Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (20): 3230-3236.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0311
Previous Articles Next Articles
Cognitive impairment and hippocampal alpha-synuclein change in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion
He Jing1, Huang Yan1, Du Guo2, Wang Zhi-qiang2, Xiang Yang2, Wang Qing-song1, 2
- 1Department of Neurology, the Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Department of Neurology, Chengdu Military General Hospital, Chengdu 610000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2018-04-24Online:2018-07-18Published:2018-07-18 -
Contact:Wang Qing-song, Department of Neurology, the Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; Department of Neurology, Chengdu Military General Hospital, Chengdu 610000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:He Jing, Master candidate, Department of Neurology, the Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation for the Youth, No. 81601112; the Scientific Research Project of Health and Family Planning Commission of Sichuan Province, No. 150002 and 16PJ014
CLC Number:
Cite this article
He Jing1, Huang Yan1, Du Guo2, Wang Zhi-qiang2, Xiang Yang2, Wang Qing-song1, 2. Cognitive impairment and hippocampal alpha-synuclein change in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(20): 3230-3236.
share this article
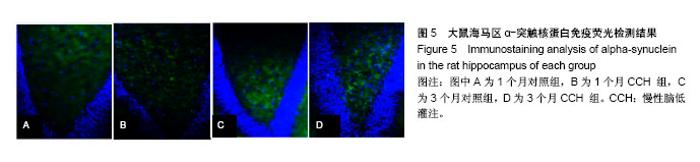
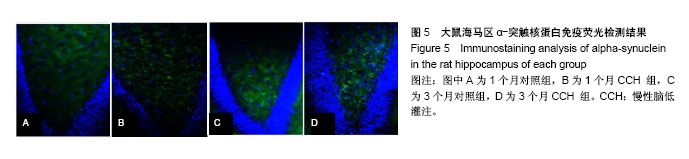
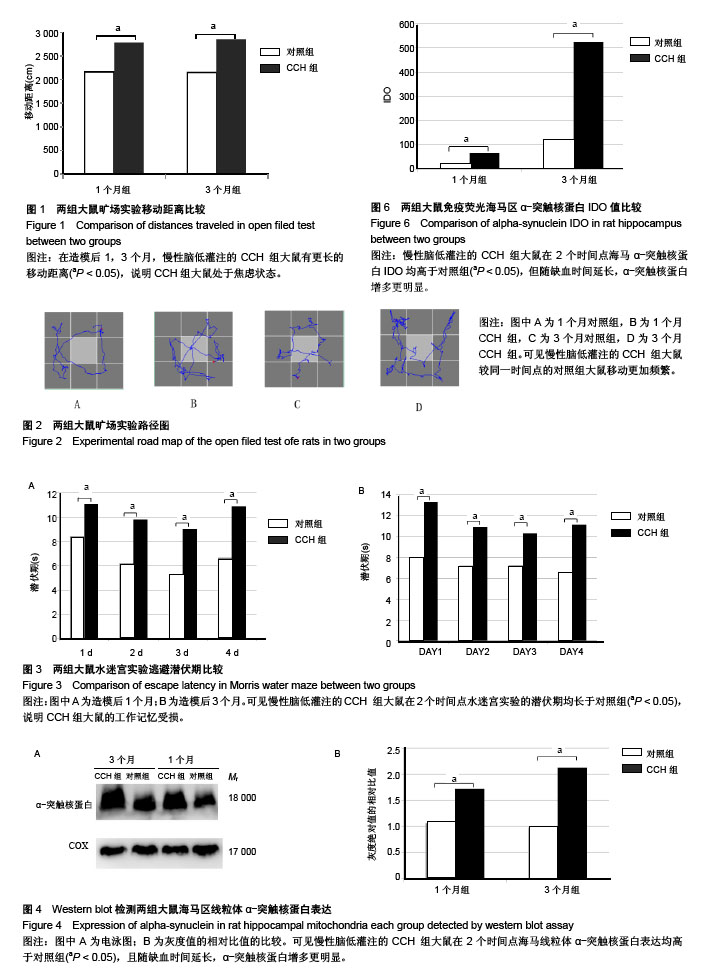
2.1 实验动物数量分析 造模完成后未有动物死亡,使用32只大鼠均进入结果分析。 2.2 行为学检测结果 结果显示:CCH致大鼠的学习记忆能力下降。 2.2.1 旷场实验 对大鼠在旷场实验中行动距离检测发现,1,3个月CCH组大鼠有更长的移动距离,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),说明CCH组大鼠处于焦虑状态(图1)。并且,从路径图中可更为直观的观察到CCH组大鼠较同一时间点的对照组大鼠移动更加频繁(图2)。 2.2.2 水迷宫实验 统计两组大鼠每天平均潜伏期,潜伏期越长代表大鼠找寻到逃生平台所需的时间越久,大鼠的记忆能力损伤越严重。图3结果显示,各时间点CCH组潜伏期长于对照组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),说明CCH组大鼠的工作记忆受损。 2.3 Western blot检测结果 提取大鼠海马区线粒体蛋白质进行α-突触核蛋白含量检测,发现1个月时,对照组灰度值为1.60±0.32,CCH组为1.72±0.17;3个月时,对照组为0.98±0.31,CCH组为2.13±0.3。造模后1,3个月,与对照组比较,CCH组海马区线粒体α-突触核蛋白含量均有明显变化,但3个月时升高更明显(P < 0.05),见图4。"
| [1] Wirth M, Pichet Binette A, Brunecker P,et al. Divergent regional patterns of cerebral hypoperfusion and gray matter atrophy in mild cognitive impairment patients. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2017;37(3): 814-824.[2] Gorelick PB, Counts SE, Nyenhuis D. Vascular cognitive impairment and dementia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1862 (5):860-868.[3] Zhu J, Wang Y, Li J, Deng J,et al. Intracranial artery stenosis and progression from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2014; 82(10): 842-849.[4] Han H, Qian Q, Yu Y,et al. Lamotrigine attenuates cerebral ischemia-induced cognitive impairment and decreases beta-amyloid and phosphorylated tau in the hippocampus in rats. Neuroreport 2015; 26(12): 723-727.[5] Liu F, Jiang YJ, Zhao HJ,et al. Electroacupuncture ameliorates cognitive impairment and regulates the expression of apoptosis-related genes Bcl-2 and Bax in rats with cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion injury. Acupunct Med 2015;33(6): 478-484.[6] Wang Z, Fan J, Wang J,et al. Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion induces long-lasting cognitive deficits accompanied by long-term hippocampal silent synapses increase in rats. Behav Brain Res 2016; 301: 243-252.[7] Thomas T, Miners S, Love S.Post-mortem assessment of hypoperfusion of cerebral cortex in Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia. Brain 2015;138(Pt 4): 1059-1069.[8] Iadecola C. The pathobiology of vascular dementia. Neuron . 2013; 80(4): 844-866.[9] O'Brien JT, Thomas A. Vascular dementia. Lancet 2015; 386(10004): 1698-706.[10] 王璐,霍帅,王亚飞,等. 慢性脑缺血模型大鼠神经突触可塑性与N-甲基-D-天门冬氨酸型受体[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2015, 19(40):6498-6503.[11] Du J, Ma M, Zhao Q,et al. Mitochondrial bioenergetic deficits in the hippocampi of rats with chronic ischemia-induced vascular dementia. Neuroscience.2013;231:345-352.[12] Li N, Kong X,Ye R,et al.Age-related differences in experimental stroke: possible involvement of mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative damage. Rejuvenation Res.2011; 14(3): 261-273.[13] Li H, Liu Y, Lin LT, et al. Acupuncture reversed hippocampal mitochondrial dysfunction in vascular dementia rats. Neurochem Int 2016; 92: 35-42.[14] 代海滨,苗晓蕾,嵇晴,等. 线粒体及凋亡相关信号途径在脑缺血性损伤细胞死亡过程中的重要角色[J].中国组织工程研究,2015, 19(15): 2425-2430.[15] Yue ZY, Dong H, Wang YF, et al. Propofol prevents neuronal mtDNA deletion and cerebral damage due to ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Brain Res.2015;1594:108-114.[16] Reeve AK, Ludtmann MH, Angelova PR, et al. Aggregated alpha-synuclein and complex I deficiency: exploration of their relationship in differentiated neurons. Cell Death Dis.2015;6: e1820.[17] Tapias V, Hu X, Luk KC, et al. Greenamyre, Synthetic alpha-synuclein fibrils cause mitochondrial impairment and selective dopamine neurodegeneration in part via iNOS-mediated nitric oxide production. Cell Mol Life Sci .2017; 74(15):2851-2874.[18] Hu X, Rea HC, Wiktorowicz JE, et al. Proteomic analysis of hypoxia/ischemia-induced alteration of cortical development and dopamine neurotransmission in neonatal rat. J Proteome Res.2006;5(9):2396-2404.[19] Yoon DK, Hwang IK, Yoo KY, et al. Comparison of alpha-synuclein immunoreactivity and protein levels in ischemic hippocampal CA1 region between adult and aged gerbils and correlation with Cu,Zn-superoxide dismutase. Neurosci Res.2006;55(4): 434-441.[20] Unal-Cevik I, Gursoy-Ozdemir Y, Yemisci M, et al. Alpha-synuclein aggregation induced by brief ischemia negatively impacts neuronal survival in vivo: a study in [A30P]alpha-synuclein transgenic mouse. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.2011;31(3): 913-923.[21] Kim T, Mehta SL, Kaimal B, et al. Vemuganti, Poststroke Induction of alpha-Synuclein Mediates Ischemic Brain Damage. J Neurosci. 2016;36(26):7055-7065.[22] Choi JY, Cui Y, Kim BG. Interaction between hypertension and cerebral hypoperfusion in the development of cognitive dysfunction and white matter pathology in rats. Neuroscience. 2015;303: 115-125.[23] Jing Z, Shi C, Zhu L, et al. Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion induces vascular plasticity and hemodynamics but also neuronal degeneration and cognitive impairment. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.2015;35(8):1249-1259.[24] Wan Q, Ma X, Zhang ZJ, et al. Ginsenoside Reduces Cognitive Impairment During Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion Through Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Regulated by Epigenetic Modulation. Mol Neurobiol .2017;54(4):2889-2900.[25] Ham PB 3rd, Raju R. Mitochondrial function in hypoxic ischemic injury and influence of aging. Prog Neurobiol.2017; 157: 92-116.[26] Keogh MJ, Chinnery PF. Mitochondrial DNA mutations in neurodegeneration. Biochim Biophys Acta.2015;1847(11): 1401-1411.[27] Sun N, Youle RJ, Finkel T. The Mitochondrial Basis of Aging. Mol Cell.2016; 61(5): 654-666.[28] Farkas E, Luiten PG, Bari F. Permanent, bilateral common carotid artery occlusion in the rat: a model for chronic cerebral hypoperfusion-related neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res Rev. 2007;54(1): 162-180.[29] Wang C, Zhao C, Li D, et al. Versatile Structures of alpha-Synuclein. Front Mol Neurosci 2016; 9: 48.[30] Vargas KJ, Makani S, Davis T,et al. Synucleins regulate the kinetics of synaptic vesicle endocytosis. J Neurosci.2014; 34(28): 9364-9376.[31] Devi L, Raghavendran V, Prabhu BM,et al. Mitochondrial import and accumulation of alpha-synuclein impair complex I in human dopaminergic neuronal cultures and Parkinson disease brain. J Biol Chem .2008; 283(14): 9089-9100.[32] Nakamura K, Nemani VM, Wallender EK,et al. Optical reporters for the conformation of alpha-synuclein reveal a specific interaction with mitochondria.J Neurosci.2008;28(47): 12305-12317.[33] Robotta M, Gerding HR, Vogel A,et al. Alpha-synuclein binds to the inner membrane of mitochondria in an alpha-helical conformation. Chembiochem .2014; 15(17): 2499-2502.[34] Pozo Devoto VM, Falzone TL. Mitochondrial dynamics in Parkinson's disease: a role for alpha-synuclein? Dis Model Mech .2017; 10(9): 1075-1087.[35] Ludtmann MH, Angelova PR, Ninkina NN, et al. Monomeric Alpha-Synuclein Exerts a Physiological Role on Brain ATP Synthase. J Neurosci. 2016; 36(41): 10510-10521.[36] Shen J, Du T, Wang X, et al. alpha-Synuclein amino terminus regulates mitochondrial membrane permeability. Brain Res. 2014;1591:14-26.[37] Ellis CE, Murphy EJ, Mitchell DC,et al. Nussbaum, Mitochondrial lipid abnormality and electron transport chain impairment in mice lacking alpha-synuclein. Mol Cell Biol 2005; 25(22): 10190-10201. [38] Chinta SJ, Mallajosyula JK, Rane A,et al.Mitochondrial alpha-synuclein accumulation impairs complex I function in dopaminergic neurons and results in increased mitophagy in vivo. Neurosci Lett. 2010;486(3): 235-239.[39] Wong YC, Krainc D. alpha-synuclein toxicity in neurodegeneration: mechanism and therapeutic strategies. Nat Med.2017; 23(2): 1-13.[40] Goedert M, Masuda-Suzukake M, Falcon B. Like prions: the propagation of aggregated tau and alpha-synuclein in neurodegeneration. Brain 2017; 140(2): 266-278.[41] Lippa CF, Fujiwara H, Mann DM,et al.Trojanowski, Lewy bodies contain altered alpha-synuclein in brains of many familial Alzheimer's disease patients with mutations in presenilin and amyloid precursor protein genes. Am J Pathol . 1998;153(5):1365-1370.[42] Roberts HL, Schneider BL, Brown DR. alpha-Synuclein increases beta-amyloid secretion by promoting beta-/gamma-secretase processing of APP. PLoS One.2017; 12(2): e0171925.[43] Guo JL, Covell DJ, Daniels JP,et al. Distinct alpha-synuclein strains differentially promote tau inclusions in neurons. Cell 2013;154(1):103-17.[44] Peelaerts W, Baekelandt V. a-Synuclein strains and the variable pathologies of synucleinopathies. J Neurochem. 2016; 139 Suppl 1: 256-274.[45] Larson ME, Greimel SJ, Amar F,et al.Selective lowering of synapsins induced by oligomeric alpha-synuclein exacerbates memory deficits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2017; 114(23): E4648-e4657.[46] Martin ZS, Neugebauer V, Dineley KT, et al. Taglialatela, alpha-Synuclein oligomers oppose long-term potentiation and impair memory through a calcineurin-dependent mechanism: relevance to human synucleopathic diseases. J Neurochem. 2012; 120(3): 440-452.[47] Diógenes MJ, Dias RB, Rombo DM, et al.Extracellular alpha-synuclein oligomers modulate synaptic transmission and impair LTP via NMDA-receptor activation. J Neurosci. 2012;32(34): 11750-11762.[48] Yasuda T, Nakata Y, Mochizuki H. alpha-Synuclein and neuronal cell death. Mol Neurobiol 2013; 47(2): 466-483.[49] Lopez MS, Dempsey RJ, Vemuganti R. Resveratrol neuroprotection in stroke and traumatic CNS injury. Neurochem Int. 2015; 89: 75-82.[50] Rodriguez-Grande B, Blackabey V, Gittens B,et al. Loss of substance P and inflammation precede delayed neurodegeneration in the substantia nigra after cerebral ischemia. Brain Behav Immun.2013; 29: 51-61.[51] Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E,et al. Nussbaum, Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson's disease. Science.1997; 276(5321): 2045-2047.[52] Levine RL,Jones JC, Bee N. Stroke and Parkinson's disease. Stroke.1992; 23(6): 839-842. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Zhao Xiang, Wei Cuilan, Zhang Yeting. Neurogenesis and neuroinflammation under exercise: alteration and regulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 813-820. |
| [5] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [6] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [7] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [8] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [9] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [10] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [11] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [12] | Bai Shengchao, Gao Yang, Wang Bo, Li Junping, Wang Ruiyuan. Dynamic changes of mitochondrial function of the skeletal muscle after acupuncture intervention in rats with heavy load exercise-induced injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3648-3653. |
| [13] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [14] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [15] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||