Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (13): 1999-2004.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0506
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve learning ability of the aging rat
Liu Yang1, Wang Fei-qing1, Liu Yan-qing1, Li Hong-ri1, Zhang Bo1, Li Yan-ju2
- 1First Affiliated Hospital of Guiyang University of TCM, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Hematology, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
-
Revised:2018-03-29Online:2018-05-08Published:2018-05-08 -
Contact:Li Yan-ju, M.D., Associate chief physician, Department of Hematology, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Liu Yang, M.D., Associate professor, First Affiliated Hospital of Guiyang University of TCM, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31660326; the grant from the Science and Technology Department of Guizhou Province, No. [2016]1019, LH[2017]7140; the Top Talent Program of Guizhou Provincial Department of Education, No. KY[2016]074; the grant from the Guizhou Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. [2016]47
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Yang, Wang Fei-qing, Liu Yan-qing, Li Hong-ri, Zhang Bo, Li Yan-ju. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve learning ability of the aging rat[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(13): 1999-2004.
share this article
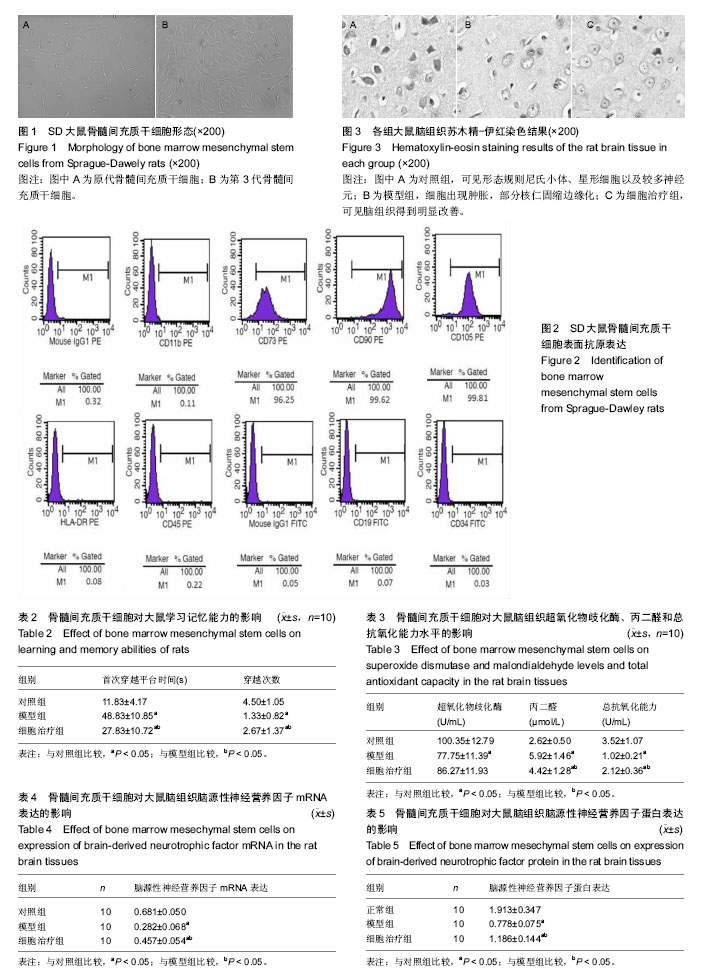
2.1 骨髓间充质干细胞的培养形态以及鉴定结果 刚接种时,于显微镜下观察可见悬浮于其中的大量骨髓细胞,无贴壁细胞;第3天换液,大量的造血干血细胞被除去,于显微镜下可观察到培养瓶底壁贴壁的细胞分布不均,部分呈巢状生长;第6天可见形成多个成纤维样细胞集落,10 d左右细胞融合80%-90%。传代培养后细胞形态基本上趋于一致,光镜下见细胞呈星形,梭形,见图1。 经流式细胞仪检测,第3代骨髓间充质干细胞的特异性表面标志物CD105,CD90,CD73呈阳性表达,阳性率分别为99.81%,99.62%,96.25%;CD11b,CD45,HLA-DR,CD19,CD34呈阴性表达,阴性率分别为0.11%,0.22%,0.08%,0.07%,0.03%,提示第3代贴壁细胞为骨髓间充质干细胞,见图2。 2.2 实验动物数量分析 30只SD大鼠均进入结果分析,无脱失。 2.3 水迷宫检测大鼠学习记忆能力变化 通过水迷宫空间探索实验,模型组和细胞治疗组大鼠首次穿越平台时间明显大于对照组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。与模型组比较,细胞治疗组大鼠穿越平台时间减少,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。穿越平台次数对照组明显多于模型组和细胞治疗组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。与模型组比较,细胞治疗组大鼠穿越平台次数明显多于模型组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表2。 2.4 光镜观察大鼠脑组织病理形态 200倍光镜下观察,对照组可见形态规则的尼氏小体、星形细胞,核仁清晰,未见衰老现象(图3A)。模型组大鼠脑组织尼氏小体明显减少,部分核仁固缩边缘化,细胞出现肿胀,呈现明显衰老的现象(图3B)。细胞治疗组大鼠脑组织尼氏小体增加,核仁清晰,脑组织未见明显肿胀衰老迹象,与模型组比较明显改善(图3C)。 2.5 衰老大鼠脑组织超氧化物歧化酶、总抗氧化能力和丙二醛水平 模型组和细胞治疗组大鼠脑组织超氧化物歧化酶活性低于对照组,模型组与对照组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。细胞治疗组大鼠脑组织超氧化物歧化酶活性与模型组比较,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。模型组和细胞治疗组大鼠脑组织丙二醛水平高于对照组 (P < 0.05),细胞治疗组大鼠脑组织丙二醛水平低于模型组(P < 0.05)。模型组和细胞治疗组大鼠脑组织总抗氧化能力水平低于对照组(P < 0.05),细胞治疗组大鼠脑组织总抗氧化能力水平高于模型组(P < 0.05),见表3。 2.6 Real-time PCR测定脑组织中BDNF mRNA表达 与对照组比较,模型组和细胞治疗组大鼠脑组织BDNF mRNA的表达降低,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。与模型组比较,细胞治疗组大鼠脑组织BDNF mRNA升高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表4。 2.7 Western Blot检测脑组织BDNF蛋白表达 与对照组比较,模型组和细胞治疗组大鼠脑组织BDNF蛋白表达明显降低,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。与模型组比较,细胞治疗组大鼠脑组织BDNF蛋白表达升高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表5。"
| [1] Cribbs DH, Berchtold NC, Perreau V, et al. Extensive innate immune gene activation accompanies brain aging, increasing vulnerability to cognitive decline and neurodegeneration: a microarray study. J Neuroinflammation. 2012;9:179.[2] Wahl D, Cogger VC, Solon-Biet SM, et al. Nutritional strategies to optimise cognitive function in the aging brain. Ageing Res Rev. 2016; 31:80-92.[3] Berchtold NC, Cribbs DH, Coleman PD, et al. Gene expression changes in the course of normal brain aging are sexually dimorphic. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(40):15605-15610. [4] De la Fuente M, Miquel J. An update of the oxidation-inflammation theory of aging: the involvement of the immune system in oxi-inflamm-aging. Curr Pharm Des. 2009;15(26):3003-3026.[5] Naumova E, Ivanova M, Pawelec G. Immunogenetics of ageing. Int J Immunogenet. 2011;38(5):373-381.[6] Ollivier-Lanvin K, Fischer I, Tom V, et al. Either brain-derived neurotrophic factor or neurotrophin-3 only neurotrophin-producing grafts promote locomotor recovery in untrained spinalized cats. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2015;29(1):90-100.[7] Munoz JR, Stoutenger BR, Robinson AP, et al. Human stem/progenitor cells from bone marrow promote neurogenesis of endogenous neural stem cells in the hippocampus of mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(50):18171-18176.[8] 崔旭,李文彬,张炳烈,等.自由基损伤与D-半乳糖所致细胞老化关系[J].基础医学与临床,2000,20(1):24-26.[9] Zanier ER, Montinaro M, Vigano M, et al. Human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells protect mice brain after trauma. Crit Care Med. 2011;39(11):2501-2510.[10] Chen J, Sanberg PR, Li Y, et al. Intravenous administration of human umbilical cord blood reduces behavioral deficits after stroke in rats. Stroke. 2001;32(11):2682-2688.[11] Krampera M, Glennie S, Dyson J, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibit the response of naive and memory antigen-specific T cells to their cognate peptide. Blood. 2003;101(9):3722-3729.[12] Le Blanc K, Tammik L, Sundberg B, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit and stimulate mixed lymphocyte cultures and mitogenic responses independently of the major histocompatibility complex. Scand J Immunol. 2003;57(1):11-20.[13] Le Blanc K, Ringdén O. Immunomodulation by mesenchymal stem cells and clinical experience. J Intern Med. 2007;262(5):509-525.[14] Duijvestein M, Wildenberg ME, Welling MM, et al. Pretreatment with interferon-γ enhances the therapeutic activity of mesenchymal stromal cells in animal models of colitis. Stem Cells. 2011;29(10): 1549-1558. [15] 李艳菊,胡亮杉,郭坤元.骨髓间充质干细胞回输对大鼠肾脏衰老的影响[J].中华肾脏病杂志,2009,25(3):241-242.[16] 李艳菊,邓兰,黄睿.骨髓间充质干细胞对大鼠肾脏衰老的影响[J].中华内科杂志,2009, 48(6):458-461.[17] López-Torres M, Barja G. Calorie restriction, oxidative stress and longevity. Rev Esp Geriatr Gerontol. 2008;43(4):252-260.[18] Pacini S. Deterministic and stochastic approaches in the clinical application of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs). Front Cell Dev Biol. 2014;2:50.[19] Wang GH, Liu Y, Wu XB, et al. Neuroprotective effects of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells combined with nimodipine against radiation-induced brain injury through inhibition of apoptosis. Cytotherapy. 2016;18(1):53-64.[20] 王欣欣,马珊珊,孟楠,等.hUC-MSCs和白藜芦醇对AD小鼠学习记忆能力及脑内SIRT1信号通路的影响[J].郑州大学学报(医学版),2016,51(5): 576-579.[21] Singh M, Kakkar A, Sharma R, et al. Synergistic Effect of BDNF and FGF2 in Efficient Generation of Functional Dopaminergic Neurons from human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):10378.[22] Chen H, Long Y, Guo L. Antiaging Effect of Inula britannica on Aging Mouse Model Induced by D-Galactose. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:6049083.[23] Aizman I, Tate CC, McGrogan M, et al. Extracellular matrix produced by bone marrow stromal cells and by their derivative, SB623 cells, supports neural cell growth. J Neurosci Res. 2009;87(14):3198-3206.[24] Liu K, Chi L, Guo L, et al. The interactions between brain microvascular endothelial cells and mesenchymal stem cells under hypoxic conditions. Microvasc Res. 2008;75(1):59-67.[25] 李艳菊,丁元廷,周媛,等.同种异体来源骨髓间充质干细胞移植可改善衰老心脏的功能[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(6):814-819.[26] Hewett SJ, Jackman NA, Claycomb RJ. Interleukin-1β in Central Nervous System Injury and Repair. Eur J Neurodegener Dis. 2012; 1(2):195-211.[27] Smith CJ, Emsley HC, Gavin CM, et al. Peak plasma interleukin-6 and other peripheral markers of inflammation in the first week of ischaemic stroke correlate with brain infarct volume, stroke severity and long-term outcome. BMC Neurol. 2004;4:2.[28] Rashid K, Sinha K, Sil PC. An update on oxidative stress-mediated organ pathophysiology. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013;62:584-600.[29] Klinker MW, Wei CH. Mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases in experimental animal models. World J Stem Cells. 2015;7(3):556-567.[30] MacFarlane RJ, Graham SM, Davies PS, et al. Anti-inflammatory role and immunomodulation of mesenchymal stem cells in systemic joint diseases: potential for treatment. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2013;17(3):243-254.[31] English K. Mechanisms of mesenchymal stromal cell immunomodulation. Immunol Cell Biol. 2013;91(1):19-26.[32] Solchaga LA, Zale EA. Prostaglandin E2: a putative potency indicator of the immunosuppressive activity of human mesenchymal stem cells. Am J Stem Cells. 2012;1(2):138-145.[33] Prockop DJ, Oh JY. Medical therapies with adult stem/progenitor cells (MSCs): a backward journey from dramatic results in vivo to the cellular and molecular explanations. J Cell Biochem. 2012;113(5): 1460-1469.[34] Vacaras V, Major ZZ, Muresanu DF, et al. Effect of glatiramer acetate on peripheral blood brain-derived neurotrophic factor and phosphorylated TrkB levels in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2014;13(4):647-651.[35] Liu Q, Wong-Riley MT. Postnatal development of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and tyrosine protein kinase B (TrkB) receptor immunoreactivity in multiple brain stem respiratory-related nuclei of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 2013;521(1):109-129.[36] Novkovic T, Mittmann T, Manahan-Vaughan D. BDNF contributes to the facilitation of hippocampal synaptic plasticity and learning enabled by environmental enrichment. Hippocampus. 2015;25(1):1-15.[37] Ikeda O, Murakami M, Ino H, et al. Effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) on compression-induced spinal cord injury: BDNF attenuates down-regulation of superoxide dismutase expression and promotes up-regulation of myelin basic protein expression. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2002;61(2):142-153.[38] Ben-Hur T, Idelson M, Khaner H, et al. Transplantation of human embryonic stem cell-derived neural progenitors improves behavioral deficit in Parkinsonian rats. Stem Cells. 2004;22(7):1246-1255. |
| [1] | Min Youjiang, Yao Haihua, Sun Jie, Zhou Xuan, Yu Hang, Sun Qianpu, Hong Ensi. Effect of “three-tong acupuncture” on brain function of patients with spinal cord injury based on magnetic resonance technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-8. |
| [2] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [3] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [4] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [5] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [6] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [7] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [8] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [9] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [10] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [11] | He Li, Tian Wei, Xu Song, Zhao Xiaoyu, Miao Jun, Jia Jian. Factors influencing the efficacy of lumbopelvic internal fixation in the treatment of traumatic spinopelvic dissociation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 884-889. |
| [12] | Liu Zhao, Xu Xilin, Shen Yiwei, Zhang Xiaofeng, Lü Hang, Zhao Jun, Wang Zhengchun, Liu Xuzhuo, Wang Haitao. Guiding role and prospect of staging and classification combined collapse prediction method for osteonecrosis of femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 929-934. |
| [13] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [14] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| [15] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||