and Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness on Perceived Physical Enjoyment Exertion during Small Sided Games. Iran J Public Health. 2018;47(3): 449-450.[3]蒋全睿,李武,刘小卫,等.按法对肱二头肌延迟性肌肉酸痛志愿者血清T-AOC和CK-MM水平的影响[J].针灸推拿医学(英文版), 2018,16(2):89-95.[4]Koutris M,Türker KS,van Selms MKA,et al.Delayed-onset muscle soreness in human masticatory muscles increases inhibitory jaw reflex responses. J Oral Rehabil.2018;45(6):430-435.[5]Imtiyaz S,Veqar Z,Shareef MY.To Compare the Effect of Vibration Therapy and Massage in Prevention of Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness(DOMS). J Clin Diagn Res.2014;8(1):133-136.[6]Koh HW,Cho SH,Kim CY,et al.Effects of vibratory stimulations on maximal voluntary isometric contraction from delayed onset muscle soreness.J Phys Ther Sci.2013;25(9):1093-1095.[7]Wheeler AA,Jacobson BH.Effect of whole-body vibration on delayed onset muscular soreness, flexibility, and power.J Strength Cond Res. 2013;27(9):2527-2532.[8]Lau WY,Nosaka K. Effect of Vibration Treatment on Symptoms Associated with Eccentric Exercise Induced Muscle Damage. Am J Phys Med Rehabil.2011;90(8):648-657.[9]黄美欢,曹建国,贠国俊,等.肌内效贴在脑瘫儿童康复中的应用进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2016, 31(1):102-105.[10]Lee YS,Bae SH,Hwang JA,et al.The effects of kinesio taping on architecture, strength and pain of muscles in delayed onset muscle soreness of biceps brachii. J Phys Ther Sci.2015;27(2):457-459.[11]Bae SH,Lee YS, Kim GD,et al.The Effects of Kinesio-taping Applied to Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness on Changes in Pain. IJPBST.2014;6(3): 133-142.[12]Haksever B,Kinikli GL,Tunay VB,et al. Effect of kinesiotaping intervention on knee muscle strength and delayed onset muscle soreness pain following eccentric fatigue training.Fizyoterapi Rehabilitasyon. 2016;27(1): 12-18.[13]张国海,王人卫.肌内效贴对延迟性肌肉酸痛和肌肉功能恢复的影响[J].体育科学,2017,37(12):46-51.[14]Rhea MR,Bunker D,Marín PJ,et al.Effect of iTonic whole-body vibration on delayed-onset muscle soreness among untrained individuals.J Strength Cond Res.2009;23(23):1677-1682.[15]Pinto NS.Effectiveness of a protocol involving acute whole-body vibration exercises in an adult and health individual with delayed-onset muscle soreness observed after running: a case report.J Med Med Sci. 2011; 2(1):612-617.[16]董启正.肌内效贴对运动性膝关节延迟性肌肉酸痛的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(3):367-371.[17]吴新华,蒋云飞,程亮,等.优秀男子跳远运动员下肢关节等速肌力特征的分析[J].成都体育学院学报, 2013,39(10):86-89.[18]李静雅,程亮.不同频率全身振动训练对老年女性平衡能力、下肢肌力和位置觉的影响[J].体育学刊, 2018, 25(2):128-134.[19]王富鸿,张金梅,程亮,等.等速训练对前交叉韧带重建运动员膝关节肌力和位置觉的影响[J].环境与职业医学, 2018,35(8):716-720.[20]杨雪清,程亮.篮球运动员躯干和下肢等速肌力分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(12):1835-1840.[21]Cardinale M,Bosco C.The use of vibration as an exercise intervention. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2003;31(1):3-7.[22]Cardinale M,Soiza RL,Leiper JB,et al.Hormonal responses to a single session of wholebody vibration exercise in older individuals.BrJ Sports Med.2010;44(4):284-288.[23]宋法明,刘北湘.全身振动介入静态伸展对离心运动后延迟性肌肉酸痛的影响研究[J].山东体育学院学报, 2017, 33(1):74-79.[24]Cochrane DJ,Stannard SR,Sargeant AJ,et al.The rate of muscle temperature increase during acute whole-body vibration exercise.Eur J Appl Physiol.2008;103(4):441-448.[25]Bakhtiary AH,Safavifarokhi Z,Aminianfar A.Influence of vibration on delayed onset of muscle soreness following eccentric exercise. Br J Sports Med.2007;41(3):145-148. [26]Souza SE,Christensen SW,Hirata RP,et al.Blood flow after contraction and cuff occlusion is reduced in subjects with muscle soreness after eccentric exercise.Scand J Med Sci Sports.2018;28(1):29-39. [27]龙志.肌内效贴对延迟性肌肉酸痛的疼痛缓解效果研究及其机制探讨[D].上海:上海体育学院,2016. [28]Hsu YH,Chen WY, Lin HC,et al.The effects of taping on scapular kinematics and muscle performance in baseball players with shoulder impingement syndrome.J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2009;19(6):1092-1099.[29]Omoigui S.The Biochemical Origin of Pain-Proposing a new law of Pain: The origin of all Pain is Inflammation and the Inflammatory Response PART 1 of 3–A unifying law of pain.Med Hypotheses. 2007;69(1):70-82.[30]Nosaka K.The effect of kinesio taping on muscular micro-damage following eccentric exercises//15th Annual Kinesio Taping Int Symposium Rev,1999:70-73. |