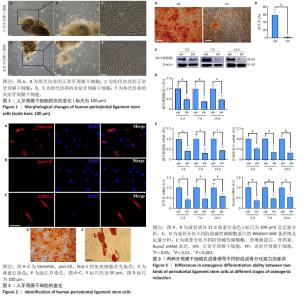
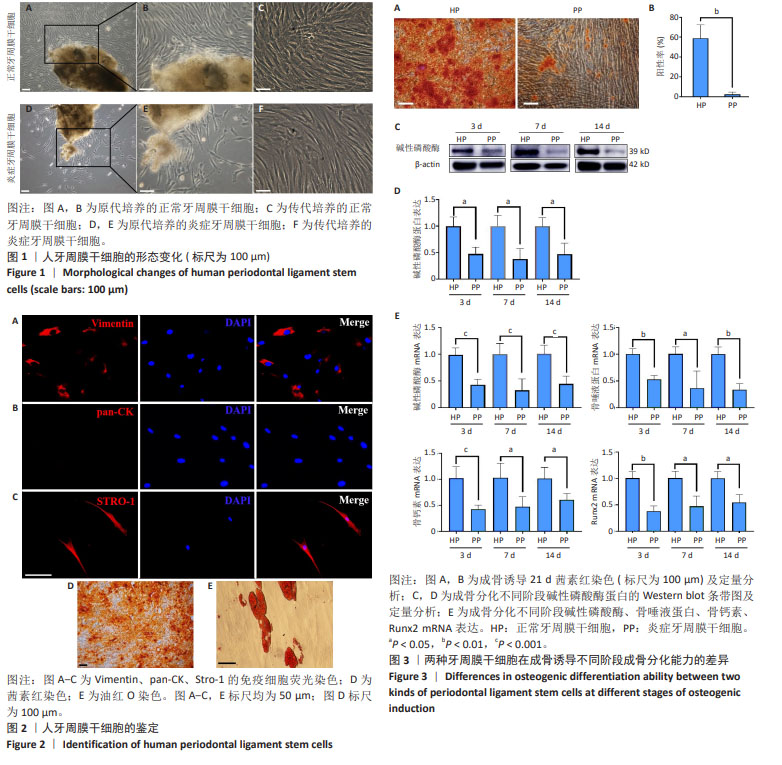
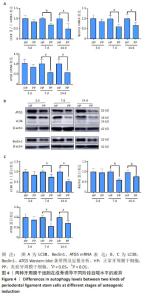
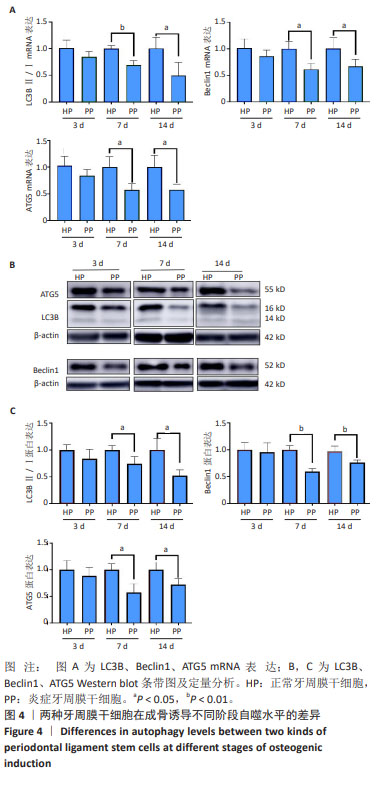
[1] CHEN FM, SUN HH, LU H, et al. Stem cell-delivery therapeutics for periodontal tissue regeneration. Biomaterials. 2012;33(27):6320-6344.
[2] QIU W, WU BL, FANG FC. Overview of noncoding RNAs involved in the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells. World J Stem Cells. 2020;12(4):251-265.
[3] YU M, SUN L, BA P, et al. Progranulin promotes osteogenic differentiation of periodontal membrane stem cells in both inflammatory and non-inflammatory conditions. J Int Med Res. 2021; 49(8):3000605211032508.
[4] CHEN Q, LIU X, WANG D, et al. Periodontal Inflammation-Triggered by Periodontal Ligament Stem Cell Pyroptosis Exacerbates Periodontitis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:663037.
[5] LU Y, ZHAO L, MAO J, et al. Rab27a-mediated extracellular vesicle secretion contributes to osteogenesis in periodontal ligament-bone niche communication. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):8479.
[6] SHANG L, LIU Z, MA B, et al. Dimethyloxallyl glycine/nanosilicates-loaded osteogenic/angiogenic difunctional fibrous structure for functional periodontal tissue regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2020;6(4): 1175-1188.
[7] ZHANG X, YAN Q, LIU X, et al. LncRNA00638 promotes the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal mesenchymal stem cells from periodontitis patients under static mechanical strain. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):177.
[8] JIN S, JIANG H, SUN Y, et al. Osteogenic differentiation of periodontal membrane stem cells in inflammatory environments. Open Life Sci. 2022;17(1):1240-1248.
[9] ZHENG W, WANG S, WANG J, et al. Periodontitis promotes the proliferation and suppresses the differentiation potential of human periodontal ligament stem cells. Int J Mol Med. 2015;36(4):915-922.
[10] DEBNATH J, GAMMOH N, RYAN KM. Autophagy and autophagy-related pathways in cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023;24(8):560-575.
[11] ZACHARI M, LONGO M, GANLEY IG. Aberrant autophagosome formation occurs upon small molecule inhibition of ULK1 kinase activity. Life Sci Alliance. 2020;3(12):e202000815.
[12] GANLEY I. The Importance of Being Autophagic. N Engl J Med. 2021; 384(25):2449-2450.
[13] ZHANG Y, WANG P, WANG Y, et al. Gold Nanoparticles Promote the Bone Regeneration of Periodontal Ligament Stem Cell Sheets Through Activation of Autophagy. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021;16:61-73.
[14] MAO CY, WANG YG, ZHANG X, et al. Double-edged-sword effect of IL-1β on the osteogenesis of periodontal ligament stem cells via crosstalk between the NF-κB, MAPK and BMP/Smad signaling pathways. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7(7):e2296.
[15] SHAO X, HU Z, SU H, et al. Effects of tension on mitochondrial autophagy and osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells. Cell Prolif. 2023:e13561. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13561.
[16] LIU H, ZHENG J, ZHENG T, et al. Exendin-4 regulates Wnt and NF-κB signaling in lipopolysaccharide-induced human periodontal ligament stem cells to promote osteogenic differentiation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;75:105801.
[17] JIANG N, HE D, MA Y, et al. Force-Induced Autophagy in Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells Modulates M1 Macrophage Polarization via AKT Signaling. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:666631.
[18] CHENG M, ZHOU Q. Targeting EZH2 Ameliorates the LPS-Inhibited PDLSC Osteogenesis via Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Cells Tissues Organs. 2020;209(4-6):227-235.
[19] WANG P, TIAN H, ZHANG Z, et al. EZH2 Regulates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Periodontal Ligament Stem Cell Proliferation and Osteogenesis through TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Pathway. Stem Cells Int. 2021;2021:7625134.
[20] SU Y, AI S, SHEN Y, et al. Regulatory Effects of Three-Dimensional Cultured Lipopolysaccharide-Pretreated Periodontal Ligament Stem Cell-Derived Secretome on Macrophages. Int J Mol Sci. 2023; 24(8):6981.
[21] RAMENZONI LL, RUSSO G, MOCCIA MD, et al. Periodontal bacterial supernatants modify differentiation, migration and inflammatory cytokine expression in human periodontal ligament stem cells. PLoS One. 2019;14(7):e0219181.
[22] ZHAO X, SUN W, GUO B, et al. Circular RNA BIRC6 depletion promotes osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells via the miR-543/PTEN/PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in the inflammatory microenvironment. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):417.
[23] LI L, LIU W, WANG H, et al. Mutual inhibition between HDAC9 and miR-17 regulates osteogenesis of human periodontal ligament stem cells in inflammatory conditions. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(5):480.
[24] SUN J, DONG Z, ZHANG Y, et al. Osthole improves function of periodontitis periodontal ligament stem cells via epigenetic modification in cell sheets engineering. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):5254.
[25] ZHANG R, LIANG Q, KANG W, et al. Metformin facilitates the proliferation, migration, and osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells in vitro. Cell Biol Int. 2020;44(1):70-79.
[26] MENG T, ZHOU Y, LI J, et al. Azithromycin Promotes the Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells after Stimulation with TNF-α. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:7961962.
[27] QIU X, YU Y, LIU H, et al. Remodeling the periodontitis microenvironment for osteogenesis by using a reactive oxygen species-cleavable nanoplatform. Acta Biomater. 2021;135:593-605.
[28] YANG XQ, YU SY, YU L, et al. Effects of tacrolimus on autophagy protein LC3 in puromycin-damaged mouse podocytes. J Int Med Res. 2020;48(12):300060520971422.
[29] KONG Z, YAO T. Role for autophagy-related markers Beclin-1 and LC3 in endometriosis. BMC Womens Health. 2022;22(1):264.
[30] ELBIALY A. In vivo autophagy quantification: Measuring LC3 and P62 puncta in 3D image system from zebrafish larvae. J Cell Biochem. 2021;122(10):1435-1444.
[31] SARKAR C, LIPINSKI MM. Autophagy in neuroinflammation after traumatic brain injury. Neural Regen Res. 2024;19(5):951-952.
[32] LI X, GAO L, ZHENG L, et al. BMP4-mediated autophagy is involved in the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma via JNK/Beclin1 signaling. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(6):3068-3077.
[33] GUI X, YANG H, LI T, et al. Autophagy induction via STING trafficking is a primordial function of the cGAS pathway. Nature. 2019;567(7747): 262-266.
[34] LUO Y, GOU H, CHEN X, et al. Lactate inhibits osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells via autophagy through the MCT1-mTOR signaling pathway. Bone. 2022;162:116444.
|