Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (11): 1767-1771.doi: 10.12307/2024.293
Previous Articles Next Articles
Research progress in mitochondrial dynamic changes regulated by exercise
Lin Jianjian1, Song Jie2
- 1University of International Relations, Beijing 100091, China; 2Beijing University of Agriculture, Beijing 100096, China
-
Received:2023-03-23Accepted:2023-05-04Online:2024-04-18Published:2023-07-27 -
Contact:Song Jie, Master, Lecturer, Beijing University of Agriculture, Beijing 100096, China -
About author:Lin Jianjian, Master, Associate professor, University of International Relations, Beijing 100091, China -
Supported by:the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, No. 3262023T25 (to LJJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lin Jianjian, Song Jie. Research progress in mitochondrial dynamic changes regulated by exercise[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(11): 1767-1771.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
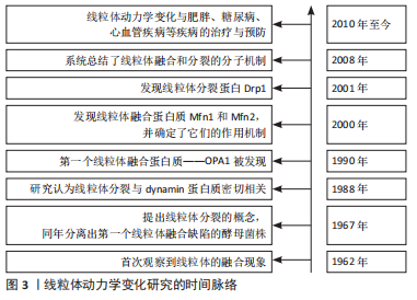
2.1 线粒体动力学相关分子调控机制 对于线粒体动力学变化的研究已经有着六十余年的历史,从最初的现象观察,到最近的与疾病相关(如图3为线粒体动力学变化研究的时间脉络),说明线粒体融合与分裂的动态变化对机体健康的重要作用。由于应激刺激,功能受损的线粒体相遇后通过融合、分裂过程,之后形成一个功能正常的线粒体和一个膜电位较低的线粒体,前者可以进入线粒体循环中重新发挥作用,而后者则不再发挥原有功能,并且通过线粒体自噬过程被选择性降解[8]。Dynamin家族的大GTPase蛋白可以通过寡聚化以及改变构象来驱动膜重塑、分裂和融合[9]。线粒体融合由线粒体融合蛋白(mitochondrial fusion protein,Mfn)1和Mfn 2以及视神经萎缩蛋白1(optic atrophy protein,Opa1)分别介导线粒体外膜(mitochondrial outer membrane,OMM)和线粒体内膜(mitochondrial inner membrane,IMM)融合来调控[10];控制线粒体分裂的蛋白分别是动力相关蛋白(dynamin-related protein1,Drp)1和Drp 2 [11]。同时线粒体动力学变化可以启动自身的自噬程序,清除受损严重的线粒体,这也是细胞的一种自我保护机制[12]。因此,线粒体动力学稳定是保证线粒体正常结构和数量、发挥线粒体正常功能的重要前提条件[13];相反,如果线粒体分裂-融合稳态失衡,也会导致线粒体功能异常的发生。"
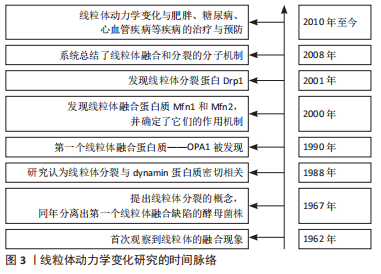
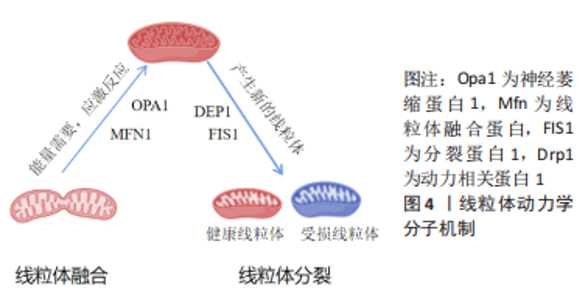
2.1.1 线粒体融合蛋白Mfn1/2与Opa1的调控机制 代谢活跃的细胞通常具有相互连接的线粒体网络,这种线粒体网络结构有利于代谢物的交换,并且将膜电位从线粒体内膜的基质侧传递到内膜外,增加ATP产生,并减少活性氧的产生数量[14-15]。线粒体融合是对轻度受损的线粒体进行潜在修复的过程[16]。正常情况下,已损伤的线粒体可以与邻近的、完整的线粒体融合,并恢复其功能[17]。如图4,线粒体融合由线粒体融合蛋白Mfn以及Opa1分别介导线粒体外膜和线粒体内膜融合来调控的[10]。外膜融合蛋白Mfn有2种同工型:即Mfn1和Mfn2,两者在结构上相似,N端区域包含一个GTP酶结构域和一个疏水性的七肽重复结构,称为HR1;C端区域包含第2个七肽重复域,称为HR2,两者之间存在一个长的跨膜结构域[18]。在线粒体外膜融合过程中,2个邻近线粒体外膜上的Mfn1和Mfn2相互连接以启动线粒体外膜融合,其作用机制如下:首先,Mfn1/2的C端螺旋在线粒体聚集过程中形成同源/异源二聚体,从而使2个相邻线粒体相互靠近[19];其次,由于Mfn1和Mfn2融合蛋白的N端均包含GTP结合域[18],所以在与GTP结合的水解作用下,相邻的线粒体被GTP酶结构域的构象变化所驱动而完全融合[19]。待线粒体外膜融合后,Opa1接着调节线粒体内膜的融合,Opa1蛋白是位于线粒体内膜上的跨膜蛋白,同时也是一种GTP酶,包括一个GTP酶结构域、一个中间区和一个C端GTP酶效应结构域[20]。线粒体融合能够控制线粒体形态以满足细胞的特定需求,所以,任何一种线粒体外膜或线粒体内膜分裂蛋白的增多或融合蛋白的缺失均会导致线粒体网络过度碎片化,从而诱发细胞凋亡。"

2.1.2 线粒体分裂蛋白Drp1与Fis1的调控机制 线粒体分裂的主要目的是通过分离损伤严重的线粒体,从而可以更好地满足细胞的能量需求[21]。如图4,调控线粒体分裂的蛋白主要是Drp1,Drp1是属于动力蛋白家族的三磷酸鸟苷(GTP)酶,GTP酶由一个C端GTP酶效应域和N端的GTP结构域以及一个中间区组成[22]。当受到应激刺激时,细胞线粒体分裂程度增加,以清除有缺陷的线粒体维持细胞内部功能的正常运行[16]。此时,线粒体分裂相关蛋白Drp1发挥了重要作用:当线粒体外膜上的ser616位点被磷酸化后,线粒体外膜蛋白与其他相关蛋白一起募集位于细胞质的Drp1蛋白,并定位到线粒体外膜上[23],之后Drp1形成螺旋状结构,相邻的GTP酶结构域就会靠近GTP并触发其水解,诱导进一步的构象变化,并且促使线粒体外膜收缩[24-25],在线粒体周围形成一个环,此环不断收紧,最终分离成2个独立的线粒体,完成线粒体外膜的分裂过程[26]。 有研究显示,线粒体外膜结合蛋白也可以招募Drp1并且启动线粒体分裂过程,如线粒体动力学蛋白(mito-chondrial dynamics proteins,MiD)-49、分裂蛋白1(fission protein 1,Fis1)和MiD51等[23-24]。另外,除了线粒体外膜分裂机制外,线粒体内膜蛋白18也可以通过与线粒体外膜连接促进线粒体内膜发生分裂[27],但是该过程的具体机制还有待进一步研究[26,28]。 2.2 运动训练与线粒体动力学变化 线粒体是不断发生融合-分裂的动态细胞器,且融合和分裂功能高度协调,始终处于动态平衡的变化中[29]。线粒体融合异常将导致其碎片化加剧,而线粒体过分裂又可以促进线粒体的融合[30]。如果调节线粒体动力学变化的蛋白,如Drp1,Mfn1,Mfn2 和Opa1等表达失调,可能会导致线粒体动力学失衡[31-33],运动训练可以调节以上蛋白表达水平,从而达到自我修复的目的[34]。 2.2.1 运动训练对骨骼肌线粒体动力学变化的影响 (1)长期运动训练对骨骼肌线粒体动力学相关蛋白变化的影响:长期规律性体育运动会改变骨骼肌中的线粒体形态和功能[35]。有研究认为,有氧耐力运动可以优化骨骼肌线粒体功能,提高能量代谢功能,这一机制可能与线粒体融合-分裂过程的相关蛋白关系密切[36]。9周耐力训练可以显著提高大鼠骨骼肌线粒体融合蛋白Mfn1、Mfn2和Opa1表达水平;同时显著降低线粒体分裂蛋白Drp1、Fis1表达,并进一步采用RT-qPCR技术在基因层面得到验证,表明有氧运动对线粒体融合分裂蛋白和基因表达具有调节作用,有氧运动能够有效增加线粒体融合,抑制线粒体分裂[37]。以耐力训练经历的男性为研究对象与无运动经历的受试者相比较,取骨骼肌活检进行相关蛋白检测,发现Mfn1没有显著性差别,而Mfn2的总蛋白表达显著增高,表明有训练经历的受试者骨骼肌线粒体融合水平提升,但是有运动经历的受试者Drp1表达也得到提高,提示骨骼肌线粒体分裂水平也可能提升[38],以上变化也可以说明长期训练可以有效改善骨骼肌线粒体动态平衡。另外,有研究认为长期耐力训练可以有效提高骨骼肌线粒体融合蛋白Mfn2、Opa1的表达水平,同时又可以降低Drp1 Ser616的磷酸化水平,有利于促进线粒体融合,而阻碍线粒体分裂过程[39-40];以上观点得到大部分学者的认可,他们认为适当的耐力训练可以有效提高线粒体融合相关蛋Mfn1/2[41-43]、Opa1[44-45],并且在基因和蛋白水平表达一致。 (2)一次性运动训练对骨骼肌线粒体动力学相关蛋白变化的影响:急性运动对线粒体动力学变化研究出现了不同的结论。有研究认为,一次性长时间剧烈运动抑制了大鼠骨骼肌融合蛋白的Mfn1和Mfn2的基因表达,同时增加了分裂蛋白Fis1的基因表达,并且作者认为这些变化的幅度取决于运动持续时间[46]。刘慧君[47]进行120 min中等负荷小鼠跑台干预,结果显示运动后骨骼肌线粒体Mfn2蛋白显著降低,表明骨骼肌线粒体融合过程可能受到一定程度的抑制。于滢[48]发现大鼠在大负荷运动后,在 0,12,24 和 48 h Mfn2 蛋白表达均显著降低,但是针刺可以逆转这种现象,结果表明运动与针刺对骨骼肌融合功能有着不同的影响,其结合的效果更会明显地改变骨骼肌线粒体动力学。 但是也有研究发现急性耐力运动能增加Mfn1和Mfn2在人体骨骼肌中的表达。实验证明急性运动后24 h人体骨骼肌中Mfn1和Mfn2 mRNA水平分别提高了2.4倍和2.7倍,作者认为运动能使Mfn1和Mfn2基因表达明显增加[49]。急性运动可以有效抑制线粒体融合蛋白Mfn2、Opa1表达,提高Drp1Ser616位点的磷酸化水平,进而抑制线粒体融合,促进线粒体分裂过程[50-51]。 出现以上不同研究结论的原因很多,其中训练形式、训练强度以及研究者关注的不同部位的线粒体变化都会导致研究结论的不一致。 (3)不同运动强度对骨骼肌线粒体动力学相关蛋白变化的影响:训练强度可能是影响线粒体动力学相关蛋白变化的因素之一,长时间大强度间歇训练和低强度的耐力训练可能会对线粒体融合-分裂基因和蛋白表达产生不同的适应性变化。研究表明,长时间、低强度的耐力运动形式可以显著提升Mfn1基因的表达水平,而大强度间歇性运动会使Mfn2 mRNA表达降低,Opa1 mRNA表达强于耐力运动[52]。大鼠4周无负荷游泳训练Mfn2 mRNA表达上调而Drp1表达减少,促进了线粒体融合,可能是运动影响了线粒体的形态和功能;同时力竭性运动可以上调Drp1和Mfn2的蛋白表达水平,从而加快线粒体融合和分裂的动态变化,以便更好地满足运动的能力需要和提高运动的适应水平。漆正堂[53]研究表明,8周低强度有氧耐力训练可以有效上调Mfn1的基因表达水平,但是对Mfn2的基因和蛋白表达没有产生明显的变化;但同时发现间歇性冲刺训练后Mfn1/2的基因表达水平下调,但Fis1基因表达反而呈上升趋势。线粒体动力学的这种基因表达的动态变化趋势可能是为了给细胞提供更多的能量,确保能够维持线粒体能量代谢的最低经济性[54]。中大强度离心跑台运动,大鼠骨骼肌Mfn1蛋白在运动后即刻表达升高,随后下降,Mfn2和Opa1蛋白表达在运动后即刻均有表达下调的趋势,而后升高[52],这表明运动后即刻骨骼肌线粒体融合过程受到抑制,而在运动后的恢复期,线粒体融合过程慢慢恢复到基础水平,并趋于正常。递增负荷跑台运动中大鼠骨骼肌Mfn1/2 mRNA表达水平被抑制,但是运动后Mfn1/2 mRNA水平得到显著性提升。6周负重游泳运动,导致实验大鼠处于疲劳状态,可以显著降低其线粒体融合蛋白1以及融合蛋白2的基因表达水平[55]。一次性大强度运动后,大鼠骨骼肌线粒体呈片段化趋势,Mfn 1和Opa1蛋白表达降低[56],同时Drp1蛋白表达升高[57]。 以上运动影响线粒体动力学与线粒体功能变化不一致的主要原因可能是,运动虽然导致线粒体动力学发生变化,但是变化的程度可能还达不到影响线粒体功能的水平。 2.2.2 运动训练对其他组织线粒体动力学变化的影响 VEERANKI等[58]研究发现,5周中等强度运动后大鼠心肌线粒体Drp1表达水平降低,从而逆转了Mfn2与Drp1的比率,有效缓解了db/db大鼠心肌线粒体的过度分裂状况。以心肌梗死大鼠模型为研究对象,8周有氧运动跑台训练干预后检测大鼠Fis1和Mfn2蛋白表达,发现进行手术治疗后运动组较安静组Fis1和Mfn2表达显著增加,但是未进行手术治疗的大鼠运动组的两种蛋白表达均降低,但心肌线粒体比例增加,表明低强度有氧运动提高心肌线粒体的呼吸效率是有条件约束的,不同的模型下运动影响心肌线粒体动力学变化的情况不同[59]。陶小平等[60]同样研究大鼠一次大负荷跑台运动,发现运动后Drp1 mRNA和蛋白表达升高而Mfn2 mRNA和蛋白表达均下降,运动后30 min组Mfn2 mRNA 和蛋白表达都下降到最低,说明一次大负荷运动后心肌线粒体倾向于分裂而线粒体融合受抑制。对于运动调控线粒体功能的研究来说,目前认为小强度运动对心肌线粒体影响不显著,中等强度运动可以提高线粒体功能,而大强度和力竭运动均可能破坏线粒体结构,造成线粒体障碍[61-62]。 一次性力竭运动可以促进小鼠肝脏中转录因子EB(transcription factor EB,TFEB)、TFE3进入细胞核中,增加核内蛋白含量,核内TFE3数量的增加,又进一步增强肝脏Fis1、Drp1、Opa1、Mfn1/2等基因表达水平,最终促进线粒体融合-分裂过程高效进行,改善线粒体功能状态;但是,当敲除小鼠肝脏中的TFE3时,则显著降低了Mfn1、Fis1和Drp1的基因表达水平,同时线粒体融合分裂能力也在一定程度上被抑制[63]。以上研究提示,TFE3可能参与了运动介导小鼠肝脏线粒体融合与分裂的动态变化过程,进而提高了线粒体的稳定状态。 对脑缺血损伤大鼠模型进行一次性运动干预后发现,OPA1和 COXⅡ/Ⅲ/Ⅳ表达水平提高,作者认为运动可能会通过改善线粒体动力学和功能来起到保护脑缺血损伤大鼠神经的作用[64]。12周中等强度跑台运动可以显著降低阿尔茨海默病小鼠模型海马区与线粒体分裂相关的Drp1、Fis1蛋白表达水平,同时与线粒体融合相关的蛋白Mfn1、Mfn2和Opa1的表达显著上升,作者认为长时间的有氧运动可以逆转阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠海马区线粒体高分裂低融合的现象,从而抑制线粒体相关的细胞凋亡和神经元损伤,有效改善阿尔茨海默病小鼠的病理症状[65]。6周中等强度游泳运动可以有效逆转阿尔茨海默病大鼠Mfn2蛋白表达降低现状,从而提高线粒体质量[66]。 以高脂饮食肥胖大鼠为研究对象,进行为期8周游泳运动后,发现训练干预显著降低了实验大鼠脂肪组织中的Mfn1总蛋白表达水平,同时降低了Drp1和Mfn2的总蛋白表达水平,但是和空白对照组相比没有发生显著性变化(P > 0.05)[67]。这说明大鼠脂肪组织中的线粒体形态和功能的改善可能与提高了Mfn1蛋白表达水平密切相关,以上变化进一步影响了大鼠脂肪细胞的线粒体正常形态及动力学变化。 机体不同组织的线粒体含量不同,运动对其中的线粒体动力学变化的影响也不尽相同。后期的研究中应该加大对运动影响不同组织线粒体动力学变化的影响。 2.3 运动改善线粒体动力学变化的机制研究 关于运动训练改善线粒体动力学变化的机制研究方面,有研究认为TFEB蛋白的表达起到关键作用,以高脂小鼠为实验对象,进行6周有氧耐力训练干预后,发现小鼠骨骼肌中TFEB蛋白和及其转录水平得到提高,同时提高了线粒体融合蛋白Mfn1表达,但是未发现Mfn2、Drp1等其他线粒体蛋白表达水平的变化[68]。因此,作者认为运动通过激活TFEB水平仅影响线粒体融合-分裂过程的部分蛋白表达,故其对线粒体融合-分裂的循环过程可能并未产生整体的影响,但是TFEB参与运动调控的线粒体融合与分裂的具体机制还有待进一步的论证。另外,TOYAMA等[69-70]认为,作为能量感受器的AMP依赖的蛋白激酶(AMP-activated protein kinase,AMPK),很容易被运动训练激活,激活后的AMPK又可以磷酸化MFF Ser155/Ser172位点,进而募集Drp1定位至线粒体外膜,随后起到线粒体分裂程序,并且,通过抑制MFF相应位点的磷酸化还可以起到阻碍线粒体分裂的作用,这说明运动可以通过活化AMPK,进而激活MFF的磷酸化水平,从而达到促进线粒体分裂的目的,这一结论也得到其他学者的认可[71]。生物过程的变化是复杂多样的,运动调控线粒体动力学变化的深层机制还需要进一步的发掘。"

| [1] 杨茂君.你的心头也有星辰大海——带你领略呼吸的奥秘[J].科学通报, 2017,62(35):4077-4082. [2] MURATA D, ARAI K, IIJIMA M, et al. Mitochondrial division, fusion and degradation. J Biochem. 2020;167(3):233-241. [3] CHAN DC. Mitochondrial dynamics and its involvement in disease. Annu Rev Pathol. 2020;15:235-259. [4] GIACOMELLO M, PYAKUREL A, GLYTSOU C, et al. The cell biology of mitochondrial membrane dynamics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(4):204-224. [5] VAN DER BLIEK AM, SHEN Q, KAWAJIRI S. Mechanisms of mitochondrial fission and fusion. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013;5(6):a011072. [6] YI X, GUO W, SHI Q, et al. SIRT3-Dependent mitochondrial dynamics remodeling contributes to oxidative stress-induced melanocyte degeneration in vitiligo. Theranostics. 2019;9(6):1614-1633. [7] ZHANG T, WU P, ZHANG JH, et al. Docosahexaenoic acid alleviates oxidative stress-based apoptosis via improving mitochondrial dynamics in early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2018;38(7):1413-1423. [8] KLUGE MA, FETTERMAN JL, VITA JA. Mitochondria and endothelial function. Circ Res. 2013;112(8):1171-1188. [9] NG MYW, WAI T, SIMONSEN A. Quality control of the mitochondrion. Dev Cell. 2021;56(7):881-905. [10] PERNAS L, SCORRANO L. Mito-morphosis: mitochondrial fusion, fission, and cristae remodeling as key mediators of cellular function. Annu Rev Physiol. 2016;78:505-531. [11] MEMME JM, ERLICH AT, PHUKAN G, et al. Exercise and mitochondrial health. J Physiol. 2021;599(3):803-817. [12] 舒田.运动干预增龄骨骼肌的线粒体UPR机制研究[D].天津:天津体育学院,2020. [13] 陈茉,文颖娟,赵欢,等.中医药调控线粒体质量控制治疗糖尿病心肌病研究进展[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2021,27(21):242-250. [14] HAILESELASSIE B, JOSHI AU, MINHAS PS, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction mediated through dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1) propagates impairment in blood brain barrier in septic encephalopathy. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):36. [15] ZHAO G, CAO K, XU C, et al. Crosstalk between mitochondrial fission and oxidative stress in paraquat-induced apoptosis in mouse alveolar type II cells. Int J Biol Sci. 2017;13(7):888-900. [16] YOULE RJ, VAN DER BLIEK AM. Mitochondrial fission, fusion, and stress. Science. 2012;337(6098):1062-1065. [17] CHAN DC. Mitochondrial fusion and fission in mammals. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2006;22:79-99. [18] COHEN MM, TARESTE D. Recent insights into the structure and function of Mitofusins in mitochondrial fusion. F1000Res. 2018;7:F1000 Faculty Rev-1983. [19] KOSHIBA T, DETMER SA, KAISER JT, et al. Structural basis of mitochondrial tethering by mitofusin complexes. Science. 2004;305(5685):858-862. [20] LI D, WANG J, JIN Z, et al. Structural and evolutionary characteristics of dynamin-related GTPase OPA1. PeerJ. 2019;7:e7285. [21] RAFELSKI SM. Mitochondrial network morphology: building an integrative, geometrical view. BMC Biol. 2013;11:71. [22] KALIA R, WANG RY, YUSUf A, et al. Structural basis of mitochondrial receptor binding and constriction by DRP1. Nature. 2018;558(7710):401-405. [23] LIU R, CHAN DC. The mitochondrial fission receptor Mff selectively recruits oligomerized Drp1. Mol Biol Cell. 2015;26(24):4466-4477. [24] MEARS JA, LACKNER LL, FANG S, et al. Conformational changes in Dnm1 support a contractile mechanism for mitochondrial fission. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011;18(1):20-26. [25] LEE JE, WESTRATE LM, WU H, et al. Multiple dynamin family members collaborate to drive mitochondrial division. Nature. 2016;540(7631):139-143. [26] SHARMA A, SMITH HJ, YAO P, et al. Causal roles of mitochondrial dynamics in longevity and healthy aging. EMBO Rep. 2019;20(12):e48395. [27] TONDERA D, CZAUDERNA F, PAULICK K, et al. The mitochondrial protein MTP18 contributes to mitochondrial fission in mammalian cells. J Cell Sci. 2005;118(Pt 14):3049-3059. [28] YU R, LIU T, JIN SB, et al. MIEF1/2 orchestrate mitochondrial dynamics through direct engagement with both the fission and fusion machineries. BMC Biol. 2021;19(1):229. [29] 刘刚,门运政,童旭辉,等.线粒体融合与裂变在右美托咪定减轻小鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤中的作用及其机制[J].南方医科大学学报,2020,40(4): 463-468. [30] HU C, HUANG Y, LI L. Drp1-Dependent mitochondrial fission plays critical roles in physiological and pathological progresses in mammals. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(1):144. [31] BAK DW, WEERAPANA E. Cysteine-mediated redox signalling in the mitochondria. Mol Biosyst. 2015;11(3):678-697. [32] TYUMENTSEV MA, STEFANOVA NA, MURALEVA NA, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction as a predictor and driver of alzheimer’s disease-like pathology in OXYS rats. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;63(3):1075-1088. [33] WILLEMS PH, ROSSIGNOL R, DIETEREN CE,et al. Redox homeostasis and mitochondrial dynamics. Cell Metab. 2015;22(2):207-218. [34] 赵永才.运动干预骨骼肌、心肌线粒体动力学研究现状——心肌线粒体动力学研究展望[J].体育科学,2016,36(11):75-81+96. [35] HERZIG S, LONG F, JHALA US, et al. CREB regulates hepatic gluconeogenesis through the coactivator PGC-1. Nature. 2001;413(6852):179-183. [36] JI LL, WU E, THOMAS DP. Effect of exercise training on antioxidant and metabolic functions in senescent rat skeletal muscle. Gerontology. 1991;37(6):317-325. [37] 胡萌.线粒体融合分裂在有氧运动改善自发性高血压大鼠心功能中的作用及机制研究[D].西安:陕西师范大学,2021. [38] TARPEY MD, DAVY KP, MCMILLAN RP, et al. Skeletal muscle autophagy and mitophagy in endurance-trained runners before and after a high-fat meal. Mol Metab. 2017;6(12):1597-1609. [39] ARRIBAT Y, BROSKEY NT, GREGGIO C, et al. Distinct patterns of skeletal muscle mitochondria fusion, fission and mitophagy upon duration of exercise training. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2019;225(2):e13179. [40] AXELROD CL, FEALY CE, MULYA A, et al. Exercise training remodels human skeletal muscle mitochondrial fission and fusion machinery towards a pro-elongation phenotype. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2019;225(4):e13216. [41] BUSQUETS-CORTÉS C, CAPÓ X, MARTORELL M, et al. Training and acute exercise modulates mitochondrial dynamics in football players’ blood mononuclear cells. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2017;117(10):1977-1987. [42] LITTLE JP, GILLEN JB, PERCIVAL ME, et al. Low-volume high-intensity interval training reduces hyperglycemia and increases muscle mitochondrial capacity in patients with type 2 diabete. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2011;111(6):1554-1560. [43] PERRY CG, LALLY J, HOLLOWAY GP, et al. Repeated transient mRNA bursts precede increases in transcriptional and mitochondrial proteins during training in human skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 2010;588(Pt 23):4795-4810. [44] JU JS, JEON SI, PARK JY, et al. Autophagy plays a role in skeletal muscle mitochondrial biogenesis in an endurance exercise-trained condition. J Physiol Sci. 2016;66(5):417-430. [45] FEALY CE, MULYA A, LAI N, et al. Exercise training decreases activation of the mitochondrial fission protein dynamin-related protein-1 in insulin-resistant human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol (1985). 20141;117(3):239-245. [46] DING H, JIANG N, LIU H, et al. Response of mitochondrial fusion and fission protein gene expression to exercise in rat skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1800(3):250-256. [47] 刘慧君. 过氧化氢、Ca~(2+)对骨骼肌线粒体移动和动态变化的调节[D].北京:中国人民解放军军事医学科学院,2010. [48] 于滢.一次大负荷运动对大鼠骨骼肌线粒体分布和功能影响及针刺干预作用[D].北京:北京体育大学,2015. [49] CARTONI R, LÉGER B, HOCK MB, et al. Mitofusins 1/2 and ERRalpha expression are increased in human skeletal muscle after physical exercise. J Physiol. 2005;567(Pt 1):349-358. [50] KRUSE R, PEDERSEN AJ, KRISTENSEN JM, et al. Intact initiation of autophagy and mitochondrial fission by acute exercise in skeletal muscle of patients with Type 2 diabetes. Clin Sci (Lond). 2017;131(1):37-47. [51] MOORE TM, ZHOU Z, COHN W, et al. The impact of exercise on mitochondrial dynamics and the role of Drp1 in exercise performance and training adaptations in skeletal muscle. Mol Metab. 2019;21:51-67. [52] 刘晓然,于滢,王蕴红,等.大负荷运动对大鼠骨骼肌线粒体融合和分裂蛋白的影响[J].首都体育学院学报,2016,28(02):167-171. [53] 漆正堂.骨骼肌线粒体对不同训练方式的适应及其基因应答机制的研究[D].上海:华东师范大学,2009. [54] 孙卫东,丁虎,刘晓然,等.骨骼肌线粒体对细胞能量需求的快速应答: mfn1/2与fis1基因在急性运动中的动态表达[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2008,27(5):544-550. [55] 娄旭佳,阮蓉,金其贯,等.白藜芦醇干预运动性疲劳模型大鼠线粒体动力学的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(17):2625-2630. [56] 白胜超. 一次大负荷离心运动后骨骼肌线粒体分裂的机制及针刺干预研究[D].北京:北京体育大学,2018. [57] 白胜超,陈圣菊,尚画雨等.针刺干预对大鼠离心运动性骨骼肌损伤后线粒体分裂的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2020,39(11):878-887. [58] VEERANKI S, GIVVIMANI S, KUNDU S, et al. Moderate intensity exercise prevents diabetic cardiomyopathy associated contractile dysfunction through restoration of mitochondrial function and connexin 43 levels in db/db mice. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016;92:163-173. [59] 刘涛. 运动对慢性心衰心肌线粒体功能、生物合成与融合分裂的调节作用[D].北京:北京体育大学,2009. [60] 陶小平,彭雄辉.一次大负荷跑台运动后大鼠心肌能量代谢及线粒体形态动力学的变化研究[J].北京体育大学学报,2014,37(3):64-70. [61] SCHOEPE M, SCHREPPER A, SCHWARZER M, et al. Exercise can induce temporary mitochondrial and contractile dysfunction linked to impaired respiratory chain complex activity. Metabolism. 2012;61(1):117-126. [62] TONDERA D, GRANDEMANGE S, JOURDAIN A, et al. SLP-2 is required for stress-induced mitochondrial hyperfusion. EMBO J. 2009;28(11):1589-1600. [63] PASTORE N, VAINSHTEIN A, KLISCH TJ, et al. TFE3 regulates whole-body energy metabolism in cooperation with TFEB. EMBO Mol Med. 2017;9(5):605-621. [64] NAVARRO A, BOVERIS A. Brain mitochondrial dysfunction in aging: conditions that improve survival, neurological performance and mitochondrial function. Front Biosci. 2007;12:1154-1163. [65] 李百侠.线粒体分裂融合与转运在运动预防AD中的机制研究[D].上海:华东师范大学,2020. [66] KOU X, LI J, LIU X, et al. Swimming attenuates d-galactose-induced brain aging via suppressing miR-34a-mediated autophagy impairment and abnormal mitochondrial dynamics. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2017;122(6):1462-1469. [67] 欧秀伶,于宝明,孙剑.运动对高脂饮食性肥胖大鼠棕色脂肪组织线粒体形态和动力学的影响及可能机制的研究[J].山东体育学院学报,2013, 29(1):70-73. [68] 钱帅伟,孙易,漆正堂,等.运动对线粒体稳态调控机制的研究述评——基于运动介导TFEB调节线粒体质量控制的关键机制探讨[J].体育科学, 2020,40(2):70-82. [69] TOYAMA EQ, HERZIG S, COURCHET J, et al. AMP-activated protein kinase mediates mitochondrial fission in response to energy stress. Science. 2016;351 (6270):275-281. [70] ZHANG CS, LIN SC. AMPK promotes autophagy by facilitating mitochondrial fission. Cell Metab. 20168;23(3):399-401. [71] 张坦,孙易,丁树哲.运动介导AMPK调控线粒体质量控制的机制研究进展[J].中国体育科技,2018,54(6):97-102. |
| [1] | Wu Jing, Yao Yingce, Yang Xiaowei, Xue Boshi, Zhao Jianbin, Yang Chen, Luan Tianfeng, Zhou Zhipeng. Intervention of muscle strength training combined with neuromuscular electrical stimulation on lower limb function and biomechanical changes in patients with patellofemoral pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1365-1371. |
| [2] | Yu Weijie, Liu Aifeng, Chen Jixin, Guo Tianci, Jia Yizhen, Feng Huichuan, Yang Jialin. Advantages and application strategies of machine learning in diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1426-1435. |
| [3] | Wei Juan, Li Ting, Huan Mengting, Xie Ying, Xie Zhouyu, Wei Qingbo, Wu Yunchuan. Mechanism by which static exercise improves insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1271-1276. |
| [4] | Lou Guo, Zhang Yan, Fu Changxi. Role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in exercise preconditioning-induced improvement of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1283-1288. |
| [5] | Lin Zeyu, Xu Lin. Research progress in gout-induced bone destruction mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1295-1300. |
| [6] | Cheng Jie, Wang Jihong, Zhang Pei. Functional exercise for tendon adhesion in a model of deep flexor tendon II injury of the third toe [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1161-1167. |
| [7] | Wang Ji, Zhang Min, Li Wenbo, Yang Zhongya, Zhang Long. Effect of aerobic exercise on glycolipid metabolism, skeletal muscle inflammation and autophagy in type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1200-1205. |
| [8] | Ruan Rong, Lou Xujia, Jin Qiguan, Zhang Libing, Xu Shang, Hu Yulong. Effect of resveratrol on gluconeogenesis in exercise-induced fatigue rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1229-1234. |
| [9] | Ma Shuwei, He Sheng, Han Bing, Zhang Liaoyun. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of animals with acute liver failure: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1137-1142. |
| [10] | Sun Teng, Han Yu, Wang Shuang, Li Jialei, Cao Jimin. miR-20a regulates pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1021-1028. |
| [11] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [12] | Liu Zhiyang, Fu Zeting, Xia Yu, Ding Haili. The role of BMAL1 and MyoD in exercise-induced skeletal muscle damage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 510-515. |
| [13] | Zhu Xiaofeng, Chen Weiwei, Huang Jian. Effects of maternal high-fat diet and exercise intervention on insulin sensitivity and the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus in male offspring mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 556-561. |
| [14] | Wang Shijie, Wen Dengtai, Wang Jingfeng, Gao Yinghui. Mammalian target of rapamycin in relation to exercise, high fat/high salt diet, and aging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 574-580. |
| [15] | Zhang Ming, Wang Bin, Jia Fan, Chen Jie, Tang Wei. Application of brain-computer interface technology based on electroencephalogram in upper limb motor function rehabilitation of stroke patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 581-586. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||