[1] COHEN L, DANHAUER SC, GARCIA MK, et al. Acupuncture for Chronic Radiation-Induced Xerostomia in Head and Neck Cancer: A Multicenter Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(5):e2410421.
[2] XIANG L, RONG JF, XIN C, et al. Reducing Target Volumes of Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy After Induction Chemotherapy in Locoregionally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Long-Term Results of a Prospective, Multicenter, Randomized Trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2023;117(4):914-924.
[3] GUAN Z, ZHANG J, JIANG N, et al. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in rodent models of radiation-induced xerostomia and oral mucositis: a systematic review. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):82.
[4] LIN Y, CHEN X, YU C, et al. Radiotherapy-mediated redox homeostasis-controllable nanomedicine for enhanced ferroptosis sensitivity in tumor therapy. Acta Biomater. 2023;159:300-311.
[5] LI HX, WANG TH, WU LX, et al. Role of Keap1-Nrf2/ARE signal transduction pathway in protection of dexmedetomidine preconditioning against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Biosci Rep. 2022;42(9):BSR20221306.
[6] LIU S, PI J, ZHANG Q. Signal amplification in the KEAP1-NRF2-ARE antioxidant response pathway. Redox Biol. 2022;54:102389.
[7] 刘璐,刘淑丹,刘晓丹,等.氧化苦参碱水凝胶通过激活角化细胞Nrf2/HO-1通路促进创面愈合[J].中国组织工程研究,2024, 28(29):4620-4627.
[8] ZHANG T, SHI L, LI Y, et al. Polysaccharides extracted from Rheum tanguticum ameliorate radiation-induced enteritis via activation of Nrf2/HO-1. J Radiat Res. 2021;62(1):46-57.
[9] LIANG ST, CHEN C, CHEN RX, et al. Michael acceptor molecules in natural products and their mechanism of action. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1033003.
[10] WANG Q, LIN D, LIU XF, et al. Engineering piperlongumine-inspired analogs as Nrf2-dependent neuroprotectors against oxidative damage by an electrophilicity-based strategy. Free Radic Biol Med. 2023;194:298-307.
[11] CHOWDHURY FA, COLUSSI N, SHARMA M, et al. Fatty acid nitroalkenes - Multi-target agents for the treatment of sickle cell disease. Redox Biol. 2023;68:102941.
[12] BAGO Á, CAYUELA ML, GIL A, et al. Nitro-oleic acid regulates T cell activation through post-translational modification of calcineurin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023;120(4):e2208924120.
[13] PIESCHE M, ROOS J, KÜHN B, et al. The Emerging Therapeutic Potential of Nitro Fatty Acids and Other Michael Acceptor-Containing Drugs for the Treatment of Inflammation and Cancer. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:1297.
[14] SCHOPFER FJ, KHOO NKH. Nitro-Fatty Acid Logistics: Formation, Biodistribution, Signaling, and Pharmacology. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2019;30(8):505-519.
[15] DI MAIO R, KEENEY MT, CECHOVA V, et al. Neuroprotective actions of a fatty acid nitroalkene in Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2023;9(1):55.
[16] 曹璐.大鼠颌下腺上皮细胞放射性损伤模型的建立与评估[D].遵义:遵义医科大学,2019.
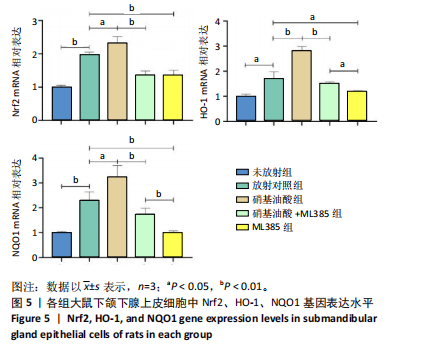
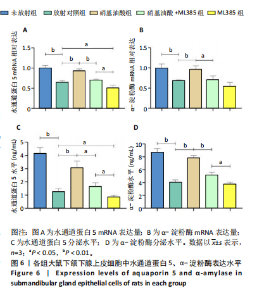
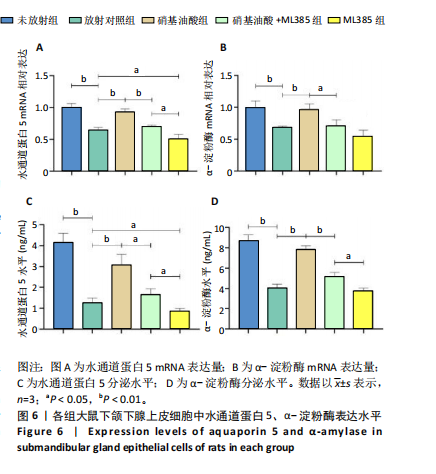
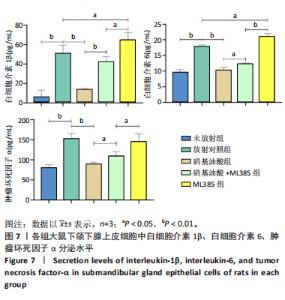
[17] 骆勤亮,张霓霓,龙远铸,等.硝基油酸经Nrf2/HO-1通路对放射性损伤大鼠颌下腺上皮细胞的抗氧化损伤作用[J].口腔医学研究, 2022,38(12):1139-1144.
[18] XIE LW, CAI S, ZHAO TS, et al. Green tea derivative (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) confers protection against ionizing radiation-induced intestinal epithelial cell death both in vitro and in vivo. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;161:175-186.
[19] SINGH A, VENKANNAGARI S, OH KH, et al. Small Molecule Inhibitor of NRF2 Selectively Intervenes Therapeutic Resistance in KEAP1-Deficient NSCLC Tumors. ACS Chem Biol. 2016;11(11):3214-3225.
[20] TANG Z, ZHAO L, YANG Z, et al. Mechanisms of oxidative stress, apoptosis, and autophagy involved in graphene oxide nanomaterial anti-osteosarcoma effect. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13:2907-2919.
[21] GUNNING JA, LIMESAND KH. Chronic Phenotypes Underlying Radiation-Induced Salivary Gland Dysfunction. J Dent Res. 2024;103(8):778-786.
[22] CHEN YC, VIET-NHI NK, DANG LH, et al. Efficacy of Office-Based Salivary Ductal Steroid Irrigation for Managing Post-Irradiation Xerostomia in Head and Neck Cancer Patients: A Retrospective Study. Biomedicines. 2024;12(5):1033.
[23] SONG W, LIU H, SU Y, et al. Current developments and opportunities of pluripotent stem cells-based therapies for salivary gland hypofunction. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024;12:1346996.
[24] GEERTSEMA S, BOURGONJE AR, FAGUNDES RR, et al. The NRF2/Keap1 pathway as a therapeutic target in inflammatory bowel disease. Trends Mol Med. 2023;29(10):830-842.
[25] JOMOVA K, RAPTOVA R, ALOMAR SY, et al. Reactive oxygen species, toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: chronic diseases and aging. Arch Toxicol. 2023;97(10):2499-2574.
[26] HU R, WU F, ZHENG YQ. Ivacaftor attenuates gentamicin-induced ototoxicity through the CFTR-Nrf2-HO1/NQO1 pathway. Redox Rep. 2024;29(1):2332038.
[27] PANATI K, THIMMANA LV, NARALA VR. Electrophilic nitrated fatty acids are potential therapeutic candidates for inflammatory and fibrotic lung diseases. Nitric Oxide. 2020;102:28-38.
[28] WILKINSON ML, ABRAMOVA E, GUO C, et al. Fatty acid nitroalkenes inhibit the inflammatory response to bleomycin-mediated lung injury. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020;407:115236.
[29] ZHANG Q, LIU J, DUAN H, et al. Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling: An important molecular mechanism of herbal medicine in the treatment of atherosclerosis via the protection of vascular endothelial cells from oxidative stress. J Adv Res. 2021;34:43-63.
[30] CHEN Y, SHEN J, ZHANG X, et al. Protective effects of ferulic acid against ionizing radiation-induced oxidative damage in rat lens through activating Nrf2 signal pathway. Int J Ophthalmol. 2023;16(5):687-693.
[31] CHANG F, GUNDERSTOFTE C, COLUSSI N, et al. Development of nitroalkene-based inhibitors to target STING-dependent inflammation. Redox Biol. 2024;74:103202.
[32] FENG X, WU Z, XU J, et al. Dietary nitrate supplementation prevents radiotherapy-induced xerostomia. Elife. 2021;10:e70710.
[33] PAZ C, GLASSEY A, FRICK A, et al. Cancer therapy-related salivary dysfunction. J Clin Invest. 2024;134(17):e182661.
[34] YAO QT, WU YH, LIU SH, et al. Pilocarpine improves submandibular gland dysfunction in irradiated rats by downregulating the tight junction protein claudin-4. Oral Dis. 2022;28(6):1528-1538.
[35] WANG Z, CHEN Z, JIANG Z, et al. Cordycepin prevents radiation ulcer by inhibiting cell senescence via NRF2 and AMPK in rodents. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):2538.
[36] ZHU X, TIAN X, YANG M, et al. Procyanidin B2 Promotes Intestinal Injury Repair and Attenuates Colitis-Associated Tumorigenesis via Suppression of Oxidative Stress in Mice. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2021;35(2):75-92.
[37] WANG C, DAI S, ZHAO X, et al. Celastrol as an emerging anticancer agent: Current status, challenges and therapeutic strategies. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;163:114882.
[38] SLEZAK J, KURA B, LEBARON TW, et al. Oxidative Stress and Pathways of Molecular Hydrogen Effects in Medicine. Curr Pharm Des. 2021; 27(5):610-625.
[39] EASSAWY MMT, SALEM AA, ISMAIL AFM. Biochemical study on the protective effect of curcumin on acetaminophen and gamma-irradiation induced hepatic toxicity in rats. Environ Toxicol. 2020. doi: 10.1002/tox.23077.
[40] ZHANG Y, ZHU XB, ZHAO JC, et al. Neuroprotective effect of resveratrol against radiation after surgically induced brain injury by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis through NRf2/HO-1/NF-κB signaling pathway. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2020;34(12):e22600.
|