Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (17): 3521-3528.doi: 10.12307/2025.665
Mechanism by which programmed cell death protein 1 influences osteoblast differentiation under high-glucose conditions
Zhang Wanli1, Bai Tao2, Han Nianrong2, Akram·Osman2, Liu Yanlu2, Huang Yifei2, Hu Wei2
- 1Second Department of Orthopedics, Friendship Hospital of Yili Kazak Autonomous Prefecture, Yining 835000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Second Department of Spine, Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-05-28Accepted:2024-08-05Online:2025-06-18Published:2024-10-30 -
Contact:Hu Wei, Chief physician, Second Department of Spine, Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Zhang Wanli, Associate chief physician, Second Department of Orthopedics, Friendship Hospital of Yili Kazak Autonomous Prefecture, Yining 835000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region - Excellent Youth Science Foundation Program, No. 2022D01E29 (to HW)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Wanli, Bai Tao, Han Nianrong, Akram·Osman, Liu Yanlu, Huang Yifei, Hu Wei. Mechanism by which programmed cell death protein 1 influences osteoblast differentiation under high-glucose conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(17): 3521-3528.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
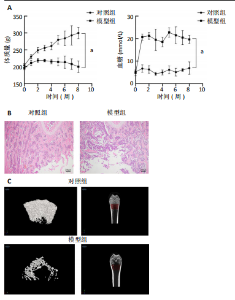
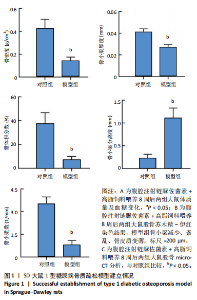
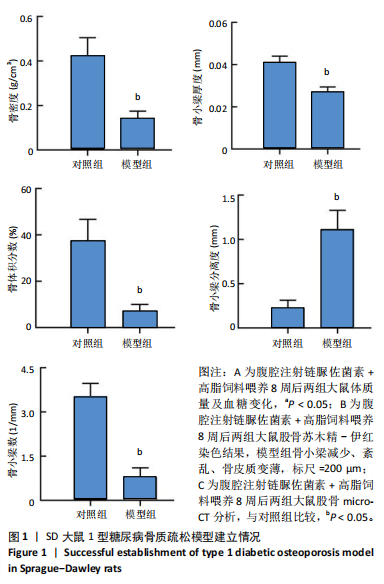
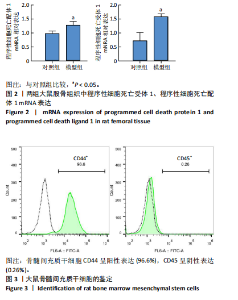
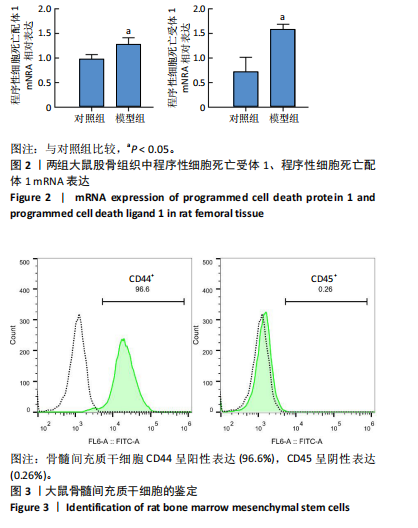
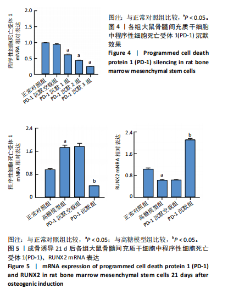
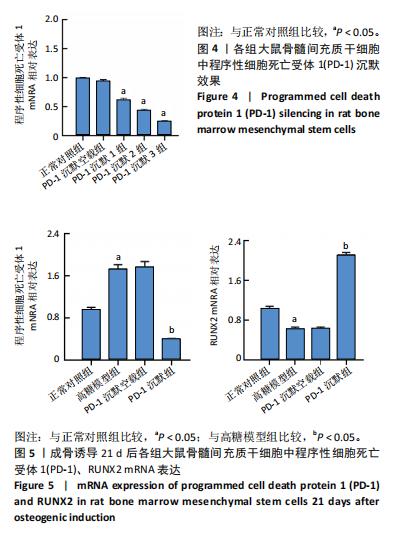
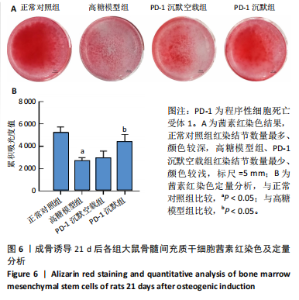
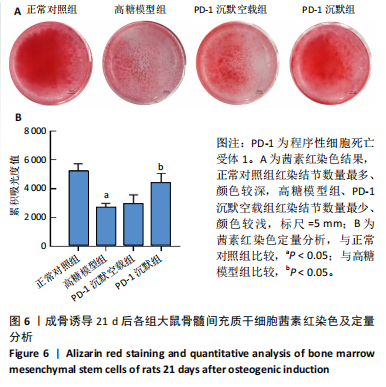
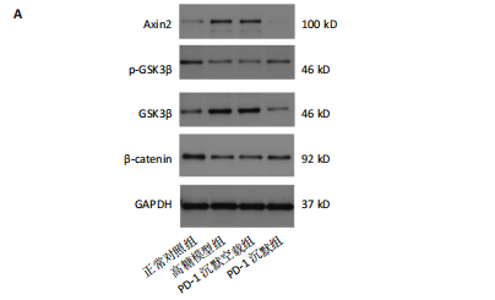
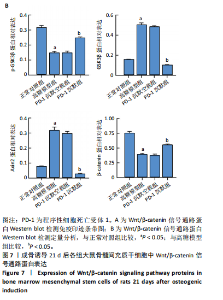
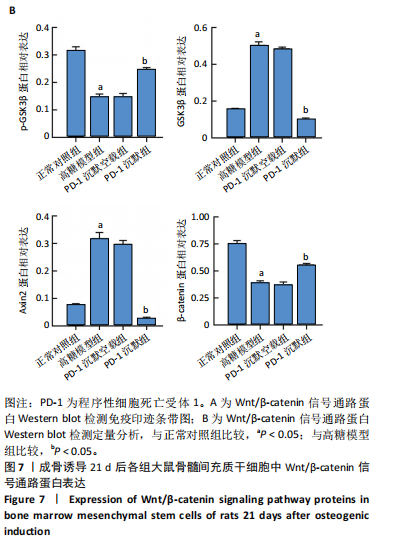
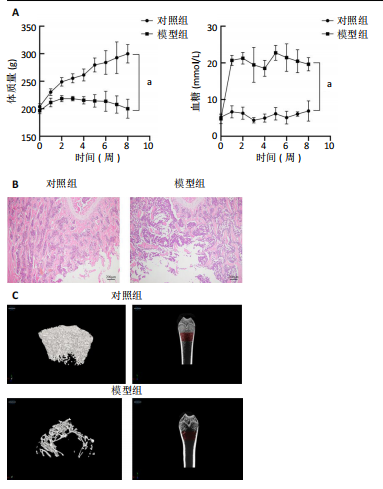
2.1 动物实验结果 2.1.1 实验动物数量分析 12只SD大鼠全部进入结果分析。 2.1.2 1型糖尿病骨质疏松动物模型建立情况 腹腔注射链脲佐菌素72,96,120 h后,对照组大鼠空腹血糖浓度 < 9 mmol/L,模型组大鼠空腹血糖浓度均> 16.7 mmol/L,说明造模组大鼠建立1型糖尿病模型成功。高脂饲料喂养期间,各组大鼠体质量与血糖变化,见图1A,显示模型组大鼠体质量始终低于对照组,血糖浓度均高于对照组。 高脂饲料喂养8周后,股骨组织苏木精-伊红染色结果显示,相较于对照组,模型组骨小梁减少、紊乱、骨皮质变薄,见图1B。micro-CT检测结果显示,模型组大鼠股骨远端骨小梁的骨量减少,松质骨断裂,股骨密度、骨体积分数、骨小梁数及骨小梁厚度均低于对照组(P < 0.05),骨小梁分离度高于对照组(P < 0.05),见图1C。以上结果表明,实验成功建立了1型糖尿病骨质疏松大鼠模型。 2.1.3 两组大鼠股骨组织中程序性细胞死亡受体1、程序性细胞死亡配体1 mNRA表达 qRT-PCR检测结果显示,模型组大鼠股骨组织中程序性细胞死亡受体1、程序性细胞死亡配体1 mNRA表达均高于对照组(P < 0.05),见图2。 2.2 细胞实验结果 2.2.1 大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞鉴定 流式细胞术分析结果显示,骨髓间充质干细胞CD44呈阳性表达(96.6%),CD45呈阴性表达(0.26%),见图3。表明骨髓间充质干细胞纯度高。 2.2.2 程序性细胞死亡受体1沉默siRNA筛选 qRT-PCR检测结果显示,正常对照组与PD-1沉默空载组大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞中程序性细胞死亡受体1 mRNA表达比较无明显差异(P > 0.05),说明空载体siRNA-NC对程序性细胞死亡受体1 mRNA表达无影响;与正常对照组比较,3个程序性细胞死亡受体1 siRNA组大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞中程序性细胞死亡受体1 mRNA表达均降低(P < 0.05),其中以程序性细胞死亡受体1 siRNA3沉默效果最好,见图4。所以,最终实验选择此组siRNA进行细胞转染。 2.2.3 各组大鼠骨髓间充干细胞中程序性细胞死亡受体1、RUNX2 mRNA表达 成骨诱导21 d后qRT-PCR检测结果显示,高糖模型组、PD-1沉默空载组程序性细胞死亡受体1 mRNA表达高于正常对照组、PD-1沉默组(P < 0.05),RUNX2 mRNA表达低于正常对照组、PD-1沉默组(P < 0.05);高糖模型组与PD-1沉默空载组程序性细胞死亡受体1、RUNX2 mRNA表达无明显差异(P > 0.05),见图5。 2.2.4 茜素红染色结果 成骨诱导21 d后茜素红染色结果显示,正常对照组大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞矿化结节形成能力最强,高糖模型组、PD-1沉默空载组大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞矿化结节形成能力较弱,PD-1沉默组大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞矿化结节形成能力居中,见图6。 2.2.5 各组大鼠骨髓间充干细胞中Wnt/β-catenin信号通路蛋白表达 Western blot检测结果显示,与正常对照组比较,高糖模型组、PD-1沉默空载组GSK3β、Axin2蛋白表达均升高(P < 0.05),p-GSK3β、β-catenin蛋白表达均降低(P < 0.05);与高糖模型组、PD-1沉默空载组比较,PD-1沉默组程GSK3β、Axin2蛋白表达均降低(P < 0.05),p-GSK3β、β-catenin蛋白表达均升高(P < 0.05),见图7。"
| [1] 谷营营,侯甜,秦雅芝,等.特立帕肽通过 Wnt3a/β-catenin 通路对高糖环境下成骨细胞分化的影响[J].安徽医科大学学报,2022, 57(11):1750-1755. [2] KALRA S, JOSHI A, KAPOOR N. Osteoporosis and diabetes: The dual pandemics. J Pak Med Assoc. 2022;72(8):1663-1664. [3] 苏婧,潘韦韦,崔镇海,等.糖尿病性骨质疏松中西医发病机制及治疗的研究进展[J].吉林中医药,2023,43(5):612-617. [4] 刘中胜,杨建虹.未羧化骨钙素对高糖条件下小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨与成脂分化的调控效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020, 24(13):2039-2046. [5] BRUNETTI G, D’AMATO G, DE SANTIS S, et al. Mechanisms of altered bone remodeling in children with type 1 diabetes. World J Diabetes. 2021;12(7):997-1009. [6] AGARWAL A, LESLIE WD. Fracture prediction tools in diabetes. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2022;29(4):326-332. [7] 焦颖华,郭倩,包凯然,等.仙灵骨葆胶囊对糖尿病骨质疏松大鼠 β-catenin、Runx2、LRP5 的影响[J].中药新药与临床药理,2023, 34(2):156-162. [8] 崔寅鹏,郭艾,马立峰,等.哇巴因体外诱导人骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(24):3796-3801. [9] MANTRIPRAGADA VP, KAPLEVATSKY R, BOVA WA, et al. Influence of Glucose Concentration on Colony-Forming Efficiency and Biological Performance of Primary Human Tissue-Derived Progenitor Cells. Cartilage. 2021;13(2_suppl):95S-106S. [10] 常俊杰,解强,刘亦冰,等.高糖对骨髓间充质干细胞作用机制的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(10):1551-1555. [11] CAI F, LIU Y, LIU K, et al. Diabetes mellitus impairs bone regeneration and biomechanics. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):169. [12] KAWADA-HORITANI E, KITA S, OKITA T, et al. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells prevent type 1 diabetes induced by immune checkpoint blockade. Diabetologia. 2022;65(7):1185-1197. [13] GAO M, SHI J, XIAO X, et al. PD-1 regulation in immune homeostasis and immunotherapy. Cancer Lett. 2024;588:216726. [14] LIN Z, XIONG Y, MENG W, et al. Exosomal PD-L1 induces osteogenic differentiation and promotes fracture healing by acting as an immunosuppressant. Bioact Mater. 2021;13:300-311. [15] GREISEN SR, KRAGSTRUP TW, THOMSEN JS, et al. The Programmed Death-1 Pathway Counter-Regulates Inflammation-Induced Osteoclast Activity in Clinical and Experimental Settings. Front Immunol. 2022; 13:773946. [16] LEE SC, SHIN MK, JANG BY, et al. Immunomodulatory Effect and Bone Homeostasis Regulation in Osteoblasts Differentiated from hADMSCs via the PD-1/PD-L1 Axis. Cells. 2022;11(19):3152. [17] SUN Y, ZHU Y, LIU X, et al. Morroniside attenuates high glucose-induced BMSC dysfunction by regulating the Glo1/AGE/RAGE axis. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(8):e12866. [18] DAAMOUCH S, EMINI L, RAUNER M, et al. MicroRNA and Diabetic Bone Disease. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2022;20(3):194-201. [19] TOMASIUK JM, NOWAKOWSKA-PŁAZA A, WISŁOWSKA M, et al. Osteoporosis and diabetes-possible links and diagnostic difficulties. Reumatologia. 2023;61(4):294-304. [20] FAN D, LU J, YU N, et al. Curcumin Prevents Diabetic Osteoporosis through Promoting Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis Coupling via NF-kappaB Signaling. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022; 2022:4974343. [21] XU C, WANG Z, LIU YJ, et al. Harnessing GMNP-loaded BMSC-derived EVs to target miR-3064-5p via MEG3 overexpression: Implications for diabetic osteoporosis therapy in rats. Cell Signal. 2024;118:111055. [22] LUO M, ZHAO Z, YI J. Osteogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell in hyperglycemia. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1150068. [23] YANG N, LIU Y. The Role of the Immune Microenvironment in Bone Regeneration. Int J Med Sci. 2021;18(16):3697-3707. [24] DING P, GAO C, GAO Y, et al. Osteocytes regulate senescence of bone and bone marrow. Elife. 2022;11:e81480. [25] ZHOU M, GRAVES DT. Impact of the host response and osteoblast lineage cells on periodontal disease. Front Immunol. 2022;13:998244. [26] DING JT, YANG KP, LIN KL, et al. Mechanisms and therapeutic strategies of immune checkpoint molecules and regulators in type 1 diabetes. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;13:1090842. [27] LI N, LI Z, FU L, et al. PD-1 Suppresses the Osteogenic and Odontogenic Differentiation of Stem Cells from Dental Apical Papilla via Targeting SHP2/NF-kappaB Axis. Stem Cells. 2022;40(8):763-777. [28] MA L, GONG F, XU J, et al. Uncarboxylated osteocalcin reverses the high glucose-induced inhibition of the osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3E1 cells via the GPRC6A/cAMP/PKA/AMPK signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2021;47(5):91. [29] ZHANG Y, YANG JH. Activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway by oxidative stress mediates high glucose-induced increase of adipogenic differentiation in primary rat osteoblasts. J Cell Biochem. 2013; 114(11):2595-2602. [30] 饶艳玲,黄威.青娥丸调控Wnt1/β-catenin信号通路治疗糖尿病性骨质疏松症[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2023,29(8):1167-1171,1181. [31] YAN Z, RUAN B, WANG S, et al. RNA-binding Protein QKI Inhibits Osteogenic Differentiation Via Suppressing Wnt Pathway. Arch Med Res. 2023;54(5):102853. [32] ZHAO SJ, KONG FQ, JIE J, et al. Macrophage MSR1 promotes BMSC osteogenic differentiation and M2-like polarization by activating PI3K/AKT/GSK3beta/beta -catenin pathway. Theranostics. 2020;10(1):17-35. [33] ZHANG YL, AN Y, SUN LJ, et al. NADPH-dependent ROS accumulation contributes to the impaired osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells under high glucose conditions. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1152845. [34] BAO K, JIAO Y, XING L, et al. The role of wnt signaling in diabetes-induced osteoporosis. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2023;15(1):84. [35] ZHANG C, BAO LR, YANG YT, et al. Role of M2 Macrophage Exosomes in Osteogenic Differentiation of Mouse Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells under High-Glucose and High-Insulin. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022;53(1):63-70. [36] DIENELT A, KELLER KC, ZUR NIEDEN NI. High glucose impairs osteogenic differentiation of embryonic stem cells via early diversion of beta-catenin from Forkhead box O to T cell factor interaction. Birth Defects Res. 2022;114(16):1056-1074. [37] MASSON SWC, DISSANAYAKE WC, BROOME SC, et al. A role for beta-catenin in diet-induced skeletal muscle insulin resistance. Physiol Rep. 2023;11(4):e15536. [38] CHEN Y, CHEN L, HUANG R, et al. Investigation for GSK3beta expression in diabetic osteoporosis and negative osteogenic effects of GSK3beta on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under a high glucose microenvironment. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021;534:727-733. [39] LI Z, ZHAO H, CHU S, et al. miR-124-3p promotes BMSC osteogenesis via suppressing the GSK-3beta/beta-catenin signaling pathway in diabetic osteoporosis rats. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2020;56(9):723-734. [40] 罗诒财,钟晓霞,李昊.罗汉果苷V通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路对糖尿病状态成骨细胞增殖与分化的影响[J].中国医院药学杂志, 2022,42(8):781-785. |
| [1] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [2] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [3] | Zhao Jiacheng, Ren Shiqi, Zhu Qin, Liu Jiajia, Zhu Xiang, Yang Yang. Bioinformatics analysis of potential biomarkers for primary osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1741-1750. |
| [4] | Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei . Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| [5] | Aikepaer · Aierken, Chen Xiaotao, Wufanbieke · Baheti. Osteogenesis-induced exosomes derived from human periodontal ligament stem cells promote osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells in an inflammatory microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [6] | Zhang Zhenyu, Liang Qiujian, Yang Jun, Wei Xiangyu, Jiang Jie, Huang Linke, Tan Zhen. Target of neohesperidin in treatment of osteoporosis and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [7] | Sun Yuting, Wu Jiayuan, Zhang Jian. Physical factors and action mechanisms affecting osteogenic/odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1531-1540. |
| [8] | Li Yueyao, Zhang Min, Yang Jiaju. Cistanoside A mediates p38/MAPK pathway to inhibit osteoclast activity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1144-1151. |
| [9] | Zheng Lin, Jin Wenjun, Luo Shanshan, Huang Rui, Wang Jie, Cheng Yuting, An Zheqing, Xiong Yue, Gong Zipeng, Liao Jian. Eucommia ulmoides promotes alveolar bone formation in ovariectomized rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1159-1167. |
| [10] |
Huang Xiaobin, Ge Jirong, Li Shengqiang, Xie Lihua, Huang Jingwen, He Yanyan, Xue Lipeng.
Mechanisms of different yin nourishing and kidney tonifying methods on osteoclastysis pathway in ovariectomized rats #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1214-1219.
|
| [11] | Qian Kun, Li Ziqing, Sun Shui . Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the occurrence and development of common degenerative bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1285-1295. |
| [12] | Wang Dongyang, Yang Qiaohui, Lin Xinchao. Relationship between vitamin D levels and reproductive characteristics and exercise dietary situation in postmenopausal women [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1021-1025. |
| [13] | Lan Shuangli, Xiang Feifan, Deng Guanghui, Xiao Yukun, Yang Yunkang, Liang Jie. Naringin inhibits iron deposition and cell apoptosis in bone tissue of osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 888-898. |
| [14] | Zhang Lichuang, Yang Wen, Ding Guangjiang, Li Peikun, Xiao Zhongyu, Chen Ying, Fang Xue, Zhang Teng. Dispersion effect of bone cement after vertebroplasty using individualized unilateral external pedicle approach and bilateral pedicle approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 800-808. |
| [15] | Ge Xiao, Zhao Zhuangzhuang, Guo Shuyu, Xu Rongyao. HOXA10 gene-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7701-7708. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||