Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (20): 3123-3129.doi: 10.12307/2024.352
Previous Articles Next Articles
Exploration of signaling pathways with unclear action status and possible effects on related diseases or functions after knockdown of silencing information regulator 1 gene in chondrocytes
Ye Haiming1, 2, 3, Zeng Hui1, 2, 3, Yang Qi4, Zhang Geng1, 2, 3, Weng Jian1, 2, 3, Yu Fei1, 2, 3
- 1Department of Bone & Joint Surgery, 4Department of Medical Ultrasound, Peking University Shenzhen Hospital, Shenzhen 518036, Guangdong Province, China; 2National & Local Joint Engineering Research Center of Orthopaedic Biomaterials, Shenzhen 518036, Guangdong Province, China; 3Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Orthopaedic Diseases and Biomaterials Research, Shenzhen 518036, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2023-05-04Accepted:2023-06-15Online:2024-07-18Published:2023-09-09 -
Contact:Yu Fei, MD, Physician, Department of Bone & Joint Surgery, Peking University Shenzhen Hospital, Shenzhen 518036, Guangdong Province, China; National & Local Joint Engineering Research Center of Orthopaedic Biomaterials, Shenzhen 518036, Guangdong Province, China; Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Orthopaedic Diseases and Biomaterials Research, Shenzhen 518036, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Ye Haiming, Associate chief physician, Department of Bone & Joint Surgery, Peking University Shenzhen Hospital, Shenzhen 518036, Guangdong Province, China; National & Local Joint Engineering Research Center of Orthopaedic Biomaterials, Shenzhen 518036, Guangdong Province, China; Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Orthopaedic Diseases and Biomaterials Research, Shenzhen 518036, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82102568 (to YF); the Basic and Applied Basic Research Fund of Guangdong Province, Nos. 2021A1515012586 and 2022A1515220111 (both to YF); the Scientific Research Foundation of Peking University Shenzhen Hospital, No. KYQD2021099 (to YF); Shenzhen Project of Three Famous Items for Medical Care and Public Health, No. SZSM201612092 (to ZH); Shenzhen Medical Key Discipline Construction Fund, No. SZXK023 (to ZH); Shenzhen High-level Hospital Construction Special Fund (to ZH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ye Haiming, Zeng Hui, Yang Qi, Zhang Geng, Weng Jian, Yu Fei. Exploration of signaling pathways with unclear action status and possible effects on related diseases or functions after knockdown of silencing information regulator 1 gene in chondrocytes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(20): 3123-3129.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

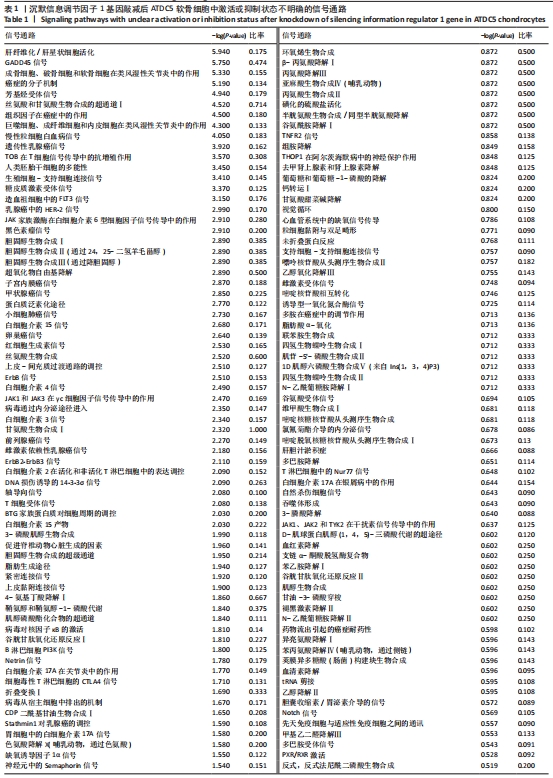
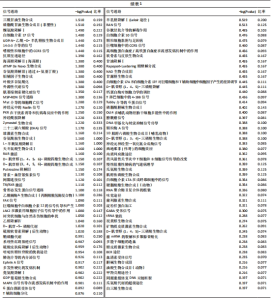
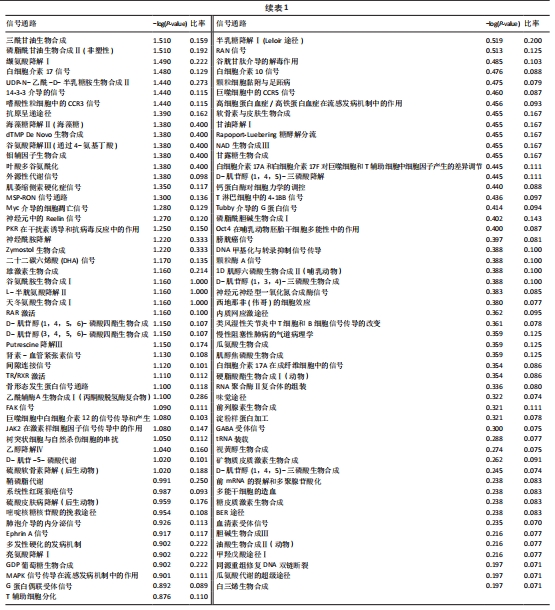
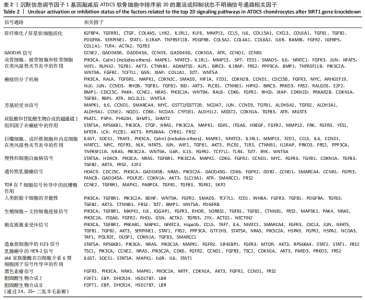
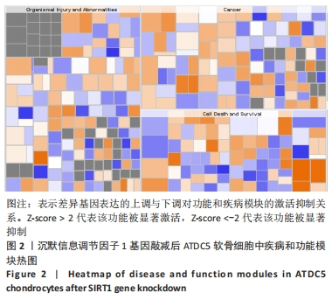
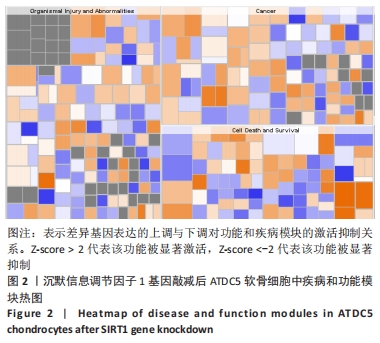
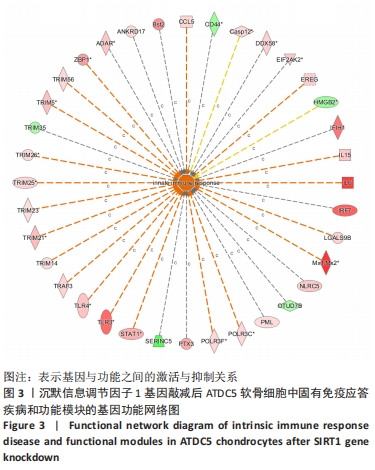
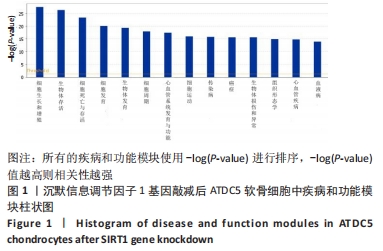
2.3 SIRT1基因敲减后ATDC5软骨细胞中疾病或功能模块的富集情况 生物信息学技术分析发现,根据-log(P-value)进行排序,ATDC5软骨细胞中SIRT1基因敲减后,细胞中细胞生长和增殖、生物体存活、细胞死亡与存活、细胞发育、生物体发育、细胞周期、心血管系统发育与功能、细胞运动、传染病、癌症、生物体损伤和异常、组织形态学、心血管疾病、血液病这些疾病和功能模块密切相关并且这些疾病和功能模块为所有富集疾病和功能模块中排名最靠前的14位(图1)。生物信息学技术分析发现,根据差异基因数量排序,ATDC5软骨细胞中SIRT1基因敲减后,细胞中生物体损伤和异常、癌症和细胞死亡与存活这些疾病和功能模块密切相关并且这些疾病和功能模块为所有富集疾病和功能模块中排名最靠前的3位(图2)。"
| [1] SUN D, LIU X, XU L, et al. Advances in the Treatment of Partial-Thickness Cartilage Defect. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022;17:6275-6287. [2] CHIANG MH, KUO YJ, CHEN YP. Expanded mesenchymal stem cell transplantation following marrow stimulation is more effective than marrow stimulation alone in treatment of knee cartilage defect: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020;106(5):977-983. [3] HACKEN BA, LAPRADE MD, STUART MJ, et al. Small Cartilage Defect Management. J Knee Surg. 2020;33(12):1180-1186. [4] KATATO H, OZEKI N, KOGA H, et al. Three-dimensional MRI shows cartilage defect extension with no separation from the meniscus in women in their 70 s with knee osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):4198. [5] LU Y, ZHOU L, WANG L, et al. The role of SIRT1 in BMP2-induced chondrogenic differentiation and cartilage maintenance under oxidative stress. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(10):9000-9013. [6] QI H, ZHAO Z, XU L, et al. Antisense Oligonucleotide-Based Therapy on miR-181a-5p Alleviates Cartilage Degradation of Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis via Promoting SIRT1. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:898334. [7] LI M, YIN H, YAN Z, et al. The immune microenvironment in cartilage injury and repair. Acta Biomater. 2022;140:23-42. [8] SALZMANN GM, OSSENDORFF R, GILAT R, et al. Autologous Minced Cartilage Implantation for Treatment of Chondral and Osteochondral Lesions in the Knee Joint: An Overview. Cartilage.2021;13(1_suppl):1124S-1136S. [9] CHEN C, ZHOU M, GE Y, et al. SIRT1 and aging related signaling pathways. Mech Ageing Dev. 2020;187:111215. [10] LIANG J, HUANG G, LIU X, et al. The ZIP8/SIRT1 axis regulates alveolar progenitor cell renewal in aging and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 2022;132(11):e157338. [11] YAN S, DONG W, LI Z, et al. Metformin regulates chondrocyte senescence and proliferation through microRNA-34a/SIRT1 pathway in osteoarthritis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):198. [12] YU X, XU X, DONG W, et al. DDIT3/CHOP mediates the inhibitory effect of ER stress on chondrocyte differentiation by AMPKα-SIRT1 pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2022;1869(8):119265. [13] ELAYYAN J, CARMON I, ZECHARYAHU L, et al. Lef1 ablation alleviates cartilage mineralization following posttraumatic osteoarthritis induction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022;119(21):e2116855119. [14] WANG Y, CHEN G, YAN J, et al. Upregulation of SIRT1 by Kartogenin Enhances Antioxidant Functions and Promotes Osteogenesis in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:1368142. [15] ZHOU ZM, BAO JP, PENG X, et al. Small extracellular vesicles from hypoxic mesenchymal stem cells alleviate intervertebral disc degeneration by delivering miR-17-5p. Acta Biomater. 2022;140:641-658. [16] YAMAKAWA A, HOJO H, OHBA S. ChIP-Seq Assays from Mammalian Cartilage and Chondrocytes. Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2245:167-178. [17] AUBOURG G, RICE SJ, BRUCE-WOOTTON P, et al. Genetics of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(5):636-649. [18] KAWATA M, TERAMURA T, ORDOUKHANIAN P, et al. Krüppel-like factor-4 and Krüppel-like factor-2 are important regulators of joint tissue cells and protect against tissue destruction and inflammation in osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022;annrheumdis-2021-221867. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-221867. [19] SUN Y, LENG P, GUO P, et al. G protein coupled estrogen receptor attenuates mechanical stress-mediated apoptosis of chondrocyte in osteoarthritis via suppression of Piezo1. Mol Med. 2021;27(1):96. [20] ZHANG J, SUN X, JIA S, et al. The role of lateral pterygoid muscle in the traumatic temporomandibular joint ankylosis: A gene chip based analysis. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(5):4297-4305. [21] 解笑宸,杨琪,翁鉴,等.沉默信息调节因子1基因敲减后ATDC5小鼠软骨细胞中被激活细胞退变相关信号通路及差异因子的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(32):5112-5118. [22] YU F, YUAN Y, LI D, et al. The Effect of Lentivirus-mediated SIRT1 Gene Knockdown in the ATDC5 Cell Line via inhibition of the Wnt Signaling Pathway. Cell Signal. 2019;53:80-89. [23] SUN K, WU Y, ZENG Y, et al. The role of the sirtuin family in cartilage and osteoarthritis: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022;24(1):286. [24] JIANG S, ZHANG C, LU Y, et al. Mechanical stress-caused chondrocyte dysfunction and cartilage injury can be attenuated by dioscin via activating sirtuin1/forkhead box O1. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2022;36(12):e23212. [25] WANG B, SUN W, BI K, et al. Apremilast prevents IL 17 induced cellular senescence in ATDC5 chondrocytes mediated by SIRT1. Int J Mol Med. 2021;47(3):12. [26] PAPAGEORGIOU AA, LITSAKI M, MOURMOURA E, et al. DNA methylation regulates Sirtuin 1 expression in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Adv Med Sci. 2023;68(1): 101-110. [27] MA CH, CHOU WC, WU CH, et al. Ginsenoside Rg3 Attenuates TNF-α-Induced Damage in Chondrocytes through Regulating SIRT1-Mediated Anti-Apoptotic and Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021;10(12):1972. [28] CHOI SM, LEE KM, RYU SB, et al. Enhanced articular cartilage regeneration with SIRT1-activated MSCs using gelatin-based hydrogel. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(9):866. [29] YU F, LI M, YUAN Z, et al. Mechanism research on a bioactive resveratrol- PLA-gelatin porous nano-scaffold in promoting the repair of cartilage defect. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13:7845-7858. [30] ZHONG J, XIANG D, MA X. Prediction and analysis of osteoarthritis hub genes with bioinformatics. Ann Transl Med. 2023;11(2):66. [31] HUANG ZY, LUO ZY, CAI YR, et al. Single cell transcriptomics in human osteoarthritis synovium and in silico deconvoluted bulk RNA sequencing. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(3):475-480. [32] JI Q, ZHENG Y, ZHANG G, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq analysis reveals the progression of human osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(1):100-110. [33] JI ML, JIANG H, LI Z, et al. Sirt6 attenuates chondrocyte senescence and osteoarthritis progression. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):7658. [34] YANG L, WANG S, ZHAO G, et al. Comparison of the toxic mechanism of T-2 toxin and deoxynivalenol on human chondrocytes by microarray and bioinformatics analysis. Toxicol Lett. 2020;321:61-68. [35] SHANG L, MA H, ZHANG X, et al. Docosahexaenoic acid alleviates the excessive degradation of extracellular matrix in the nucleus pulposus by reducing the content of lncRNA NEAT1 to prevent the progression of intervertebral disc degeneration. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2023;50(5):403-414. [36] HUANG M, LIN Y, CHEN X, et al. The value of gene chip detection of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in the diagnosis of nontuberculous mycobacterial lung disease. Ann Palliat Med. 2021;10(6):6438-6445. [37] FUNATO N. New Insights Into Cranial Synchondrosis Development: A Mini Review. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:706. [38] MEO BURT P, XIAO L, HURLEY MM. FGF23 Regulates Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling-Mediated Osteoarthritis in Mice Overexpressing High-Molecular-Weight FGF2. Endocrinology. 2018;159(6):2386-2396. [39] DESHMUKH AP, VASAIKAR SV, TOMCZAK K, et al. Identification of EMT signaling cross-talk and gene regulatory networks by single-cell RNA sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2021;118(19):e2102050118. [40] WYPYCH D, BARANSKA J. Cross-Talk in Nucleotide Signaling in Glioma C6 Cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1202:35-65. [41] MISHRA AK, SHARMA V, MUTSUDDI M, et al. Signaling cross-talk during development: Context-specific networking of Notch, NF-κB and JNK signaling pathways in Drosophila. Cell Signal. 2021;82:109937. |
| [1] | Yang Yifeng, Ye Nan, Wang Lin, Guo Shuaicheng, Huang Jian. Signaling pathway of dexmedetomidine against ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1464-1469. |
| [2] | Yue Yun, Wang Peipei, Yuan Zhaohe, He Shengcun, Jia Xusheng, Liu Qian, Li Zhantao, Fu Huiling, Song Fei, Jia Menghui. Effects of croton cream on JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1186-1192. |
| [3] | Liu Xin, Hu Man, Zhao Wenjie, Zhang Yu, Meng Bo, Yang Sheng, Peng Qing, Zhang Liang, Wang Jingcheng. Cadmium promotes senescence of annulus fibrosus cells via activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1217-1222. |
| [4] | Wei Juan, Li Ting, Huan Mengting, Xie Ying, Xie Zhouyu, Wei Qingbo, Wu Yunchuan. Mechanism by which static exercise improves insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1271-1276. |
| [5] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [6] | Wei Yuanxun, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Zhang Chi, Pan Chengzhen, Wei Zongbo. The mechanism of Notch signaling pathway in osteoporosis and its prevention and treatment with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 587-593. |
| [7] | Wen Huaneng, Lin Run, Wang Yixiao, Wang Bingshui, Liu Lu, Liu Chuanyao, Cai Canxin, Cui Shaoyang, Xu Mingzhu. Effects of electroacupuncture with “Zhi San Zhen” on Notch signaling pathway and synaptic plasticity in 5xFAD mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(32): 5148-5153. |
| [8] | Ren Weiliang, Jiao Yongwei, Zhang Jian, Yang Liying, Yang Qi. Modulatory effect of resveratrol on oxidative stress and inflammatory factors in the joint fluid of rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(32): 5154-5158. |
| [9] | Wu Qixiang, Fang Chenyu, Zhang Lei. Interleukin-1beta enhances migration and adhesion of mesenchymal stem cells in inflammatory environments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(31): 5048-5054. |
| [10] | Cao Jiawei, Ding Shaorui, Tie Hua, Xue Jing, Jia Yuanyuan, Liang Xueyun, Li Feng. Human placental mesenchymal stem cells inhibit occurrence of pulmonary fibrosis by regulating transforming growth factor-beta 1/Smad3 signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(31): 4970-4974. |
| [11] | Teng Yilin, Xi Deshuang, Feng Yanbin, Liang Yu, Deng Hao, Zeng Gaofeng, Zong Shaohui. Indolepropionic acid inhibition of microglial cell M1 polarization for treatment of spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(31): 5010-5016. |
| [12] | Yu Jingwen, Guo Minfang, Zhang Bingxin, Mu Bingtao, Meng Tao, Zhang Huiyu, Ma Cungen, Yin Jinzhu, Song Lijuan, Yu Jiezhong. Astragaloside inhibits astrocyte activation and inflammatory response induced by inflammation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(31): 5022-5028. |
| [13] | Gu Mingxi, Wang Changcheng, Tian Fengde, An Ning, Hao Ruihu, Guo Lin. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of a three-dimensional porous cartilage scaffold made of silk fibroin/gelatin/chitosan [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 366-372. |
| [14] | Qian Longjie, Su Wenli, Zhu Wenxian, Wang Yixin. SRT1720, an activator of silent information regulator 1, alleviates acute traumatic brain injury in a rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4447-4454. |
| [15] | Zhai Sheng, Aikeremujiang • Aerken, Zhang Zheng, Rixiati • Paerhati, Hao Feihu. CircCDR1as/miR-7-5p/RAF1 axis promotes autophagy levels in steroid-induced necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4455-4460. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||