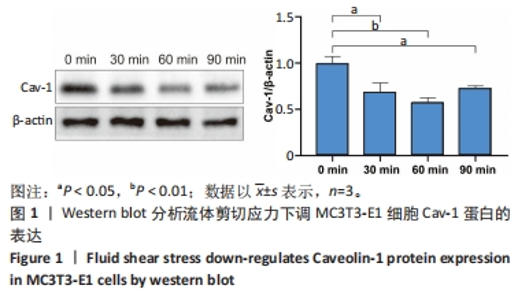
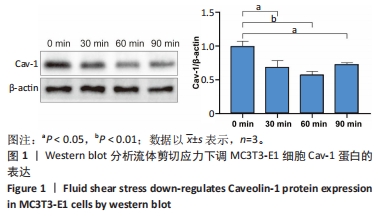
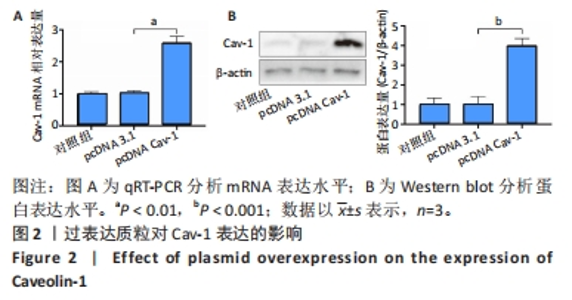
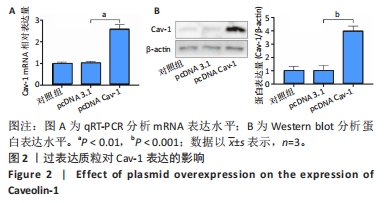
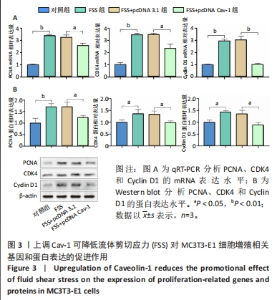
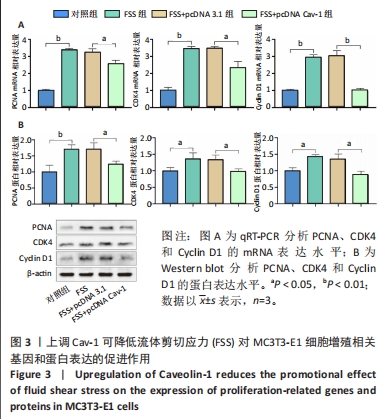
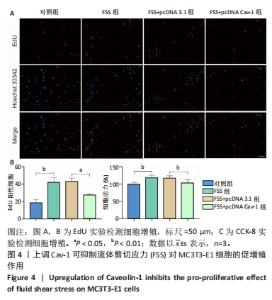
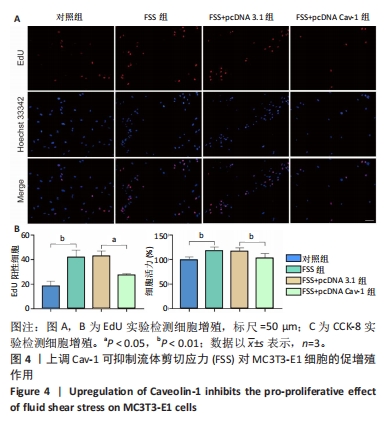
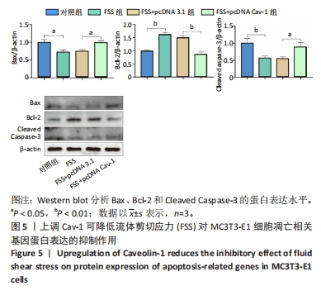
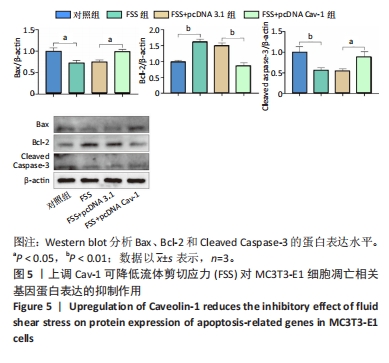
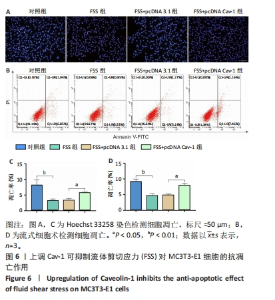
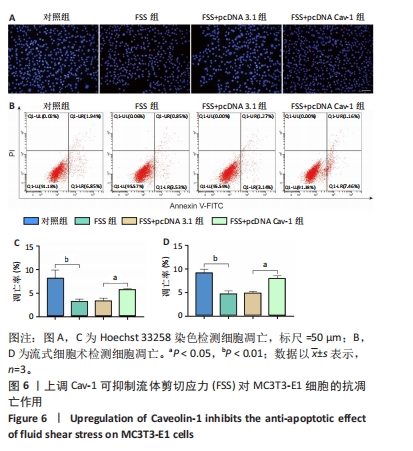
[1] GOPINATH V.Osteoporosis. Med Clin North Am. 2023;107(2):213-225.
[2] SALARI N, GHASEMI H, MOHAMMADI L, et al. The global prevalence of osteoporosis in the world: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):609.
[3] 毛贝尼, 张钟, 付维力, 等.中国骨质疏松性骨折疾病负担的系统评价[J].中国循证医学杂志,2018,18(2):151-155.
[4] CHEN X, WANG Z, DUAN N, et al.Osteoblast-osteoclast interactions.Connect Tissue Res. 2018;59(2):99-107.
[5] KIM J M, LIN C, STAVRE Z, et al. Osteoblast-Osteoclast Communication and Bone Homeostasis. Cells. 2020;9(9):2073.
[6] KAUR M, NAGPAL M, SINGH M. Osteoblast-n-Osteoclast: Making Headway to Osteoporosis Treatment.Curr Drug Targets. 2020;21(16): 1640-1651.
[7] NEVE A, CORRADO A, CANTATORE FP. Osteoblast physiology in normal and pathological conditions. Cell Tissue Res. 2011;343(2):289-302.
[8] WOLFF J. Das Gesetz der Transformation der Knochen. Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift. 1893;19(47):1222 - 1224.
[9] BASSO N, HEERSCHE JN. Characteristics of in vitro osteoblastic cell loading models. Bone. 2002;30(2):347-351.
[10] BIN G, BO Z, JING W, et al. Fluid shear stress suppresses TNF-α-induced apoptosis in MC3T3-E1 cells: Involvement of ERK5-AKT-FoxO3a-Bim/FasL signaling pathways. Exp Cell Res. 2016;343(2):208-217.
[11] WANG X, GENG B, WANG H, et al. Fluid shear stress-induced down-regulation of microRNA-140-5p promotes osteoblast proliferation by targeting VEGFA via the ERK5 pathway. Connect Tissue Res. 2022;63(2): 156-168.
[12] WANG X, HE J, WANG H, et al. Fluid shear stress regulates osteoblast proliferation and apoptosis via the lncRNA TUG1/miR-34a/FGFR1 axis. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(18):8734-8747.
[13] MAO L, GUO J, HU L, et al. The effects of biophysical stimulation on osteogenic differentiation and the mechanisms from ncRNAs.Cell Biochem Funct. 2021;39(6):727-739.
[14] ZHAO X, ZHAO D, GENG B, et al. A novel ceRNA regulatory network involving the long noncoding NEAT1, miRNA-466f-3p and its mRNA target in osteoblast autophagy and osteoporosis. J Mol Med (Berl). 2022;100(11):1629-1646.
[15] PEI T, SU G, YANG J, et al.Fluid Shear Stress Regulates Osteogenic Differentiation via AnnexinA6-Mediated Autophagy in MC3T3-E1 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(24):15702.
[16] ENGELMAN J A, WYKOFF CC, YASUHARA S, et al. Recombinant expression of caveolin-1 in oncogenically transformed cells abrogates anchorage-independent growth. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(26):16374-16381.
[17] BAKER N, ZHANG G, YOU Y, et al. Caveolin-1 regulates proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 2012;113(12):3773-3787.
[18] DALTON CM, SCHLEGEL C, HUNTER CJ. Caveolin-1: A Review of Intracellular Functions, Tissue-Specific Roles, and Epithelial Tight Junction Regulation. Biology (Basel). 2023;12(11):1402.
[19] LAI X, GUO Y, CHEN M, et al. Caveolin1: its roles in normal and cancer stem cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021;147(12):3459-3475.
[20] GOKANI S, BHATT LK.Caveolin-1: A Promising Therapeutic Target for Diverse Diseases. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2022;15(5):701-715.
[21] SAWAI Y, SUZUKI Y, ASAGIRI M, et al. Caveolin-1 forms a complex with P2X7 receptor and tunes P2X7-mediated ATP signaling in mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024; 326(1):C125-C142.
[22] KRUGLIKOV IL, SCHERER PE. Caveolin-1 as a possible target in the treatment for acne. Exp Dermatol. 2020;29(2):177-183.
[23] SAMARAKOON R, HIGGINS SP, HIGGINS CE, et al. The TGF-β1/p53/PAI-1 Signaling Axis in Vascular Senescence: Role of Caveolin-1. Biomolecules. 2019;9(8):341.
[24] RUBIN J, SCHWARTZ Z, BOYAN BD, et al. Caveolin-1 knockout mice have increased bone size and stiffness.J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22(9):1408-1418.
[25] JIN Z, KHO J, DAWSON B, et al. Nitric oxide modulates bone anabolism through regulation of osteoblast glycolysis and differentiation. J Clin Invest. 2021;131(5):e138935.
[26] RAZANI B, ENGELMAN JA, WANG XB, et al. Caveolin-1 null mice are viable but show evidence of hyperproliferative and vascular abnormalities. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(41):38121-38138.
[27] CEREZO A, GUADAMILLAS MC, GOETZ JG, et al. The absence of caveolin-1 increases proliferation and anchorage- independent growth by a Rac-dependent, Erk-independent mechanism. Mol Cell Biol. 2009; 29(18):5046-5059.
[28] XIA H, KHALIL W, KAHM J, et al. Pathologic caveolin-1 regulation of PTEN in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 2010;176(6):2626-2637.
[29] KARIMIAN A, AHMADI Y, YOUSEFI B.Multiple functions of p21 in cell cycle, apoptosis and transcriptional regulation after DNA damage.DNA Repair (Amst).2016;42:63-71.
[30] VOUSDEN KH, PRIVES C. Blinded by the Light: The Growing Complexity of p53. Cell. 2009;137(3):413-431.
[31] ZHANG J, LAZARENKO OP, BLACKBURN ML, et al. Soy protein isolate down-regulates caveolin-1 expression to suppress osteoblastic cell senescence pathways. FASEB J. 2014;28(7):3134-3145.
[32] GALBIATI F, VOLONTE D, ENGELMAN JA, et al. Targeted downregulation of caveolin-1 is sufficient to drive cell transformation and hyperactivate the p42/44 MAP kinase cascade. EMBO J. 1998;17(22):6633-6648. |