[1] ALAN EF, KURRE TL, DAVID JS, et al. Fracture and Injuries of the Distal Radius and Carpus: the Cuttings: W.b. Saunders, 2009:27-36.
[2] NELLANS KW, KOWALSKI E, CHUNG KC. The Epidemiology of Distal Radius Fractures. Hand Clin. 2012;28(2):113-125.
[3] KATT B, SEIGERMAN D, LUTSKY K, et al. Distal Radius Malunion. J Hand Surg Am. 2020;45(5):433-443.
[4] 刘跃辉,龙宁,吴辉,等. 桡骨远端不稳定性骨折两种固定方式的生物力学对比试验研究[J]. 解放军医药杂志,2014,26(11):48-51.
[5] DOUGLAS PH, MARCI DJ, THOMAS ET. Iconography: Wrist Fractures. Curr Opin Immunol. 2011;23(6):784-788.
[6] YU YR, MAKHNI MC, TABRIZI S, et al. Complications of Low-Profile Dorsal Versus Volar Locking Plates in the Distal Radius: A Comparative Study. J Hand Surg Am. 2011;36(7):1135-1141.
[7] RAUSCH S, SCHLONSKI O, KLOS K, et al. Volar versus dorsal latest-generation variable-angle locking plates for the fixation of AO type 23C 2.1 distal radius fractures: A biomechanical study in cadavers. Injury. 2013;44(4):523-526.
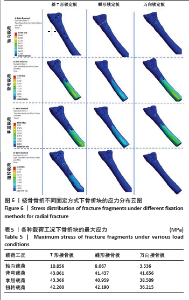
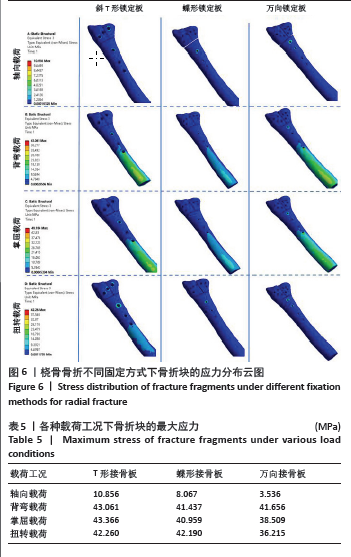
[8] 钟环,欧阳汉斌,魏波,等. 桡骨远端骨折锁定钢板的拓扑优化及有限元分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(23):2189-2194.
[9] 白桓安,陆清达,刘趁心,等. 不同固定方式治疗儿童肱骨近端骨折的有限元分析[J]. 医用生物力学,2023,38(2):297-302,323.
[10] CHENG HY, LIN CL, LIN YH, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of the modified double-plating fixation for the distal radius fracture. Clin Biomech. 2007;22(5): 510-517.
[11] WILLIS AA, KUTSUMI K, ZOBITZ ME, et al. Internal fixation of dorsally displaced fractures of the distal part of the radius. A biomechanical analysis of volar plate fracture stability (vol 88, pg 2411, 2006). J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89A(1):158.
[12] TAYLOR KF, PARKS BG, SEGALMAN KA. Biomechanical stability of a fixed-angle volar plate versus fragment-specific fixation system: Cyclic testing in a C2-type distal radius cadaver fracture model. J Hand Surg Am. 2006;31A(3):373-381.
[13] IMATANI J, AKITA K, YAMAGUCHI K, et al. An Anatomical Study of the Watershed Line on the Volar, Distal Aspect of the Radius: Implications for Plate Placement and Avoidance of Tendon Ruptures. J Hand Surg Am. 2012;37A(8):1550-1554.
[14] RACHEL S,SONYA K,RACHEL T, et al. Distal Radius Fractures in Patients Aged 50 Years or Older: Obstacles to Bone Health Analysis and Follow-Up in a Community Setting. J Hand Surg Global Online. 2021;3(2):88-93.
[15] 夏长江,袁志峰,方宁. 基于尺桡骨三维有限元模型分析桡骨远端骨折的生物力学特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(6):893-897.
[16] KIM JK, YI JW, JEON SH. The Effect of Acute Distal Radioulnar Joint Laxity on Outcome After Volar Plate Fixation of Distal Radius Fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2013;27(12):735-739.
[17] SOONG M, VAN LEERDAM R, GUITTON TG, et al. Fracture of the Distal Radius: Risk Factors for Complications After Locked Volar Plate Fixation. J Hand Surg Am. 2011;36(1):3-9.
[18] STANBURY SJ, SALO A, ELFAR JC. Biomechanical Analysis of a Volar Variable-Angle Locking Plate: The Effect of Capturing a Distal Radial Styloid Fragment. J Hand Surg. 2012;37:2488-2494.
[19] FOWLER JR, ILYAS AM. Prospective Evaluation of Distal Radius Fractures Treated With Variable-Angle Volar Locking Plates. J Hand Surg Am. 2013;38A(11): 2198-2203.
[20] 马涛. 桡骨远端C型骨折的手术入路解剖研究和临床观察[D]. 南京:南京医科大学,2018.
[21] 葛文龙. 桡骨极远端骨折不同内固定方式的有限元分析[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2020.
[22] 孙丹丹,石更强,杜科伟. 空心螺钉不同固定方式治疗后踝骨折的生物力学研究[J]. 医用生物力学,2023,38(1):110-115.
[23] TERESA A, DAVID J, MICHAEL K. 3-D computer modelling of malunited posterior malleolar fractures: effect of fragment size and offset on ankle stability, contact pressure and pattern. J Foot Ankle Rese. 2017:10:13.
[24] 殷浩,陈光,李燕,等. 背侧克氏针增强AOC型桡骨远端骨折尺背侧骨折块稳定性的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(31):4921-4925.
[25] TAI CL, CHEN WP, CHEN HH, et al. Biomechanical optimization of different fixation modes for a proximal femoral L-osteotomy. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2009;10:112.
[26] MOHAMED A, AHMED ABDEL-ZAHER K, MAHMOUD AHMED E. Volar locking plate fixation for distal radius fractures: did variable-angle plates make difference? Int Orthop. 2022;46:2165-2176. |