Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (11): 2252-2260.doi: 10.12307/2025.363
Previous Articles Next Articles
Repetitive trans-spinal magnetic stimulation promotes motor function recovery in mice after spinal cord injury
Song Haiwang1, Jiang Guanhua1, Mu Yingying2, Fu Shanyu2, Sun Baofei1, Li Yumei1, Yu Zijiang1, Yang Dan1
- 1Human Anatomy Teaching and Research Laboratory, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Guizhou Medical University, Guian New District 561113, Guizhou Province, China; 2School of Basic Medical Sciences, Guizhou Medical University, Guian New District 561113, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2024-03-27Accepted:2024-05-09Online:2025-04-18Published:2024-08-10 -
Contact:Yang Dan, MD, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Human Anatomy Teaching and Research Laboratory, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Guizhou Medical University, Guian New District 561113, Guizhou Province, China Co-corresponding author: Yu Zijiang, MD, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Human Anatomy Teaching and Research Laboratory, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Guizhou Medical University, Guian New District 561113, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Song Haiwang, Master candidate, Human Anatomy Teaching and Research Laboratory, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Guizhou Medical University, Guian New District 561113, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Planning Foundation of Guizhou Province, Nos. QKH-ZK-[2024]-General 120 and QKH-ZK-[2021]-General 472 (to YD); the Technology Personnel Training Foundation of Guizhou Provincial Education Department, No. QKH-KY-[2022]-226 (to YD); the PhD Research Start-Up Foundation of Guizhou Medical University, No. XBH-J-[2020]-009 (to YD); the Guizhou Provincial Health Commission’ s Scientific and Technological Fund Project, No. gzwkj-2021-509 (to YZJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Song Haiwang, Jiang Guanhua, Mu Yingying, Fu Shanyu, Sun Baofei, Li Yumei, Yu Zijiang, Yang Dan. Repetitive trans-spinal magnetic stimulation promotes motor function recovery in mice after spinal cord injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(11): 2252-2260.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
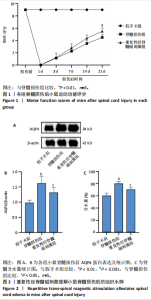
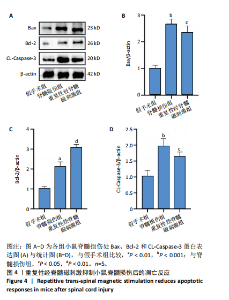
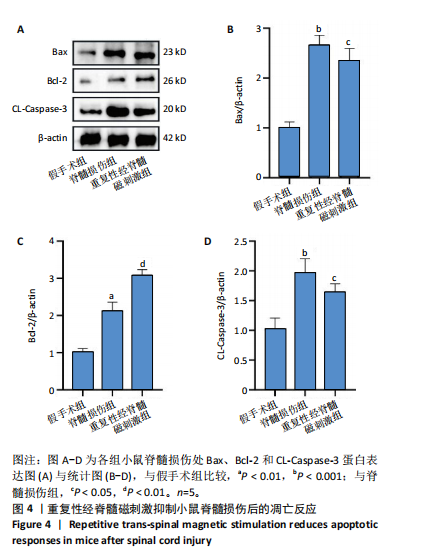
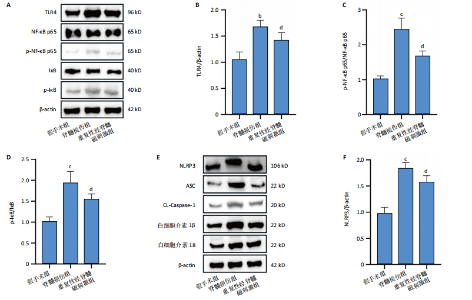
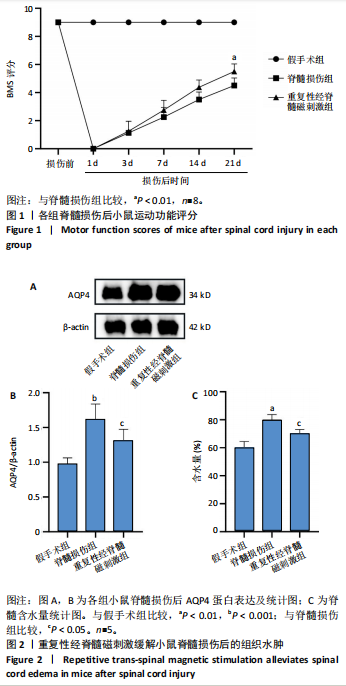
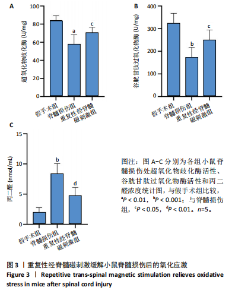
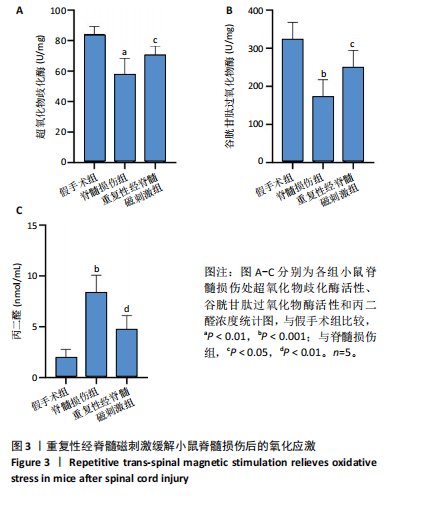
2.1 实验动物数量分析及一般情况 120只雄性C57BL/6J小鼠随机分3组,在脊髓损伤模型建造过程中,死亡7只,因损伤后双下肢BMS评分> 0分而脱失5只。最后每组仅随机选取了32只小鼠,共计96只小鼠完成后续实验。脊髓夹伤后小鼠立即出现后肢抽动,苏醒后双下肢运动功能丧失,术后的前2 d天出现血尿,之后尿液正常,无感染。 2.2 重复性经脊髓磁刺激能够促进脊髓损伤小鼠运动功能的恢复 假手术组BMS评分均为满分,与脊髓损伤组相比,重复性经脊髓磁刺激组所获评分高于脊髓损伤组(P < 0.05),见图1。 2.3 重复性经脊髓磁刺激缓解脊髓水肿 与假手术组相比,脊髓损伤组的脊髓组织含水量和AQP4蛋白表达均升高(P < 0.05)。 重复性经脊髓磁刺激组脊髓组织含水量和AQP4蛋白表达均低于脊髓损伤组(P < 0.05),见图2。 2.4 重复性经脊髓磁刺激抑制脊髓损伤后的氧化应激 与假手术组相比,脊髓损伤组超氧化物歧化酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶活性均降低,丙二醛浓度升高(P < 0.05)。重复性经脊髓磁刺激组超氧化物歧化酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶活性均高于脊髓损伤组,丙二醛浓度低于脊髓损伤组(P < 0.05),见图3。 2.5 重复性经脊髓磁刺激能够抑制脊髓损后的凋亡反应 与脊髓损伤组相比,经过重复性经脊髓磁刺激干预后,重复性经脊髓磁刺激组的Bax、CL-Caspase-3蛋白表达低于脊髓损伤组(P < 0.05),而Bcl-2的蛋白表达水平高于脊髓损伤组(P < 0.05),见图4。"
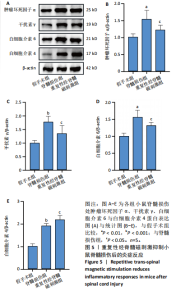
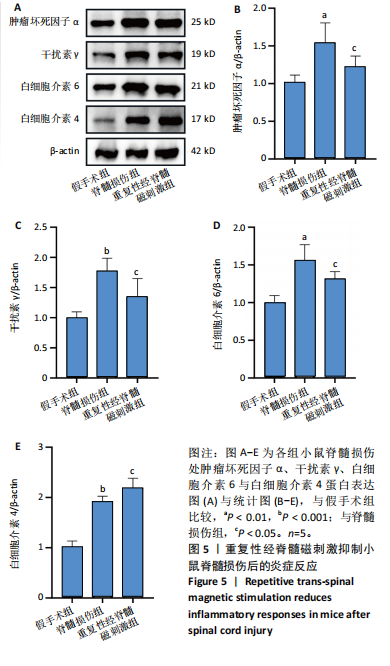
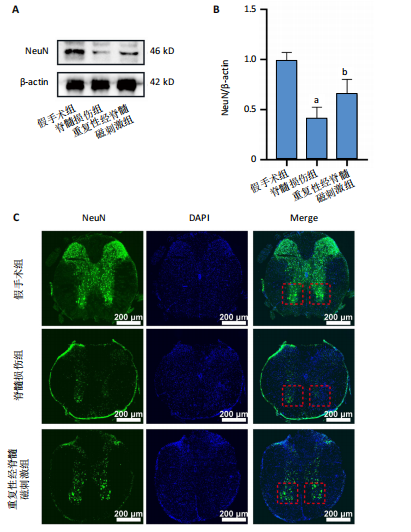
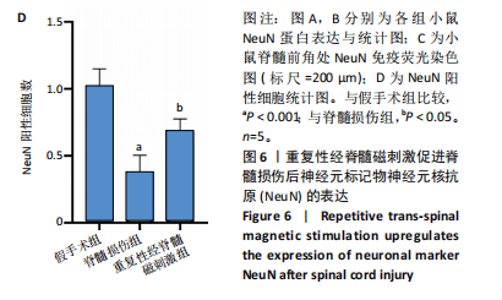
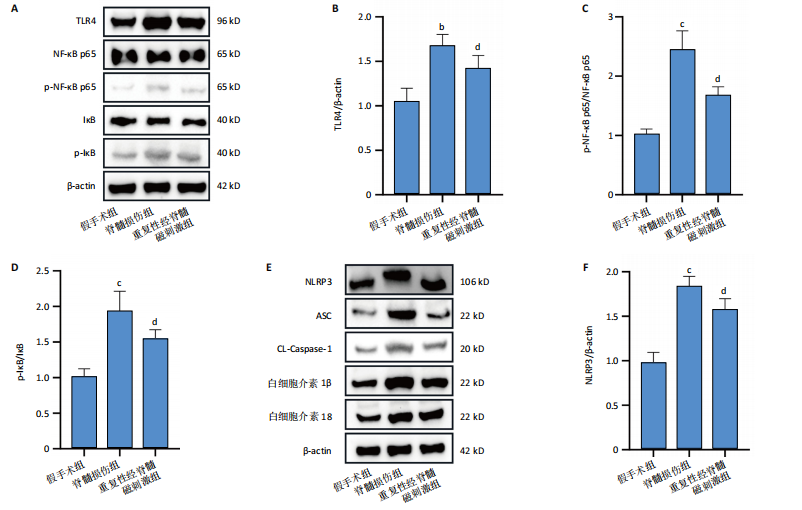
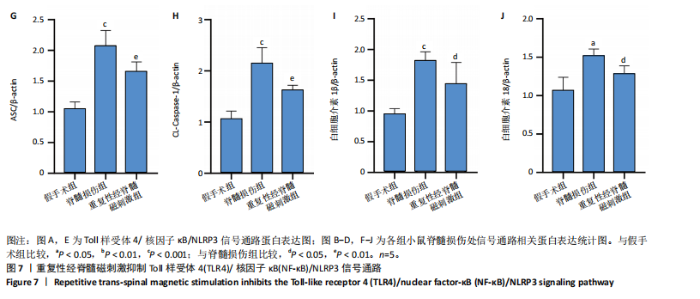
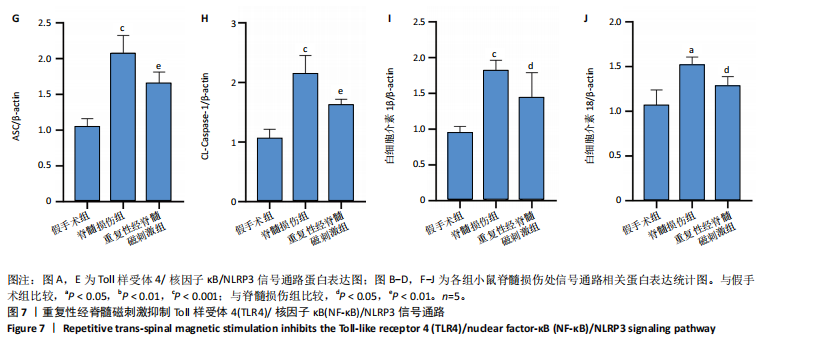
2.6 重复性经脊髓磁刺激能够抑制脊髓损伤后的炎症反应 与脊髓损伤组相比,重复性经脊髓磁刺激组肿瘤坏死因子α、干扰素γ与白细胞介素6蛋白表达均低于脊髓损伤组(P < 0.05),白细胞介素4蛋白表达高于脊髓损伤组(P < 0.05),见图5。 2.7 重复性经脊髓磁刺激促进脊髓损伤后的神经保护作用 在损伤后21 d,Western Blot显示,与假手术组相比,脊髓损伤后神经元核抗原蛋白水平表达降低(P < 0.05),重复性经脊髓磁刺激组神经元核抗原的表达高于脊髓损伤组(P < 0.05)。免疫荧光染色显示假手术组脊髓前角处神经元核抗原的数量最多(P < 0.05),重复性经脊髓磁刺激组神经元核抗原的数量高于脊髓损伤组(P < 0.05),见图6。"
| [1] ANJUM A, YAZID MD, FAUZI DAUD M, et al. Spinal Cord Injury: Pathophysiology, Multimolecular Interactions, and Underlying Recovery Mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7533. [2] XIA H, WANG D, GUO X, et al. Catalpol Protects Against Spinal Cord Injury in Mice Through Regulating MicroRNA-142-Mediated HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:630222. [3] SHEN H, XU B, YANG C, et al. A DAMP-scavenging, IL-10-releasing hydrogel promotes neural regeneration and motor function recovery after spinal cord injury. Biomaterials. 2022;280:121279. [4] SIEBNER HR, FUNKE K, ABERRA AS, et al. Transcranial magnetic stimulation of the brain: What is stimulated? - A consensus and critical position paper. Clin Neurophysiol. 2022;140:59-97. [5] ROBAC A, NEVEU P, HUGEDE A, et al. Repetitive Trans Spinal Magnetic Stimulation Improves Functional Recovery and Tissue Repair in Contusive and Penetrating Spinal Cord Injury Models in Rats. Biomedicines. 2021;9(12):1827-1843. [6] CHALFOUH C, GUILLOU C, HARDOUIN J, et al. The Regenerative Effect of Trans-spinal Magnetic Stimulation After Spinal Cord Injury: Mechanisms and Pathways Underlying the Effect. Neurotherapeutics. 2020;17(4):2069-2088. [7] LUO J, FENG Y, HONG Z, et al. High-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation promotes neural stem cell proliferation after ischemic stroke. Neural Regen Res. 2024;19(8):1772-1780. [8] ADEEL M, LIN BS, CHEN H C, et al. Motor Neuroplastic Effects of a Novel Paired Stimulation Technology in an Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury Animal Model. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(16):9447. [9] LI H, MA J, ZHANG J, et al. Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS) Modulates Thyroid Hormones Level and Cognition in the Recovery Stage of Stroke Patients with Cognitive Dysfunction. Med Sci Monit. 2021;27:e931914. [10] PAN J, LI H, WANG Y, et al. Effects of low-frequency rTMS combined with antidepressants on depression in patients with post-stroke depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Neurol. 2023; 14:1168333. [11] YAO L, CAI H, FANG Q, et al. Piceatannol alleviates liver ischaemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 in hepatic macrophages. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023;960:176149. [12] CAI Q, ZHAO C, XU Y, et al. Qingda granule alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling in microglia. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024;324:117712. [13] LI Y, LIANG W, GUO C, et al. Renshen Shouwu extract enhances neurogenesis and angiogenesis via inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway following ischemic stroke in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;253:112616. [14] 文峰, 周磊, 李扬, 等. 通腑逐瘀法指导下抵当汤加减可抑制大鼠急性脊髓损伤后胶质瘢痕的形成[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023, 27(20):3180-3187. [15] LIU Z, YAO X, JIANG W, et al. Advanced oxidation protein products induce microglia-mediated neuroinflammation via MAPKs-NF-κB signaling pathway and pyroptosis after secondary spinal cord injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):90-110. [16] FAN L, LIU C, CHEN X, et al. Exosomes-Loaded Electroconductive Hydrogel Synergistically Promotes Tissue Repair after Spinal Cord Injury via Immunoregulation and Enhancement of Myelinated Axon Growth. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(13):e2105586. [17] JIN Z, TIAN L, ZHANG Y, et al. Apigenin inhibits fibrous scar formation after acute spinal cord injury through TGFβ/SMADs signaling pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022;28(11):1883-1894. [18] WANG R, BAI J. Pharmacological interventions targeting the microcirculation following traumatic spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2024;19(1):35-42. [19] MITSUI T, ARII Y, TANIGUCHI K, et al. Efficacy of Repetitive Trans-spinal Magnetic Stimulation for Patients with Parkinson’s Disease: a Randomised Controlled Trial. Neurotherapeutics. 2022;19(4):1273-1282. [20] YIN M, LIU Y, ZHANG L, et al. Effects of rTMS Treatment on Cognitive Impairment and Resting-State Brain Activity in Stroke Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Front Neural Circuits.2020;14: 563777. [21] BAO Z, BAO L, HAN N, et al. rTMS alleviates AD-induced cognitive impairment by inhibitng apoptosis in SAMP8 mouse. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(24):26034-26045. [22] KHEDR LH, RAHMO RM, ELDEMERDASH OM, et al. Implication of M2 macrophage on NLRP3 inflammasome signaling in mediating the neuroprotective effect of Canagliflozin against methotrexate-induced cognitive impairment. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024;130:111709. [23] DAI Y, WANG S, CHANG S, et al. M2 macrophage-derived exosomes carry microRNA-148a to alleviate myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via inhibiting TXNIP and the TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2020;142:65-79. [24] TONG L, ZHANG X, HAO H, et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Derived Extracellular Vesicles Modulate Gut Microbiota and Attenuate Inflammatory in DSS-Induced Colitis Mice. Nutrients. 2021;13(10): 3319. [25] KITCHEN P, SALMAN MM, HALSEY AM, et al. Targeting Aquaporin-4 Subcellular Localization to Treat Central Nervous System Edema. Cell. 2020;181(4):784-799.e719. [26] LIU S, MAO J, WANG T, et al. Downregulation of Aquaporin-4 Protects Brain Against Hypoxia Ischemia via Anti-inflammatory Mechanism. Mol Neurobiol. 2017;54(8):6426-6435. [27] HELLENBRAND DJ, QUINN CM, PIPER ZJ, et al. Inflammation after spinal cord injury: a review of the critical timeline of signaling cues and cellular infiltration. J Neuroinflammation. 2021;18(1):284-299. [28] LIU J, ZHANG N, ZHANG M, et al. N-acetylserotonin alleviated the expression of interleukin-1β in retinal ischemia-reperfusion rats via the TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway. Exp Eye Res. 2021;208:108595. [29] LONG JX, TIAN MZ, CHEN XY, et al. The role of NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis in ischemic stroke and the intervention of traditional Chinese medicine. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1151196. [30] YAO J, LI Y, JIN Y, et al. Synergistic cardioptotection by tilianin and syringin in diabetic cardiomyopathy involves interaction of TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 and PGC1a/SIRT3 pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;96: 107728. [31] ZHOU Y, ZHANG H, ZHENG B, et al. Retinoic Acid Induced-Autophagic Flux Inhibits ER-Stress Dependent Apoptosis and Prevents Disruption of Blood-Spinal Cord Barrier after Spinal Cord Injury. Int J Biol Sci. 2016; 12(1):87-99. [32] LUO Y, CHENG J, FU Y, et al. D-allose Inhibits TLR4/PI3K/AKT Signaling to Attenuate Neuroinflammation and Neuronal Apoptosis by Inhibiting Gal-3 Following Ischemic Stroke. Biol Proced Online. 2023;25(1):30. [33] 成建平, 李华, 李雄杰. 胡椒叶提取物干预可减轻急性脊髓损伤模型大鼠的氧化应激及炎症反应 [J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019,23(31): 5010-5016. [34] FU K, XU W, LENAHAN C, et al. Autophagy regulates inflammation in intracerebral hemorrhage: Enemy or friend? . Front Cell Neurosci. 2022;16:1036313. [35] LONG JX, TIAN MZ, CHEN XY, et al. The role of NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis in ischemic stroke and the intervention of traditional Chinese medicine. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1151196. [36] JIN X, LIU M Y, ZHANG D F, et al. Baicalin mitigates cognitive impairment and protects neurons from microglia-mediated neuroinflammation via suppressing NLRP3 inflammasomes and TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019;25(5):575-590. [37] ZOU X, YANG XJ, GAN YM, et al. Neuroprotective Effect of Phthalide Derivative CD21 against Ischemic Brain Injury: Involvement of MSR1 Mediated DAMP peroxiredoxin1 Clearance and TLR4 Signaling Inhibition. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2021;16(2):306-317. [38] LUO L, LIU M, FAN Y, et al. Intermittent theta-burst stimulation improves motor function by inhibiting neuronal pyroptosis and regulating microglial polarization via TLR4/NFκB/NLRP3 signaling pathway in cerebral ischemic mice. J Neuroinflammation. 2022;19(1):141-167. |
| [1] | Yu Shuai, Liu Jiawei, Zhu Bin, Pan Tan, Li Xinglong, Sun Guangfeng, Yu Haiyang, Ding Ya, Wang Hongliang. Hot issues and application prospects of small molecule drugs in treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [2] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [3] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [4] | Li Kaiying, Wei Xiaoge, Song Fei, Yang Nan, Zhao Zhenning, Wang Yan, Mu Jing, Ma Huisheng. Mechanism of Lijin manipulation regulating scar formation in skeletal muscle injury repair in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1600-1608. |
| [5] | Jin Kai, Tang Ting, Li Meile, Xie Yuan. Effects of conditioned medium and exosomes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [6] | Wan Lingling, Wu Mengying, Zhang Yujiao, Luo Qingqing. Inflammatory factor interferon-gamma affects migration and apoptosis of human vascular smooth muscle cells through pyroptosis pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1422-1428. |
| [7] | Zhao Ruihua, Chen Sixian, Guo Yang, Shi Lei, Wu Chengjie, Wu Mao, Yang Guanglu, Zhang Haoheng, Ma Yong. Wen-Shen-Tong-Du Decoction promoting spinal cord injury repair in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1118-1126. |
| [8] | Liu Zhezhe, Yu Meiqing, Wang Tingting, Zhang Min, Li Baiyan. Troxerutin modulates nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway to inhibit brain injury and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral infarction rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1137-1143. |
| [9] | He Guanghui, Yuan Jie, Ke Yanqin, Qiu Xiaoting, Zhang Xiaoling. Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [10] | He Bo, Chen Wen, Ma Suilu, He Zhijun, Song Yuan, Li Jinpeng, Liu Tao, Wei Xiaotao, Wang Weiwei, Xie Jing . Pathogenesis and treatment progress of flap ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1230-1238. |
| [11] | Wang Yuru, Li Siyuan, Xu Ye, Zhang Yumeng, Liu Yang, Hao Huiqin. Effects of wogonin on joint inflammation in collagen-induced arthritis rats via the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1026-1035. |
| [12] | Xu Fei, Yan Jinqiang, Chai Shoudong. Mechanical stress regulates apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1064-1072. |
| [13] | Lan Shuangli, Xiang Feifan, Deng Guanghui, Xiao Yukun, Yang Yunkang, Liang Jie. Naringin inhibits iron deposition and cell apoptosis in bone tissue of osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 888-898. |
| [14] | Bai Jing, Zhang Xue, Ren Yan, Li Yuehui, Tian Xiaoyu. Effect of lncRNA-TNFRSF13C on hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in periodontal cells by modulation of #br# miR-1246 #br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 928-935. |
| [15] | Zhi Fang, Zhu Manhua, Xiong Wei, Lin Xingzhen. Analgesic effect of acupuncture in a rat model of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 936-941. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||