Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (23): 5051-5060.doi: 10.12307/2025.094
Visualization analysis of knowledge map and trends in glymphatic system research
Ma Xingyi1, Li Huijing2, Li Juan1, 3, Zhong Dongling1, Zhang Yuan1, Tang Hong4, Li Yuxi1, Jin Rongjiang1
- 1School of Health Preservation and Rehabilitation, 2SCollege of Clinical Medicine, 4School of Acupuncture and Massage, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, Sichuan Province, China; 3Affiliated Sichuan Provincial Rehabilitation Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 611135, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2024-03-07Accepted:2024-05-21Online:2025-08-18Published:2024-09-30 -
Contact:Jin Rongjiang, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, School of Health Preservation and Rehabilitation, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, Sichuan Province, China; Corresponding author: Li Yuxi, PhD, Assistant researcher, School of Health Preservation and Rehabilitation, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Ma Xingyi, Master candidate, School of Health Preservation and Rehabilitation, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (Young Scientist Fund), No. 82305363 (to LYX); National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program) No. 82374559 (to JRJ); Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province, No. 2023NSFSC1824 (to LYX); China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (The 73rd Batch), No. 2023MD734102 (to LYX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ma Xingyi, Li Huijing, Li Juan, Zhong Dongling, Zhang Yuan, Tang Hong, Li Yuxi, Jin Rongjiang. Visualization analysis of knowledge map and trends in glymphatic system research[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 5051-5060.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

2.1 胶质淋巴系统相关文献发文量可视化分析 研究共筛选得到胶质淋巴系统相关英文文献687篇,据此绘制年发文量增长趋势统计图(图1)。覆盖2012-2023年的时间范围,数据展示了胶质淋巴系统研究的文献发表量随时间的增长趋势,并可分为3个发展阶段:①2012-2015年为研究的初期发展阶段,文献量相对较少;②2016-2020年标志着研究进入稳定增长期;③2021-2023年,研究迎来迅猛发展期。鉴于研究数据收集截止于2024年初,2024年的发文量尚未包含在内。 2.2 胶质淋巴系统相关文献作者分析 运用CiteSpace进行作者共现分析如图2,该图可以直观反映研究领域的主要学者群体和科研团队的合作情况,图谱共生成节点266个(图谱剪切后,只显示能够反映重要信息的节点),直线为502条,密度为0.014 2,节点分布并不密集。如表1所示,发文量第一(65篇)的是美国罗切斯特大学Maiken Nedergaard教授,该作者与多个团队交流合作,在胶质淋巴系统研究领域较为活跃。发文量第二(28篇)与发文量第三(27篇)的作者分别是日本名古屋大学研究者Shinji Naganawa和Toshiaki Taoka ,他们发表论文的时间主要在集中在近几年,虽然有大量产出但其合作关系较为局限,团队内合作紧密与团队外合作松散。"

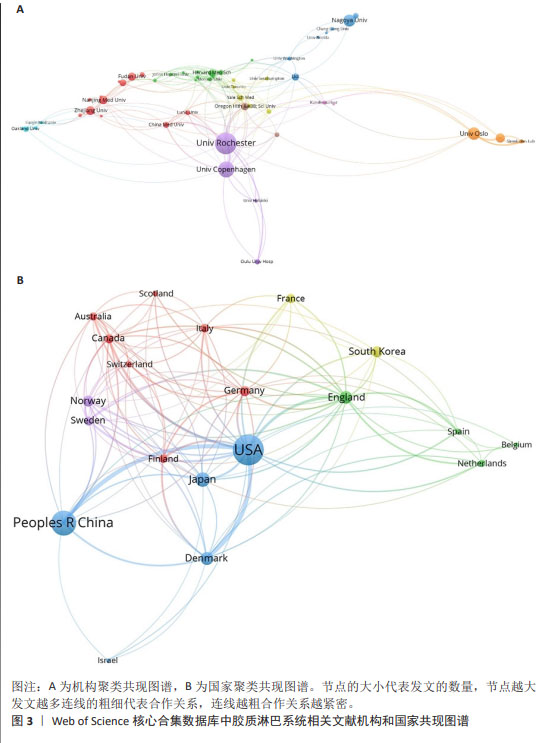
2.3 胶质淋巴系统相关文献机构与国家分析 运用VOSviewer,选择“co-authership”工具栏下的“organization”和 “country”得到图3。图3A为机构聚类共现图谱,由图可知,研究胶质淋巴系统的机构主要是高校和其附属医院,图中发文量最多的机构是美国罗切斯特大学(64篇),其次是丹麦哥本哈根大学(45篇),二者合作紧密,并分别与多个机构存在合作关系;发文量第三的是挪威奥斯陆大学(33篇),该机构与其附属医院合作较多。中国研究机构发文量较多的主要为浙江大学、南京医科大学和复旦大学,与国外机构合作较多是中国医科大学。 图3B为国家聚类共现图谱,全球发文量前5的国家分别是美国(286篇)、中国(188篇)、日本(65篇)、丹麦(50篇)、英国(48篇),图谱中共有5个合作聚类团,发文量前4的国家都位于绿色聚类中,除美国外,各个国家所在节点与其他节点间的连线都比较浅,说明除美国外其他国家间的合作较少,美国是胶质淋巴系统研究领域合作交流最活跃的国家。"
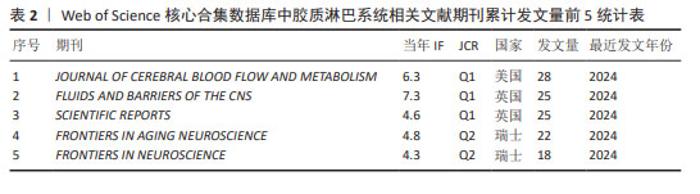
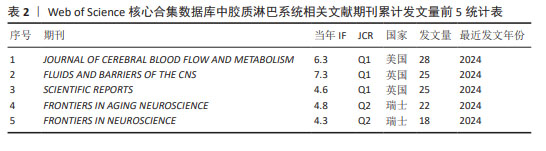
2.4 胶质淋巴系统相关文献来源分析 运行R语言下的Bibliometrix工具包,选择“Source”工具栏下的“Most Relevant Source”导出累计发文量前5的期刊信息,见表2。由表2可知发文量前3的期刊均属于Q1分区,说明胶质淋巴系统理论在医学科学研究领域具有一定影响力。发表胶质淋巴系统相关文献最多的期刊是《JOURNALOF CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW AND METABOLISM》,该期刊报道的影响力最高的胶质淋巴系统相关文献是一篇运用超快速磁共振脑电图技术来探索脑脊液的生理脉动机制的研究[13];发文量第二的期刊《FLUIDS AND BARRIERS OF THE CNS》所报道的影响力最高的胶质淋巴系统相关文献研究了颅内压对脑脊液流出途径(筛板、胶质淋巴系统、蛛网膜颗粒)中脑脊液分布的影响[14]。"

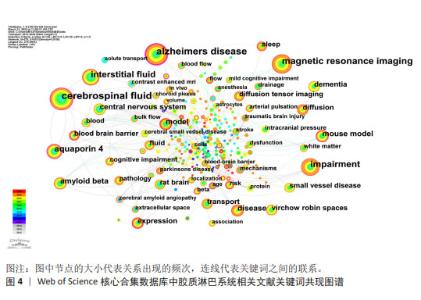
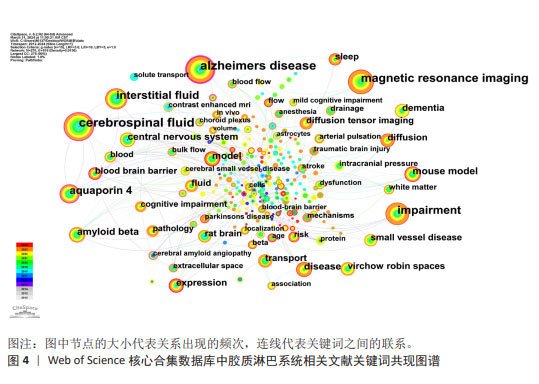
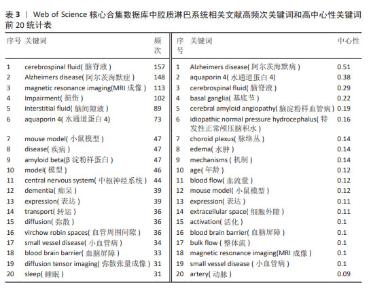
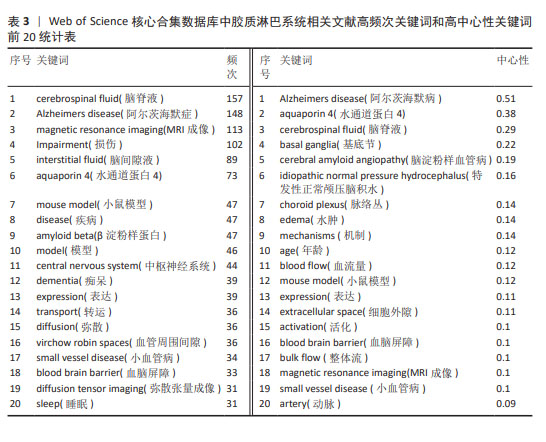
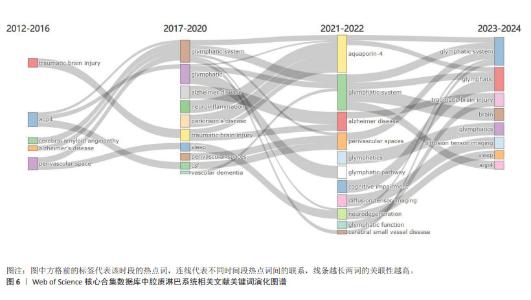
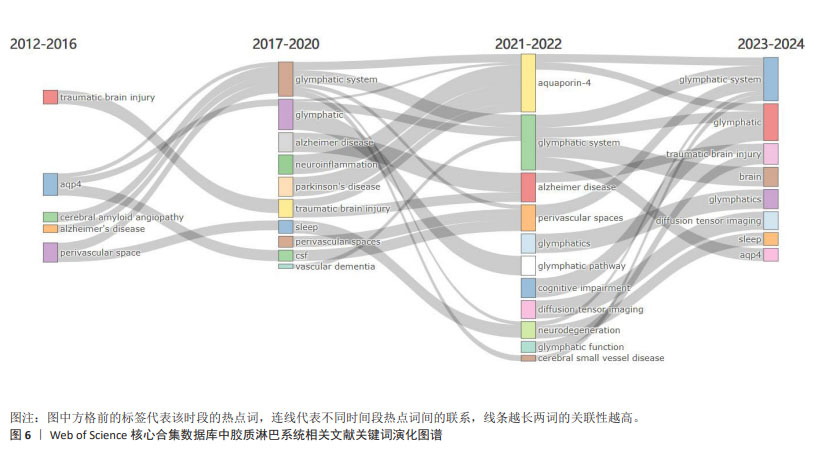
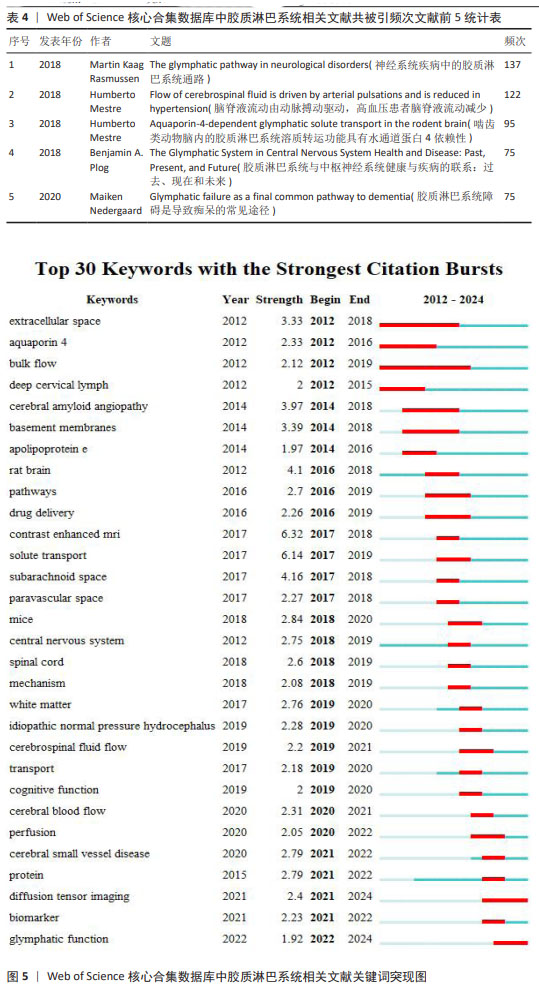
2.5.2 关键词突现情况 关键词突现是指某一段时间高频词出现的关键词,可以用于观察相关领域的发展趋势和研究前沿。运用CiteSpace得出前30的突现词见图5。图中突现时间延续最长的关键词是“整体流”,整体流是胶质淋巴系统中脑脊液的一种流动方式,但尚未得到证实[19]。图中突现强度最强的关键词是“增强磁共振成像”。增强MRI成像可以通过对比示踪剂在脑内的分布情况来评估胶质淋巴系统功能[20]。现阶段的突现词是“弥散张量成像”和“胶质淋巴系统功能”,弥散张量成像是一种非侵入型MRI成像技术[21],后衍生出的血管周围弥散指数已经成为现阶段的胶质淋巴系统研究的热门影像学指标。 2.5.3 关键词演化趋势 运用R语言-Bibliometrix工具包,在“Conceptual Structure”工具栏下“Thematic Evolution”选择作者关键词,得到作者关键词演化图如图6。由图可知,研究早期(2012-2016年)创伤性脑损伤、水通道蛋白4、阿尔茨海默症等主题是胶质淋巴系统研究的焦点;2017-2020年,胶质淋巴系统理论被应用于研究帕金森病、神经炎症、血管性痴呆等神经系统疾病;2021-2022年,弥散张量成像出现,说明研究人员开始采用新技术来研究胶质淋巴系统的功能。脑小血管病在这几年受到研究者的大量关注;2023年1月至2024年3月,创伤性脑损伤、弥散张量成像、睡眠、水通道蛋白4这些领域热度较高,这些词与胶质淋巴系统功能的评估与调控密切相关。阿尔茨海默症、水通道蛋白4、睡眠等在多个时间段中都是持续研究的主题,这说明它们在胶质淋巴系统领域的重要性和相关研究的连续性。 2.6 胶质淋巴系统相关文献共被引分析 2.6.1 共被引高频次文献分析 绘制高频次共被引文献前5统计表,见表4。被引用次数最多的文献是RASMUSSEN等[22]2018年在《LANCET NEUROL》上发表的一篇关于胶质淋巴系统的经典综述论文;其次是MESTRE等[23]2018年在《NAT COMMUN》期刊发表的文章,主要探索了高血压对脑脊液的影响,证明高血压导致胶质淋巴系统功能抑制;共被引频次第三的文章是MESTRE等[24]2018年在《ELIFE》期刊发表的文章,报道了水通道蛋白4介导脑脊液内溶质转运的重要作用。"
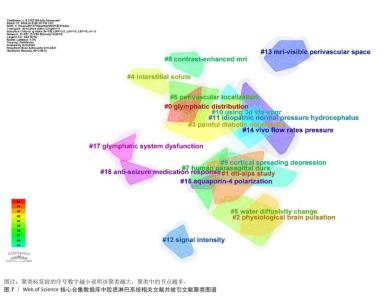
2.6.2 共被引文献聚类分析 运用CiteSpace对共被引文献的标题进行聚类,得到图7。图中共有17个聚类:#0胶质淋巴的分布、#1血管周围间隙弥散指数研究、#2脑生理性搏动、#3痛性糖尿病周围神经病变、#4间隙液溶质、#5水扩散系数的变化、#6血管周围定位、#7人矢状窦旁硬脑膜、#8增强磁共振成像、#9皮质传播抑制、#10可变翻转角快速自旋回波成像技术、#11特发性正常颅压脑积水、#12信号强度、#13磁共振可见的血管周围间隙、#14活体脑脊液压力流动率、#15水通道蛋白极化、#16抗癫痫药物抵抗反应、#17胶质淋巴系统功能障碍。其中,#1、#5、#6、#7、#8、#10、#12、#13都与MRI成像有关,这反映了胶质淋巴系统在神经影像学研究领域的研究热度;#0、#2、#14、#11均与胶质淋巴系统中脑脊液进入脑实质的流体动力学相关,#4、#15、#16都与胶质淋巴系统的溶质清除功能有关。因此,可以推测:神经影像学技术观察脑脊液流向、流量、流速等流体动力学研究和水通道蛋白4极化相关溶质运输功能的评估是研究胶质淋巴系统功能的两大趋势。"

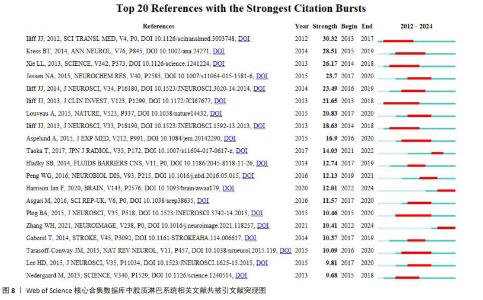
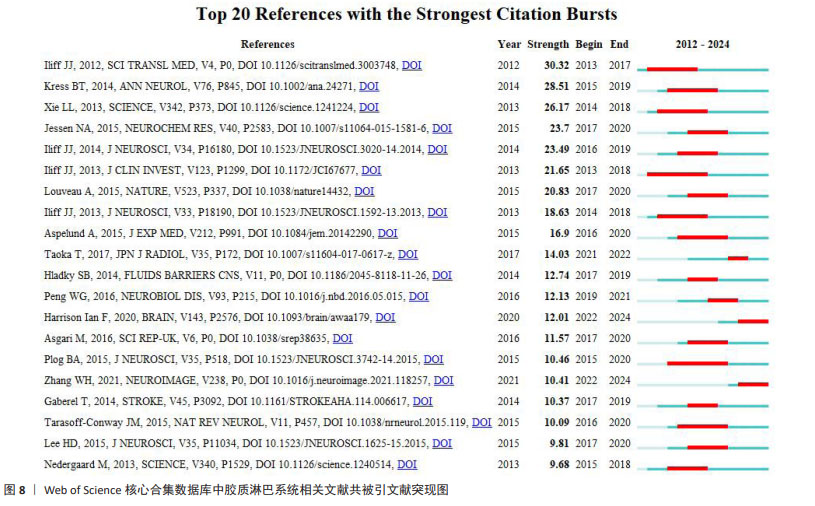
2.6.3 共被引文献突现分析 图8为共被引文献前10突现图,图中突现强度最大的是2012年Iliff与Nedergaard 两位教授在《SCIENCE TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE》上发表的最早报道胶质淋巴系统的经典文章,文中提到的荧光示踪技术、活体双光子显微成像技术和水通道蛋白4基因敲除技术,在胶质淋巴系统的基础研究中广泛应用[1]。ILIFF等[25]在2013年发表于《JOURNAL OF CLINICAL INVESTIGATION》的文献突现延续时间最长,该文献主要描述了采用增强MRI成像扫描全脑观察胶质淋巴系统清除代谢废物的全过程。正处于突现状态的文献有2篇,分别是HARRISON等[26]2020年在《BRAIN》发表的文献,该文献证明了胶质淋巴系统对异常tau蛋白的清除作用,提示胶质淋巴系统是治疗微管相关蛋白疾病的潜在靶点;以及ZHANG等[27]2021年在《NEUROIMAGE》发表的利用血管周围间隙弥散张量成像技术来评估脑小血管疾病患者的胶质淋巴系统功能的临床研究。"
| [1] ILIFF JJ, WANG MH, LIAO YH, et al. A Paravascular Pathway Facilitates CSF Flow Through the Brain Parenchyma and the Clearance of Interstitial Solutes, Including Amyloid β. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4(147):11. [2] 王琳辉,王紫兰,陈文悦,等.胶质淋巴系统:概念、功能和研究进展[J].生理学报,2018,70(1):52-60. [3] NYCZ B, MANDERA M. The features of the glymphatic system. Auton Neurosci Basic Clin. 2021;232:8. [4] TRUMBORE CN, RAGHUNANDAN A. An Alzheimer’s Disease Mechanism Based on Early Pathology, Anatomy, Vascular-Induced Flow, and Migration of Maximum Flow Stress Energy Location with Increasing Vascular Disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2022; 90(1):33-59. [5] HE PK, GAO YY, SHI L, et al. Motor progression phenotypes in early-stage Parkinson’s Disease: A clinical prediction model and the role of glymphatic system imaging biomarkers. Neurosci Lett. 2023; 814: 9. [6] KRESS BT, ILIFF JJ, XIA MS, et al. Impairment of Paravascular Clearance Pathways in the Aging Brain. Ann Neurol. 2014;76(6):845-861. [7] VINJE V, ZAPF B, RINGSTAD G, et al. Human brain solute transport quantified by glymphatic MRI-informed biophysics during sleep and sleep deprivation. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2023;20(1):15. [8] HAN GX, ZHOU Y, ZHANG KM, et al. Age- and time-of-day dependence of glymphatic function in the human brain measured via two diffusion MRI methods. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023;15:12. [9] LEE HD, XIE LL, YU M, et al. The Effect of Body Posture on Brain Glymphatic Transport. J Neurosci. 2015;35(31): 11034-10344. [10] 陈悦,陈超美,刘则渊,等.CiteSpace知识图谱的方法论功能[J].科学学研究, 2015,33(2):242-253. [11] 陈超美,陈悦,侯剑华,等.CiteSpace Ⅱ:科学文献中新趋势与新动态的识别与可视化[J].情报学报,2009,28(3): 401-421. [12] ARIA M, CUCCURULLO C. bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J Informetr. 2017;11(4): 959-975. [13] KIVINIEMI V, WANG XD, KORHONEN V, et al. A Ultra-fast magnetic resonance encephalography of physiological brain activity - Glymphatic pulsation mechanisms? J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2016;36(6): 1033-1045. [14] VINJE V, EKLUND A, MARDAL K A, et al. Intracranial pressure elevation alters CSF clearance pathways. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2020;17(1): 19. [15] KIM HJ, LIM TS, LEE SM, et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Levels of β-Amyloid 40 and β-Amyloid 42 are Proportionately Decreased in Amyloid Positron-Emission Tomography Negative Idiopathic Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus Patients. J Clin Neurol. 2019; 15(3):353-359. [16] PEROSA V, OLTMER J, MUNTING LP, et al. Perivascular space dilation is associated with vascular amyloid-β accumulation in the overlying cortex. Acta Neuropathol. 2022;143(3):331-348. [17] 卢鹤扬,冯一苇,崔梅.类淋巴系统与中枢神经系统病变的相关性研究进展[J].中国临床神经科学,2020,28(1): 78-84+92. [18] 杨逸飞,李昊.脑部类淋巴系统的研究进展[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2021, 15(1): 52-56. [19] FAGHIH MM, SHARP MK. Is bulk flow plausible in perivascular, paravascular and paravenous channels? Fluids Barriers CNS. 2018;15:10. [20] 陈心怡,卢艳丽,桂千,等.胶质淋巴转运MRI研究进展[J].中国医学影像技术, 2023,39(8):1249-1252. [21] THOMAS C, SADEGHI N, NAYAK A, et al. Impact of time-of-day on diffusivity measures of brain tissue derived from diffusion tensor imaging. Neuroimage. 2018;173:25-34. [22] RASMUSSEN MK, MESTRE H, NEDERGAARD M. The glymphatic pathway in neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2018;17(11): 10161024. [23] MESTRE H, TITHOF J, DU T, et al. Flow of cerebrospinal fluid is driven by arterial pulsations and is reduced in hypertension . Nat Commun. 2018;9:9. [24] MESTRE H, HABLITZ LM, XAVIER ALR, et al. Aquaporin-4-dependent glymphatic solute transport in the rodent brain. eLife. 2018; 7:31. [25] ILIFF JJ, LEE H, YU M, et al. Brain-wide pathway for waste clearance captured by contrast-enhanced MRI. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(3):1299-1309. [26] HARRISON IF, ISMAIL O, MACHHADA A, et al. Impaired glymphatic function and clearance of tau in an Alzheimer’s disease model. Brain. 2020;143(8):2576-2593. [27] ZHANG WH, ZHOU Y, WANG JA, et al. Glymphatic clearance function in patients with cerebral small vessel disease. Neuroimage. 2021;238:8. [28] GAN YM, HOLSTEIN-RONSBO S, NEDERGAARD M, et al. Perivascular pumping of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain with a valve mechanism. J R Soc Interface. 2023;20(206):17. [29] LUNDGAARD I, WANG W, EBERHARDT A, et al. Beneficial effects of low alcohol exposure, but adverse effects of high alcohol intake on glymphatic function. Sci Rep. 2018;8:16. [30] SIGURDSSON B, HAUGLUND NL, LILIUS TO, et al. A SPECT-based method for dynamic imaging of the glymphatic system in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2023;43(7): 1153-1165. [31] LI MS, KITAMURA A, BEVERLEY J, et al. Impaired Glymphatic Function and Pulsation Alterations in a Mouse Model of Vascular Cognitive Impairment. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;13:16. [32] PENG WG, ACHARIYAR TM, LI BM, et al. Suppression of glymphatic fluid transport in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2016;93:215-25. [33] TAOKA T, MASUTANI Y, KAWAI H, et al. Evaluation of glymphatic system activity with the diffusion MR technique: diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) in Alzheimer’s disease cases. Jpn J Radiol. 2017;35(4):172-178. [34] HOU CK, REN W, WANG BY, et al. A bibliometric and knowledge-map analysis of the glymphatic system from 2012 to 2022. Front Molec Neurosci. 2023;16:16. [35] ILIFF JJ, WANG MH, ZEPPENFELD DM, et al. Cerebral Arterial Pulsation Drives Paravascular CSF-Interstitial Fluid Exchange in the Murine Brain. J Neurosci. 2013;33(46):18190-18199. [36] ROBELIN F, LENFANT M, RICOLFI F, et al. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: From physiopathological mechanisms to therapeutic decision. Rev Med Interne. 2022;43(11):661-668. [37] BAE YJ, KIM JM, CHOI BS, et al. Glymphatic function assessment in Parkinson’s disease using diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2023;114:7. [38] JIN BJ, SMITH AJ, VERKMAN AS. Spatial model of convective solute transport in brain extracellular space does not support a “glymphatic” mechanism. J Gen Physiol. 2016;148(6):489-501. [39] BORK PAR, LADRON-DE-GUEVARA A, CHRISTENSEN AH, et al. Astrocyte endfeet may theoretically act as valves to convert pressure oscillations to glymphatic flow. J R Soc Interface. 2023;20(204):5. [40] LLOYD RA, STOODLEY MA, FLETCHER DF, et al. The effects of variation in the arterial pulse waveform on perivascular flow. J Biomech. 2019;90:65-70. [41] WANG YC, VAN GELDEREN P, DE ZWART JA, et al. Cerebrovascular activity is a major factor in the cerebrospinal fluid flow dynamics. Neuroimage.2022;258:10. [42] OZTURK B, KOUNDAL S, AL BIZRI E, et al. Continuous positive airway pressure increases CSF flow and glymphatic transport. JCI Insight. 2023;8(12):18. [43] RAITAMAA L, HUOTARI N, KORHONEN V, et al. Spectral analysis of physiological brain pulsations affecting the BOLD signal. Hum Brain Mapp. 2021;42(13):4298-4313. [44] BOSTER KAS, CAI SZ, LADRóN-DE-GUEVARA A, et al. Artificial intelligence velocimetry reveals in vivo flow rates, pressure gradients, and shear stresses in murine perivascular flows. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023;120(14):12. [45] SUNDARAM S, HUGHES RL, PETERSON E, et al. Establishing a framework for neuropathological correlates and glymphatic system functioning in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2019;103:305-315. [46] CAO XJ, XU HR, FENG WX, et al. Deletion of aquaporin-4 aggravates brain pathology after blocking of the meningeal lymphatic drainage. Brain Res Bull. 2018;143:83-96. [47] LIU SW, SUN XH, REN QG, et al. Glymphatic dysfunction in patients with early-stage amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain. 2024; 147(1):100-108. [48] KIM ST, KIM SE, LEE DA, et al. Anti-seizure medication response and the glymphatic system in patients with focal epilepsy. Eur J Neurol. 2024;31(1):9. [49] LIANG T, CHANG FY, HUANG ZG, et al. Evaluation of glymphatic system activity by diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI- ALPS) in dementia patients. Br J Radiol. 2023;96(1146):6. [50] RINGSTAD G, VATNEHOL SAS, EIDE PK. Glymphatic MRI in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Brain. 2017;140:2691-2705. [51] AKIYAMA Y, YOKOYAMA R, TAKASHIMA H, et al. Accumulation of Macromolecules in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Neurol Med Chir. 2021;61(3):211-218. [52] OTA M, SATO N, NAKAYA M, et al. Relationships Between the Deposition of Amyloid-β and Tau Protein and Glymphatic System Activity in Alzheimer’s Disease: Diffusion Tensor Image Study. J Alzheimers Dis. 2022;90(1):295-303. [53] KIKUTA J, KAMAGATA K, TAOKA T, et al. Water Diffusivity Changes Along the Perivascular Space After Lumboperitoneal Shunt Surgery in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Front Neurol. 2022;13:9. [54] TANG J, ZHANG MY, LIU N, et al. The Association Between Glymphatic System Dysfunction and Cognitive Impairment in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:9. [55] MORTENSEN KN, SANGGAARD S, MESTRE H, et al. Impaired Glymphatic Transport in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. J Neurosci. 2019;39(32):6365-6377. [56] XUE Y, LIU N, ZHANG MY, et al. Concomitant enlargement of perivascular spaces and decrease in glymphatic transport in an animal model of cerebral small vessel disease. Brain Res Bull. 2020;161:78-83. [57] BUONGIORNO M, GRANELL E, CARUANA G, et al. Impairments in sleep and brain molecular clearance in people with cognitive deterioration and biological evidence of AD: a report of four cases. BMC Neurol. 2023;23(1):8. [58] WRIGHT AM, WU YC, CHEN NK, et al. Exploring Radial Asymmetry in MR Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Its Impact on the Interpretation of Glymphatic Mechanisms. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2023. doi: 10.1002/jmri.29203. [59] LEE DA, LEE HJ, PARK KM. Structural connectivity as a predictive factor for responsiveness to levetiracetam treatment in epilepsy. Neuroradiology. 2024;66(1):93-100. [60] TUERXUN R, KAMAGATA K, SAITO Y, et al. Assessing interstitial fluid dynamics in type 2 diabetes mellitus and prediabetes cases through diffusion tensor imaging analysis along the perivascular space. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024;16:11. [61] TU Y, LI Z, XIONG F, et al. Decreased DTI-ALPS and choroid plexus enlargement in fibromyalgia: a preliminary multimodal MRI study. Neuroradiology. 2023;65(12): 1749-1755. |
| [1] | Liang Haobo, Wang Zeyu, Ma Wenlong, Liu Hao, Liu Youwen. Hot issues in the field of joint revision: infection, rehabilitation nursing, bone defect, and prosthesis loosening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1963-1971. |
| [2] | Lyu Liting, Yu Xia, Zhang Jinmei, Gao Qiaojing, Liu Renfan, Li Meng, Wang Lu. Bibliometric analysis of research process and current situation of brain aging and exosomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1457-1465. |
| [3] | Xie Liugang, Cui Shuke, Guo Nannan, Li Aoyu, Zhang Jingrui. Research hotspots and frontiers of stem cells for Alzheimer’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1475-1485. |
| [4] | Chang Jinxia, Liu Yufei, Niu Shaohui, Wang Chang, Cao Jianchun. Visualization analysis of macrophage polarization in tissue repair process [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1486-1496. |
| [5] | Li Huijun, Li Huangyan, Zhang Yeting. Physical activity and cognition in older adults: research hotspot and topic evolution [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1073-1080. |
| [6] | Dang Xiaowen, Huang Hailiang, Huang Lei, Wang Yajie . Research frontiers and hotspots of carbon nanomaterials in biomedical field over the past 10 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 752-760. |
| [7] | Ma Yucong, Ouyang Zhengzheng, Liu Xiaojie, Yang Sifei. Tracking of research trends and hotspots in medical magnesium alloy materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7470-7480. |
| [8] | Guo Haizhen, Cong Zidong, Zhao Yuke, Li Xiaofeng, Yu Lu, Qian Shule, Wang Runying, Du Wuxun. Development of patch clamp technology in the past 10 years: visual analysis based on CiteSpace and VOSviewer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6717-6726. |
| [9] | Xu Qiang, Qin Jialin, Lian Zeshuang, Wang Aoting, Li Ding, Wang Ye, Wang Junfang. Visual analysis of hot spots and trends in the study of ligamentum flavum ossification [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 628-636. |
| [10] | Song Haoran, Zhang Yuqiang, Gu Na, Zhi Xiaodong, Wang Wei. Visualization analysis of artificial intelligence in bone trauma research based on Citespace [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 493-502. |
| [11] | Zheng Xiaodong, Gao Shan, Han Wenjin, Liu Lijun, Jia Menglong, Yu Longtan. Visual analysis of treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 645-653. |
| [12] | Nan Songhua, Peng Chaojie, Cui Yinglin. Mitochondrial dysfunction and brain aging: a bibliometrics analysis based on the Web of Science Core Collection database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5642-5651. |
| [13] | Zeng Hao, Zou Shunyi, Li Zhengpeng, Chai Yuan, Huang Yourong, Zhang Xiaoyun. Intestinal flora regulates bone metabolism: a visual analysis of literature from the Web of Science Core Collection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5652-5661. |
| [14] | Tian Hao, Chen Dingding, Wang Deng, Ye Qiang. Research hotspots, frontier changes, and trend prospects of neuromuscular training [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5148-5157. |
| [15] | Zou Shunyi, Chai yuan, Li Kunjian. Involvement of macrophage polarization in osteoarticular diseases: a visual analysis based on SCI-Expanded information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5245-5253. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||