Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (16): 2538-2544.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1211
Previous Articles Next Articles
Etiology and diagnostic imaging of heterotopic ossification after total hip arthroplasty
Mu Xinyan1, Chang Xiaodan1, 2, Zhao Dewei3
- 1Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563099, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Radiography, 3Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Zhongshan Hospital of Dalian University, Dalian 116001, Liaoning Province, China
-
Online:2019-06-08Published:2019-06-08 -
Contact:Chang Xiaodan, Master, Professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563099, Guizhou Province, China; Department of Radiography, Affiliated Zhongshan Hospital of Dalian University, Dalian 116001, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Mu Xinyan, Master candidate, Physician, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563099, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 81672139 (to ZDW)| the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province, No. 20180550032 (to CXD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Mu Xinyan, Chang Xiaodan, Zhao Dewei. Etiology and diagnostic imaging of heterotopic ossification after total hip arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(16): 2538-2544.
share this article
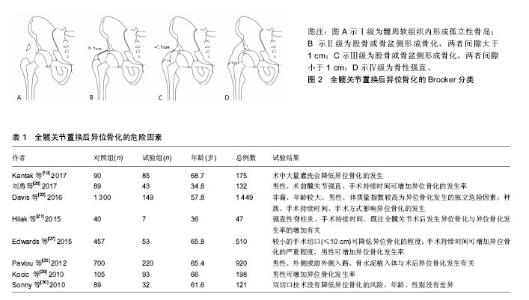
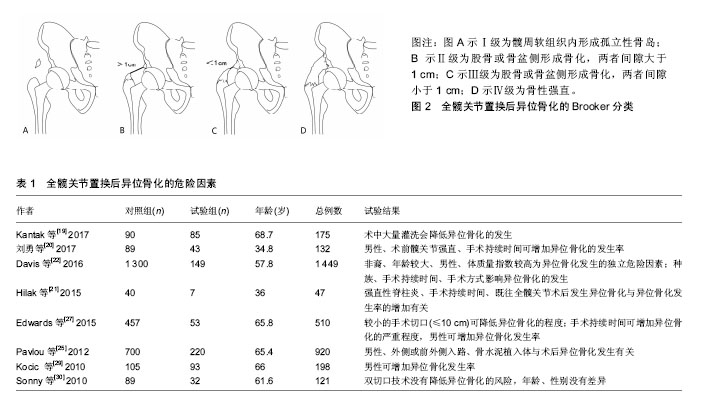
2.1 异位骨化的发病机制 目前对异位骨化的发病机制尚不明确,其病理生理学是由细胞诱导分化的失调和适当的诱导骨形成条件引起[5],通常认为与相应的前体细胞、信号通路和局部微环境有关[6],三者均可影响相应细胞及分子的调节过程,但目前仍缺乏综合研究囊括这3种要素。 2.1.1 异位骨化中的前体细胞 异位骨化的形成需要具有分化成骨和/或软骨潜力的前体细胞,可促进异位骨化发生的组织微环境和出现可诱导骨形成细胞和分子的事件[5],在软组织损伤部位,发生间充质凝结,接着发生软骨形成及软骨内骨化。间充质干细胞被认为是参与形成异位骨化的主要细胞群,在创伤诱导的异位骨化中,肌源性间充质干细胞通过增加骨形态发生蛋白4的表达来增加成骨潜能[7]。纤维细胞也可分化为成骨细胞和软骨细胞,并促进异位骨化的形成[8]。 2.1.2 信号传导通路 异位骨化过程中有许多的重要信号传导途径。骨形态发生蛋白是组织动态平衡和成骨的中心[9],作为转化生长因子β超家族的一部分,骨形态发生蛋白可诱导形成具有固有的丝氨酸-苏氨酸激酶活性的受体复合物,尤其是骨形态发生蛋白2/4亚家族与骨诱导密切相关。骨形态发生蛋白2受体的激活是导致异位骨化形成的主要途径之一[10]。骨形态发生蛋白2受体激活,导致下游的物质磷酸化,并最终影响基因转录、细胞分化及细胞增殖,增加成骨因子的产生。在Yu等[11]的大鼠模型中,骨形态发生蛋白受体抑制剂预防异位骨化被认为是有效的。除了局部骨形态发生蛋白介导的机制外,类视黄醇受体在软骨形成中也起着重要作用,外源性类维生素A可抑制异位骨化的形成,并能够抑制创伤和先天性小鼠模型中的异位骨化[12]。 2.1.3 局部微环境 微环境包括局部神经、肌肉、血管及各种细胞释放物质的动态内环境,在创伤、烧伤等刺激下,微环境改变可引起一系列异常增加或延长的炎症反应,从而容易发生异位骨化[13]。局部缺氧、pH值、微量元素和机械刺激也可影响异位骨化的形成[9]。 2.2 异位骨化的分类 在1973年,Brooker博士及其同事发现异位骨化是全髋关节置换后常见的放射学检查结果,并随后提出了一种用以对全髋关节置换后异位骨形成进行分类的系统。目前已有多种不同的分类方案用来描述全髋关节置换后异位骨化的程度,包括Brooker 等[2]、DeLee等[14]、Kjaersgaar-Andersen等[15]提出的分类系统。这些分类都基于前后位骨盆或髋关节X射线片进行观测。 2.2.1 Brooker分类 Brooker分类是最早描述异位骨化的分类之一[2],该分类将异位骨化分为4级,见图2。Ⅰ级为髋周软组织内形成孤立性骨岛;Ⅱ级为股骨或骨盆侧形成骨化,两者间隙大于1 cm;Ⅲ级为股骨或骨盆侧形成骨化,两者间隙小于1 cm;Ⅳ级为形成骨桥,骨性强直。在Brooker最初的文献中没有描述0级,但在随后使用Brooker分类的研究中,将0级定义为在X射线片上没有发现异位骨化。 2002年Della Valle等[16]提出了1个Brooker分类的改进方式。A级为没有异位骨化和长度小于1 cm的骨岛;B级为至少1个骨岛测量长度大于1 cm或出现股骨和骨盆侧的骨刺,但两者间隙大于1 cm(BrookerⅡ级);C级为股骨和骨盆侧的骨刺,两者间隙小于1 cm(Brooker Ⅲ级)或明显的髋关节强直(BrookerⅣ级)。他们的研究表明Brooker分类缺乏足够的观察者间一致性。在前后位上重叠的骨岛或骨形成常与关节强直相混淆,此外,拍摄技术上的变化也可以影响Brooker分类,不同的X射线照射量可改变异位骨化的外观尺寸,甚至观察不到异位骨化[17]。 尽管Brooker分类存在一定的缺陷,但使用简单便捷,临床医生对其也较为熟悉,且前后位骨盆或双髋关节X射线片仍然普遍应用于全髋关节置换后随访评价,因此Brooker分类仍然广泛应用于异位骨化的评价和研究中[17],并且目前已有部分研究参考Brooker分类对其他关节置换术,如膝关节、肘关节置换术后发生的异位骨化进行评价。 2.2.2 DeLee分类 1975年DeLee等[14]在其研究中设计了一种分类方式来评价异位骨化的骨量及分类,其将异位骨化分为3类。Ⅰ类为关节周围任何位置,存在直径大于5 mm的骨岛;Ⅱ类为植入物外侧的异位骨,并附着于骨盆(ⅡA)或股骨(ⅡB);Ⅲ类植入物内侧的异位骨,并附着骨盆(ⅢA)或股骨(ⅢB)。为了对骨量进行分类,增加了3个子分类,1类为骨化范围占据股骨与骨盆距离的50%以下;2类为骨化范围占据股骨与骨盆距离的50%以上,但不到100%;3类为骨化范围占据股骨与骨盆距离的100%,形成骨性强直。 2.3 异位骨化的危险因素 软组织损伤的程度是导致异位骨化发展的一个重要原因[18]。有报道称异位骨化可能在手术16 h就开始形成[19]。既往的研究表明,异位骨化的危险因素分为2类[20-22],一类为不可变因素,包括年龄、男性、髋关节强直[20]、强直性脊柱炎[21]、既往髋部手术史双侧全髋关节置换手术、非洲裔人群[22]、体质量指数较高、肥厚性骨关节炎[23]、佩吉特病[24];另一类为可变因素,包括假体类型[25]、术后感染、全髋关节置换后3周内进行急性翻修髋关节置换术[26]、切口长度[27]、外侧或前外侧手术入路[25]、手术时长[20-22,27]、术中灌洗量[19]。但也有研究认为高龄并不是异位骨化的危险因素[28]。部分研究中类风湿关节炎被认为是异位骨化的风险因素,但是也有研究指出类风湿关节炎为保护性因素[28]。异位骨化危险因素相关研究的部分文献及结果见表1。"

2.4 临床表现 早期异位骨化可出现局部肿胀、发热及红斑,但没有特异性。严重的异位骨化明显降低了髋关节运动的整体范围,包括屈曲、外展、外旋等部分,而较低程度的异位骨化不会出现明显的临床症状,且不会显著影响髋关节运动及疼痛[33]。骨化程度较严重时,即BrookerⅢ、Ⅳ级与术后疼痛呈正相关[34],患者术后满意度也可受到异位骨化程度的影响[35],出现术后关节的屈曲范围和扩展距离的减小,行走能力降低或跛行,使患者满意度下降。 2.5 异位骨化影像学检查及表现 2.5.1 X射线数字化摄影 X射线为全髋关节置换后评价及随访应用最为广泛、经济简便的影像学检查方法,多采用双髋关节前后位或骨盆前后位进行检查。在影像表现上,异位骨化通常滞后于临床表现。在异位骨化初期,X射线片上很少或不能观察到异位骨的形成,可能仅显示脂肪层的消失。早期异位骨化可显示为模糊、不确切的钙化区域,没有明确的骨小梁形成[36],然而当病灶进展,表现为边缘逐渐清晰,骨化区密度增高改变,提示异位骨化趋向成熟[37]。通常在4-6周可以在X射线片上明确的观察到异位骨化,其影像学特征与正常骨组织相似[38]。大多数学者认为异位骨化的发生和数量在术后1年后没有变化[39]。异位骨化好发的解剖学位置为髋关节外侧臀中、小肌之间、大转子顶部、髂腰肌及小转 子[32],股骨前侧也可发现异位骨化,往往在仅有正位X射线片时被忽略[40],提示在怀疑异位骨化时应加做侧位或蛙式位,以明确异位骨化的位置及分类。 2.5.2 电子计算机断层扫描 CT是可准确评估异位骨化的影像学手段,可更为全面的显示异位骨化的位置和形态。由于金属伪影的影响,全髋关节置换后的CT图像质量下降,假体周围结构显示不清,进而对诊断造成干扰。运用迭代重建算法及提高kV值,采用薄层扫描,混合插值方法等方式可减少金属伪影[41],宝石能谱CT、双源CT也可大幅度减少植入物周围的伪影。CT图像上可显示病变部位软组织肿胀、钙化。在CT图像上将异位骨化分为3类[42]:无定形钙化,即为没有明确定义的无骨小梁结构;未成熟钙化,显示为骨化边缘不清晰及初始骨小梁形成;成熟骨化,其特征为具有骨皮质以及明确的松质骨中心。由于X射线片结构叠加可影响对Brooker Ⅳ级的判断,在这种情况下,CT可准确的评价。因此在X射线无法提供精准的病灶信息时,CT可作为相应的补充检查手段。 2.5.3 MRI MRI有较高的软组织分辨率,且没有电离辐射,能够更清楚地确定局部软组织或神经血管受累的程度,但对骨组织的显示不及X射线和CT。使用相应的金属伪影减少技术,如多采集可变共振图像组合及用于金属伪影矫正层面编码,可显著减少金属伪影[43]。较低的场强可减低磁敏感伪影,因此应避免使用3.0T MR进行检查[44]。在MRI图像上,可观察到早期不成熟的异位骨化[42],表现为T1加权相上局灶性等低信号,T2加权/ STIR相上高信号,增强可显示病灶强化,同时可以观察到滑膜和周围软组织的改变。但不成熟的异位骨化往往与血肿、软组织肿块或感染相类似,因此在怀疑异位骨化时,应结合X射线或CT的影像表现[45]。成熟的异位骨化表现为典型的松质骨信号,内部在T1和T2加权相上呈高信号,STIR相上被抑制[45],边缘为低信号[46]。在晚期发生肌肉萎缩,脂肪大量存在时,由于异位骨化在MRI上信号与脂肪组织较为相似,检测异位骨化可能存在一定的困难[43],需要仔细观察大转子和外侧髋臼之间的区域,以发现较小的异位骨化。虽然MRI对诊断异位骨化的敏感度较高,但由于其特异度低,检查费用较高,且易受植入物影响,因此不作为异位骨化诊断的首选。 2.5.4 超声 超声不受金属相关伪影的影响,可以良好地评估关节积液、滑膜增厚、组织充血等[43],观察异位骨化对神经、血管及周围软组织的影响,并可比X射线片更早的发现异位骨化。未成熟的异位骨化在超声检查中表现为关节周围软组织肿胀[47],其内可见轻微、不连续、边界不清的混合高、低混合回声,典型表现为云状改变,相应肌肉纹理也可发生改变。随着异位骨化的发展,异位骨形成组织的回声和均匀性逐渐增加,不连续的钙化回声形成连续的层状异位骨组织。成熟的异位骨化在超声上的典型表现为中央低回声[37],外围高回声,周围软组织低回声的环带状表现,其后方可见声影。其灰度值较早期异位骨化显著增加,并明显高于正常软组织[47]。超声具有便携方便、价格低廉、检查方式简单的优势,为诊断及评价异位骨化的良好方法。 2.5.5 单光子发射计算机断层扫描 与MRI相比,单光子发射计算机断层扫描不易受金属植入物引起的伪影所影响,并且可用于有MRI检查禁忌证的患者[48]。单光子发射计算机断层扫描/CT能够提供更为精准的定位及病变性质[49],确定全髋关节置换后疼痛原因明显优于仅使用单光子发射计算机断层扫描成像。在术后两至三周,血管和血池图像即可显示关节周围软组织中出现异常的示踪剂摄取[42],并在随后的1周摄取量增加。示踪剂摄取的峰值在初始损伤后几个月内发生,随后在发病后6-12个月逐渐减少[4],提示此时异位骨化已趋于稳定。此外,示踪剂摄取的强度反映了疾病活动的程度,可为外科手术干预的提供重要信息。虽然单光子发射计算机断层扫描/CT对于异位骨化的检测十分敏感,但在早期并不具备典型的骨形成特征,往往与感染、血管增生及肿瘤表现相类似,特异度较低。并且由于其价格高昂,需要注射放射性药物,检查时间长,限制了单光子发射计算机断层扫描/CT临床诊断异位骨化方面的应用。 2.6 异位骨化的预防与治疗 在影像学上可观察到的异位骨化对非手术治疗没有明显作用,在部分研究中运用药物或放疗手段仅可防止其进一步发展,因此目前临床上多采用对高危人群预防为主的方法控制异位骨化。 非类固醇抗炎药是一种常用药物,可抑制前列腺素的产生,而前列腺素则是骨基质骨化的介质之一[50],从而达到降低及预防异位骨化的目的。非选择性非类固醇抗炎药阻断环氧化酶1与环氧化酶2,选择性非类固醇抗炎药则仅阻断环氧化酶2。在功能方面,环氧化酶1能够保护胃肠道,环氧化酶2可促进前列腺素的形成,阻断环氧化酶1可引起胃肠道症状,而仅阻断环氧化酶2则能有效预防异位骨化且避免了相应副反应。因此,近年来关于非类固醇抗炎药预防异位骨化的研究集中于选择性非类固醇抗炎药的功效及副作用上[51]。面对有高危因素的患者,临床往往采用短期服用非类固醇抗炎药的方式用以预防异位骨化。 放射治疗是高危患者的有效预防性治疗方法,可抑制间充质干细胞颗粒化,从而达到预防目的。在Rumi等[52]的兔异位骨化模型研究中,发现术前24 h进行放疗为最佳的预防异位骨化的方式。有研究表明,在患者术后6周或12周接受晚期放疗的患者,可防止全髋关节置换后出现异位骨化的患者病灶进一步发展[53]。 绝大多数患者仅出现较低级别的异位骨化,对术后评价影响较低,多不采取治疗手段。但当患者出现明显疼痛、关节活动障碍时,需要进行手术切除。术前需要对异位骨化进行评价,当异位骨化处于稳定期时为最佳时机,且术后易复发,需要及时采取相应的预防措施[32]。"

| [1] Zeckey C, Hildebrand F, Frink M, et al. Heterotopic ossifications following implant surgery--epidemiology, therapeutical approaches and current concepts. Semin Immunopathol. 2011;33(3):273-286.[2] Brooker AF, Bowerman JW, Robinson RA, et al. Ectopic ossification following total hip replacement. Incidence and a method of classification. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973;55(8): 1629-1632.[3] Neal B. Effects of heterotopic bone formation on outcome after hip arthroplasty. ANZ J Surg. 2003;73: 422-426.[4] Shehab D, Elgazzar AH, Collier BD. Heterotopic ossification. J Nucl Med. 2002;43:346-353.[5] Shore EM, Kaplan FS. Inherited human diseases of heterotopic bone formation. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010; 6: 518-527.[6] 陈松,高悠水,周祖彬,等. 获得性异位骨化发病机制研究进展[J]. 国际骨科学杂志,2014,35(1):21-23.[7] Shore EM, Kaplan FS. Fibroregulation of mesenchymal progenitor cells by BMP-4 after traumatic muscle injury. J Orthop Trauma. 2012;26: 693-698.[8] Davis TA, O'Brien FP, Anam K, et al. Heterotopic ossification in complex orthopaedic combat wounds: quantification and characterization of osteogenic precursor cell activity in traumatized muscle.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93: 1122-1131.[9] Ranganathan K, Loder S, Agarwal S, et al. Heterotopic ossification: basic-science principles and clinical correlates. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97: 1101-1111.[10] Ramirez DM, Ramirez MR, Reginato AM, et al. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of heterotopic ossification. Histol. Histopathol. 2014;29:1281-1285.[11] Yu PB, Deng DY, Lai CS, et al. BMP type I receptor inhibition reduces heterotopic [corrected] ossification. Nat Med. 2008; 14(12): 1363-1369.[12] Medici D, Olsen BR. The role of endothelial-mesenchymal transition in heterotopic ossification. J Bone Miner Res. 2012; 27: 1619-1622.[13] Coons D, Godleski M. Range of motion exercises in the setting of burn-associated heterotopic ossification at the elbow: case series and discussion. Burns. 2013;39: e34-38.[14] DeLee J,Ferrari A,Charnley J, et al. Ectopic bone formation following low friction arthroplasty of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976;(121): 53-59.[15] Kjaersgaard-Andersen P,Sletgård J,Gjerløff C, et al. Heterotopic bone formation after noncemented total hip arthroplasty. Location of ectopic bone and the influence of postoperative antiinflammatory treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;(252):156-162.[16] Della Valle AG, Ruzo PS, Pavone V, et al. Heterotopic ossification after total hip arthroplasty: a critical analysis of the Brooker classification and proposal of a simplified rating system. J Arthroplasty. 2002; 17: 870-875.[17] Hug KT, Alton TB, Gee AO. Classifications in brief: Brooker classification of heterotopic ossification after total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015; 473: 2154-2157.[18] Ekelund A,Brosjö O,Nilsson O S, Experimental induction of heterotopic bone. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991;(263):102-112.[19] Kantak AP, Shah NN. Extensive surgical wound lavage reduces the incidence and severity of heterotopic ossification in primary total hip replacement: a study of 175 hip replacements. Hip Pelvis. 2017;29(4):234-239.[20] 刘勇,霍少川,唐宏宇,等. 强直性脊柱炎患者全髋关节置换后异位骨化的危险因素[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2017, 21(11): 1641-1646.[21] Thilak J, Panakkal JJ, Kim TY, et al. Risk Factors of Heterotopic Ossification Following Total Hip Arthroplasty in Patients With Ankylosing Spondylitis. J Arthroplasty. 2015; 30: 2304-2307.[22] Davis G,Patel RP,Tan TL, et al. Ethnic differences in heterotopic ossification following total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2016;98-B(6):761-766.[23] Fahrer H, Koch P, Ballmer P, et al. Ectopic ossification following total hip arthroplasty: is diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis a risk factor? Br J Rheumatol. 1988; 27: 187-190.[24] Ferguson DJ, Itonaga I, Maki M, et al. Heterotopic bone formation following hip arthroplasty in Paget's disease. Bone. 2004; 34(6): 1078-1083.[25] Pavlou G, Salhab M, Murugesan L, et al. Risk factors for heterotopic ossification in primary total hip arthroplasty. Hip Int. 2012; 22: 50-55.[26] Aljurayyan A, Tanzer D, Tanzer M. Acute revision hip arthroplasty: a previously unrecognized risk factor for heterotopic ossification. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2016;26(2):1-6.[27] Edwards DS,Barbur SA,Bull AM, et al. Posterior mini-incision total hip arthroplasty controls the extent of post-operative formation of heterotopic ossification. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015;25(6):1051-1055.[28] Zhu Y, Zhang F, Chen W, et al. Incidence and risk factors for heterotopic ossification after total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2015;135(9): 1307-1314.[29] Kocic M, Lazovic M, Mitkovic M, et al Clinical signi?cance of the heterotopic ossi?cation after total hip arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2010; 33(1):16.[30] Bal BS, Lowe JA, Gietler A, et al. Heterotopic ossification after 2-incision total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2010;25: 538-540.[31] Eggli S,Woo A. Risk factors for heterotopic ossification in total hip arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2001;121: 531-535.[32] 吴锋锋,吴立东.全髋关节置换术后异位骨化及其研究进展[J].中华骨科杂志, 2006,26(8):558-561.[33] Kocic M, Lazovic M, Mitkovic M, et al. Clinical significance of the heterotopic ossification after total hip arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2010; 33(1): 16.[34] Grzegorzewski A,Koz?owski P,Synder M,et al. Heterotopic ossification as a complication of total hip replacement. Chir Narzadow Ruchu Ortop Pol. 2000; 65: 255-260.[35] Eggli S, Rodriguez J, Ganz R. Heterotopic ossification in total hip arthroplasty: the significance for clinical outcome. Acta Orthop Belg. 2000;66(2): 174-180.[36] Bressler EL,Marn CS,Gore RM, et al. Evaluation of ectopic bone by CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987; 148: 931-935.[37] 鞠金勇,喻都,王永建,等. 异位骨化影像学早期诊断研究进展[J]. 国际骨科学杂志, 2016, 37(5):282-285.[38] Foley KL, Hebela N, Keenan MA, et al. Histopathology of periarticular non-hereditary heterotopic ossification. Bone. 2018;109: 65-70.[39] Rama KR, Vendittoli PA, Ganapathi M, et al. Heterotopic ossification after surface replacement arthroplasty and total hip arthroplasty: a randomized study. J Arthroplasty. 2009; 24(2): 256-262.[40] Metzner G,Lindner B,Neumann D, et al. Incidence of anterior intertrochanteric ossifications after total hip arthroplasty--a retrospective long-term follow-up study. Z Orthop Unfall. 2010; 148(2): 174-179.[41] Lee YH, Park KK, Song HT, et al. Metal artefact reduction in gemstone spectral imaging dual-energy CT with and without metal artefact reduction software. Eur Radiol. 2012; 22(6): 1331-1340.[42] Zagarella A, Impellizzeri E, Maiolino R, et al. Pelvic heterotopic ossification: when CT comes to the aid of MR imaging. Insights Imaging. 2013; 4(5): 595-603.[43] Fritz J, Lurie B, Miller TT. Imaging of hip arthroplasty. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2013;17: 316-327.[44] Hayter CL, Koff MF, Potter HG. Magnetic resonance imaging of the postoperative hip. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012;35(5): 1013-1025.[45] Khodarahmi I, Fritz J. Advanced MR imaging after total hip arthroplasty: the clinical impact. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2017;21(5): 616-629.[46] De Smet AA, Norris MA, Fisher DR. Magnetic resonance imaging of myositis ossificans: analysis of seven cases. Skeletal Radiol. 1992;21(8):503-507.[47] Wang Q, Zhang P, Li P, et al. Ultrasonography monitoring of trauma-induced heterotopic ossification: guidance for rehabilitation procedures. Front Neurol. 2018; 9: 771.[48] Van den Wyngaert T, Paycha F, Strobel K, et al. SPECT/CT in postoperative painful hip arthroplasty. Semin Nucl Med. 2018;48: 425-438.[49] Dobrindt O, Amthauer H, Krueger A, et al. Hybrid SPECT/ CT for the assessment of a painful hip after uncemented total hip arthroplasty. BMC Med Imaging. 2015;15: 18.[50] Vasileiadis GI, Sioutis IC, Mavrogenis AF, et al. COX-2 inhibitors for the prevention of heterotopic ossification after THA. Orthopedics. 2011;34(6): 467.[51] Joice M,Vasileiadis GI,Amanatullah DF. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for heterotopic ossification prophylaxis after total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2018;100-B(7):915-922.[52] Rumi MN, Deol GS, Bergandi JA, et al. Optimal timing of preoperative radiation for prophylaxis against heterotopic ossification. A rabbit hip model. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87(2): 366-373.[53] Morcos M, Smith K, Tanzer M. The effect of late radiotherapy on the progression of heterotopic ossification following total hip arthroplasty. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2018;28(6): 1125-1131. |
| [1] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [2] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [3] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [4] | Xiang Feifan, Ye Junwu, Zhang Xihai, Ge Jianhua, Tang Lian, Yang Yunkang. Comparison of three different internal fixation methods in treatment of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 403-408. |
| [5] | Xie Chengxin, Wang Wei, Wang Chenglong, Li Qinglong, Yin Dong. Systematic review and meta-analysis of bone morphogenetic protein for the treatment of acute tibial fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 486-492. |
| [6] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [7] | Fu Panfeng, Shang Wei, Kang Zhe, Deng Yu, Zhu Shaobo. Efficacy of anterolateral minimally invasive approach versus traditional posterolateral approach in total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3409-3415. |
| [8] | Ren Xingyu, Zhang Yi, Xu Haoran, Fan Bin, Dai Shifeng, Liang Chunyu. Meta-analysis of the postoperative effects of robot-assisted unicompartmental knee arthroplasty versus conventional surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3416-3422. |
| [9] | Song Kaikai, Du Gangqiang, Li Peng, Jiang Shengyuan, Gong Zhihao, Zhang Zhiwei, Zhang Kai . Application of head-neck ratio in the treatment of femoral neck fracture in aged patients with artificial femoral head replacement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2805-2809. |
| [10] | Li Haifeng, Liu Yu, Yin Qudong, Sun Zhenzhong, Rui Yongjun, Gu Sanjun. Risk of complications of early postoperative weight-bearing after internal fixation of intracapsular femoral neck fractures: 2-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2875-2880. |
| [11] | Yuan Jiaqin, Luan Fujun, Chen Yangfan, Deng Yi, Li Bo. Meta-analysis of bipolar and unipolar hemiarthroplasties for displaced femoral neck fracture in the elderly patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2915-2922. |
| [12] | Liu Pengran, Jiao Rui, Tao Jin, Chen Hui, Dai Jihang, Yan Lianqi. Comparison of the effects of total hip arthroplasty with different interface prostheses in the treatment of elderly hip diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2347-2351. |
| [13] | Li Yonghe, Wang Xiankang, Meng Yu, Liu Lu, Zhang Chunqiu, Ye Jinduo . Mechanical analysis on the position difference of short-stemmed prosthesis in hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2394-2399. |
| [14] | Gao Fenghe, Chen Tongying, Lin Jiebin, Liang Zujian. Efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid combined with rivaroxaban in primary total knee and hip arthroplasties: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2453-2460. |
| [15] | Zhang Tengfei, Wang Kun, Zhu Yanyu, Mei Wei, Wang Qingde. Meta-analysis of risk factors associated with adjacent segment degeneration after lumbar posterior fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1936-1943. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||