Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (19): 3097-3103.doi: 10.12307/2024.152
Previous Articles Next Articles
Improving the strategy of mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of flap ischemia-reperfusion injury
He Bo1, He Zhijun2, Li Jinpeng2, Liu Tao2, Ma Suilu1, Wei Xiaotao1, Wang Weiwei1, Xie Jing1
- 1Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730030, Gansu Province, China; 2Gansu Provincial Hospital of TCM, Lanzhou 730050, Gansu Province, China
-
Received:2023-01-28Accepted:2023-05-19Online:2024-07-08Published:2023-09-26 -
Contact:He Zhijun, Professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Gansu Provincial Hospital of TCM, Lanzhou 730050, Gansu Province, China Li Jinpeng, Associate chief physician, Master, Gansu Provincial Hospital of TCM, Lanzhou 730050, Gansu Province, China -
About author:He Bo, Master candidate, Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730030, Gansu Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81660802 (to HZJ); Gansu Province Traditional Chinese Medicine Project, No. GZKZ-2020-2 (to HZJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
He Bo, He Zhijun, Li Jinpeng, Liu Tao, Ma Suilu, Wei Xiaotao, Wang Weiwei, Xie Jing. Improving the strategy of mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of flap ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(19): 3097-3103.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
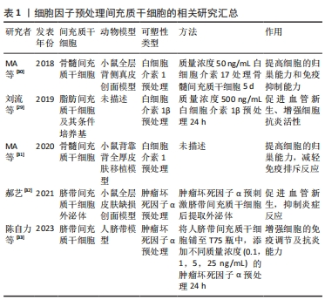
自20世纪70年代间充质干细胞被发现以来,关于间充质干细胞的研究领域在不断扩展,并逐步从实验研究迈入临床,在许多疾病的治疗中发挥着重要作用。间充质干细胞在皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤中的应用开辟了皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤治疗的新道路,展现出巨大潜力,然而间充质干细胞的固有缺陷也限制了其广泛应用。鉴于间充质干细胞在治疗皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤中存在的缺陷,一些学者开始尝试用预处理、基因修饰、药物联合应用及生物材料封装干细胞等方法,这些不仅克服了间充质干细胞的缺陷,还提高了其治疗效果,文章也将从这4个方面进行综述。 2.1 预处理 是一种用于改善组织或细胞群对特定环境的反应的策略。近年来,研究发现预处理间充质干细胞不仅可以提高间充质干细胞存活率而且能促进其增殖、迁移及分化[19-23],能够有效促使间充质干细胞向损伤部位归巢[24]。目前预处理策略已被广泛应用于治疗组织或器官的缺血再灌注损伤,研究表明,利用细胞因子、低氧和药物等不同方法对间充质干细胞进行预处理,可以有效治疗皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤,提高皮瓣移植的存活率。 2.1.1 细胞因子处理 间充质干细胞含有多种细胞因子和营养因子,具有免疫调节特性和抗炎能力等生物学功能。众所周知,在损伤组织的修复和愈合阶段,炎症是影响组织修复和愈合的重要原因,损伤组织的炎症主要是由血小板和巨噬细胞释放炎症递质如白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α引起[25-26],而白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α在预处理间充质干细胞后能够显著增强间充质干细胞的抗炎活性和对组织损伤的修复能力[27-28]。 刘流等[29]研究发现,白细胞介素1β预处理脂肪间充质干细胞能够促进血管内皮生长因子蛋白和前列腺素E2的分泌并上调COX-2蛋白的表达,促进血管新生;而预处理其条件培养基通过上调PMA-U937巨噬细胞的白细胞介素10 mRNA和CD163的表达,促进PMA-U937细胞M2极化,提高脂肪间充质干细胞的抗炎活性,促进损伤组织的修复和再生。白细胞介素17是一种关键的促炎因子,主要由Th17细胞分泌,能够强间充质干细胞的免疫抑制作用和对T细胞增殖的抑制作用。MA等[30]在研究中发现,白细胞介素17预处理骨髓间充质干细胞不仅增加了骨髓间充质干细胞的数量,还下调干扰素(IFN-g)水平、上调转化生长因子β和白细胞介素10水平及Treg亚群百分比,表明白细胞介素17预处理可以增强骨髓间充质干细胞的免疫抑制能力和归巢能力。不仅如此,白细胞介素17预处理骨髓间充质干细胞还能够减轻皮肤移植中的免疫排斥反应[31],延长移植皮肤的生存时间。郝艺[32]在肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的脐带间充质干细胞外泌体的研究中发现,肿瘤坏死因子α预处理能够促进人包皮成纤维细胞(HFF)的迁移和增殖及血管内皮细胞的成管,并能够降低白细胞介素6、转化生长因子β和α平滑肌肌动蛋白(α-SMA)的mRNA的表达,进而促进损伤组织的修复和再生,且其效果优于未经预处理的脐带间充质干细胞外泌体。既然肿瘤坏死因子α预处理能够增强脐带间充质干细胞在促进组织愈合中的能力,那么不同质量浓度肿瘤坏死因子α的效果是否一样呢?有研究发现,不同质量浓度的肿瘤坏死因子α预处理的脐带间充质干细胞通过核因子κB信号通路上调白细胞介素10的表达水平和下调肿瘤坏死因子α的表达水平[33],并能促进Treg细胞增殖及抑制T细胞增殖,从而显著增强脐带间充质干细胞的抗炎和免疫调节功能,且1 ng/mL的肿瘤坏死因子α预处理的作用效果最好。上述研究表明,细胞因子预处理间充质干细胞在提高细胞的归巢能力和免疫调节及抗炎能力方面作用显著,并有一定的促进血管新生能力,这与细胞因子的抗炎特性有关。未来应对各种细胞因子预处理作用进行比较研究,筛选最佳效果和最佳浓度的细胞因子。 文章总结了细胞因子预处理间充质干细胞的相关研究进展[29-33],见表1。"
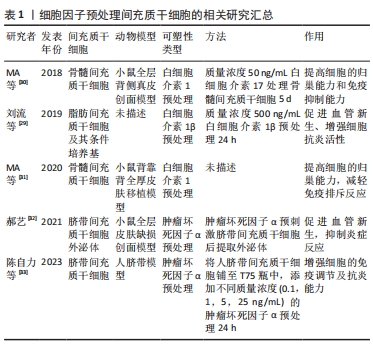
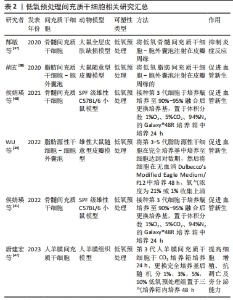
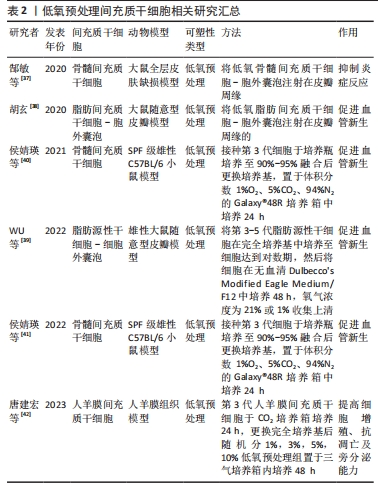
2.1.2 低氧预处理 氧对于几乎所有的生命都是必需的,它维持能量代谢及细胞的功能,间充质干细胞在体内存在于一般氧张力较低的微环境中(即1%-5%O2),实验证明,适度的低氧并不引发间充质干细胞凋亡,反而可以刺激间充质干细胞合成促生存因子,如血管内皮生长因子、胰岛素样生长因子1、成纤维细胞生长因子2和肝细胞生长因子[34]。虽然缺氧降低了间充质干细胞的细胞活力和增殖,但随后的复氧促进了干细胞的恢复,缺氧复氧过程提高了间充质干细胞中促生存基因和各种营养因子的表达[35]。此外,在体外确定的微环境中,缺氧复氧过程还可以促进间充质干细胞的多能性[36],这些都有利于促进皮瓣组织的修复和再生。 郜敏等[37]研究发现,低氧预处理脂肪间充质干细胞条件培养基可以通过抑制炎症细胞浸润来抑制局部缺血组织的炎症反应,进而提高损伤皮肤组织的修复和再生。此外,低氧预处理脂肪间充质干细胞外囊泡还可以提高血管内皮生长因子和缺氧诱导因子1α的表达,通过促进皮瓣组织血管新生来提高皮瓣移植的存活率[38-39]。侯婧瑛等[40]在缺氧预处理骨髓间充质干细胞的研究中发现,缺氧预处理骨髓间充质干细胞通过激活缺氧诱导因子1α/MALAT1/血管内皮生长因子A通路,提高了缺氧诱导因子1α、血管内皮生长因子A和肺腺癌转移相关转录物1(MALAT1)的表达,提高了间充质干细胞的存活率并促进了血管新生,而且还通过激活MALAT1靶向抑制miR-195提高间充质干细胞存活率和毛细血管的新生,改善了局部组织的微循环[41]。 既然低氧预处理,改善间充质干细胞的生物学特性,提高间充质干细胞的治疗效力,那体积分数越低的氧气预处理是否效果就越好,唐建宏等[42]利用体积分数1%,3%,5%,10%和21%的低氧预处理人羊膜间充质干细胞,发现不同体积分数的低氧预处理都能提高人羊膜间充质干细胞的增殖、抗凋亡和旁分泌细胞因子的能力,且体积分数1%氧气预处理效果最好。但这项研究存在一个缺陷,即没有确定最佳的体积分数,日后还需进一步研究。文章总结了低氧预处理间充质干细胞的相关研究进展,见表2。"
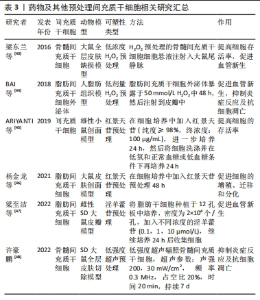
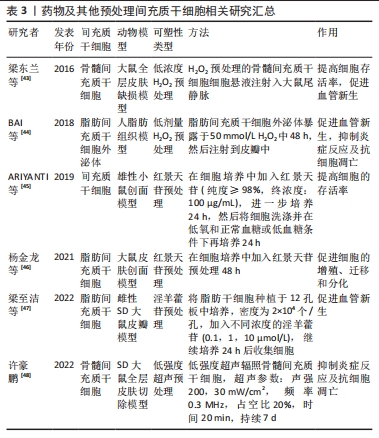
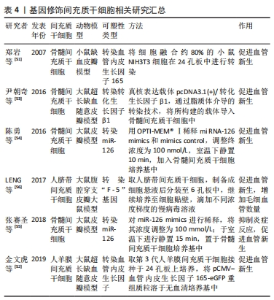
2.1.3 药物及其他预处理 药物预处理被认为是在间充质干细胞移植过程中防止缺血损伤并进一步激活内源性细胞再生机制的原因。高浓度H2O2暴露能够导致细胞损伤甚至死亡,而一定低剂量H2O2能够提高细胞对氧化耐受的能力,梁东兰等[43]在低浓度过氧化氢预处理骨髓间充质干细胞的研究中发现,H2O2预处理能够显著提高间充质干细胞存活率和存活时间,促进血管新生,进而促进损伤组织的修复。BAI等[44]研究表明,低剂量H2O2刺激脂肪间充质干细胞衍生外泌体可促进缺血再灌注损伤损伤后皮瓣新生血管形成,减轻皮瓣的炎症反应,减少细胞凋亡,提高皮瓣存活率。红景天苷是藏药红景天中的活性成分,能够调控间充质干细胞的增殖、迁移和分化,而且红景天苷预处理不仅能够提高间充质干细胞的存活率[45],还能提高损伤组织中的CK-19、Ⅰ型胶原、Ⅲ型胶原和CD31的表达来促进脂肪间充质干细胞增殖、迁移及向血管内皮和血管平滑肌的分化,进而促进损伤组织的修复和再生[46]。淫羊藿苷是一种天然类黄酮,近期在一项淫羊藿苷预处理脂肪的研究中发现淫羊藿苷预处理能够通过提高血管内皮生长因子、胰岛素样生长因子2(IGF-2)和血小板源性生长因子BB(PDGF-BB)蛋白的表达来促进血管新生,提高大鼠超长随意皮瓣存活率[47]。除了药物预处理外,超声是一种安全、有效的疗法,主要依靠机械效应发挥作用。许豪鹏[48]在低强度超声预处理骨髓间充质干细胞研究中发现,低强度超声预处理可以促进细胞因子血小板衍生因子、基质细胞衍生因子1和肿瘤坏死因子α的分泌,增加损伤组织内皮细胞、巨噬细胞以及肥大细胞的数量,还能通过Bcl-2凋亡路径下调皮损区Bax相关mRNA和上调Bcl-2相关mRNA表达,减少细胞凋亡。上述研究汇总见表3。"
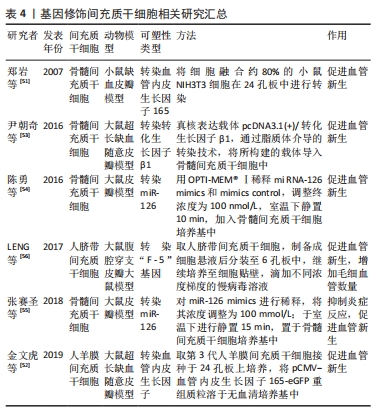
预处理能够改善间充质干细胞在体外和体内的生物活性,提高对损伤组织的修复能力,然而预处理间充质干细胞仍然存在很多问题:①目前未研究出最佳的预处理方案;②预处理是否对间充质干细胞有不良作用;③未研究其是否存在致瘤性;④目前还没有一个简单的调控途径来保护间充质干细胞免受损伤。因此未来研究者们仍然需要投入更多理论的研究和临床应用,以便确定预处理间充质干细胞最佳治疗方案以及明确其作用机制。 2.2 基因修饰 单纯间充质干细胞移植会受诸多影响因素而造成移植后早期细胞减少,作用减弱,而基因修饰为间充质干细胞充分发挥作用提供了一个新的契机。移植前对间充质干细胞进行基因修饰,不仅可以提高它们的存活率,发挥干细胞归巢和修复的作用,同时还可以大量表达如细胞因子等目的基因,扩大间充质干细胞治疗范围,增强在细胞治疗中的功能,提高损伤部位的修复概率和修复效果。很多实验结果证明经过基因修饰的间充质干细胞明显较未修饰的间充质干细胞在组织修复中更加有效。 血管内皮生长因子具有很强的促内皮细胞增殖作用,与新生血管的关系密切,是潜在的血管形成激活物[49]。血管内皮生长因子能够通过特异性作用于血管内皮细胞来维持血管的正常状态和血管的完整性,进而提高血管通透性和舒张血管并诱导微血管新生,最后促进组织血管化[50],提高毛细血管的数量。鉴于血管内皮生长因子在促进血管新生方面独特的作用,一些学者开始尝试利用血管内皮生长因子对间充质干细胞进行修饰,经修饰后皮瓣组织的毛细血管数量和密度都有显著的提升,皮瓣成活率也明显提高,说明血管内皮生长因子转导的间充质干细胞可诱导皮瓣新生血管的形成,改善微循环,进而提高皮瓣的存活率[51-52]。既往研究表明,转化生长因子β1在血管生成过程中具有关键性的作用,尹朝奇等[53]在研究中发现,经转染转化生长因子β1的间充质干细胞能够显著增加皮瓣组织中的血管数量和密度,改善皮瓣组织微循环,提高移植皮瓣存活率。 miR-126是在内皮细胞中特异性高表达的一个小分子miRNA,对于新生血管的形成和发育具有重要的促进作用,同时还能显著抑制血管的炎症反应,显著调节着血管的新生。陈勇等[54]在转染miR-126的骨髓间充质干细胞研究发现,miR-126不仅能够提高激活血管内皮生长因子和成纤维细胞生长因子等介导PI3k和MAPK信号通路,来促进pAKT和pERK1/2的活化,还能抑制血管细胞黏附分子1(vascular cell adhesion molecule-1,VCAM-1)和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达,来发挥促进血管新生和抑制炎症反应的作用,进而提高移植皮瓣的存活率。此外,骨髓间充质干细胞中miR-126高表达还能促进皮瓣组织中血管新生腺管蛋白活化来促进血管新生,同时还可以通过降低VCAM-1、MIP-1α和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达水平来抑制炎症反应,进而提高皮瓣的存活率[55]。热休克蛋白90对损伤组织的修复具有显著的促进作用,而且在热休克蛋白90基因序列中起这一主要作用的是“F-5”基因。因此LENG等[56]尝试F-5基因转染人脐带间充质干细胞治疗皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤,结果发现,经转染“F-5”基因的人脐带间充质干细胞皮瓣组织的毛细血管数量和密度显著增加,皮瓣组织的愈合效果更好,愈合时间也更短,移植皮瓣的存活率明显提高。 肝细胞生长因子由间充质干细胞分泌,在间充质干细胞的治疗中起着重要作用。有报道称肝细胞生长因子基因的修饰可以提高间充质干细胞的治疗效果,能够显著抑制细胞凋亡和炎症,促进血管生成。张月等[57]在研究中发现肝细胞生长因子修饰的脂肪间充质干细胞通过促进Akt信号通路及抑制核因子κB信号通路来促进Ⅰ型和Ⅲ型胶原、血管内皮生长因子及白细胞介素10的表达,并抑制白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达来诱导血管新生和抑制炎症反应,从而促进损伤组织的修复和再生。不仅如此,肝细胞生长因子修饰脂肪间充质干细胞外泌体还能通过激活PI3K/Akt信号通路来促进损伤组织中内皮型一氧化氮合酶的表达,诱导血管的新生,进而促进损伤组织的愈合[58]。 间充质干细胞技术与基因治疗技术的紧密结合,增强了间充质干细胞的功能,成为治疗皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤重要方法。尽管基因修饰具有巨大的作用,然而,转基因间充质干细胞仍然存在生物分布、生存时间、已定义的分化比例和毒性等问题,最重要的是,缺乏评估转基因间充质干细胞安全性和有效性的临床试验。因此研究者们还需要更多理论研究和临床试验。 文章总结了基因修饰间充质干细胞相关研究进展[51-56],见表4。"
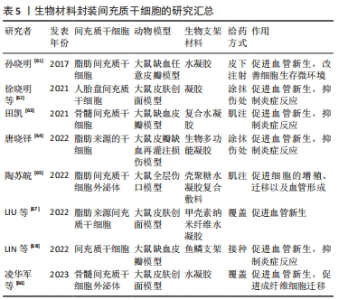
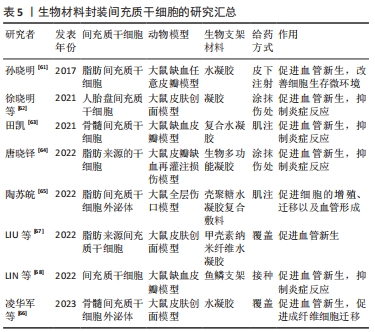
2.3 生物材料封装 尽管间充质干细胞治疗在组织工程中显示出无与伦比的潜力,但在调控干细胞移植、存活、黏附、迁移、干性维持、增殖、分化、细胞因子、生长因子和外泌体的分泌等行为(或命运)方面仍然困难。近年,生物支架的出现和发展有效解决了这类问题,生物支架负载间充质干细胞植入到损伤部位不仅影响了干细胞的行为和命运,还显著提升了间充质干细胞治疗潜力。由于水凝胶具有模拟细胞外基质的能力、良好的适应性和生物相容性、无创给药和可调的理化性质等优点,成为间充质干细胞组织工程的理想生物活性支架材料[59],广泛应用于间充质干细胞移植治疗、组织工程支架、药物输送和细胞包封等领域[60]。孙晓明[61]研究发现,水凝胶包裹脂肪间充质干细胞可促进局部毛细血管的新生,增加微血管数量,改善细胞生存微环境,进而提高皮瓣移植的存活率。此外,负载间充质干细胞的水凝胶不仅可以通过促进皮瓣组织血管新生、增加移植皮瓣组织的血管数量和密度来改善局部缺血缺氧的微环境,还能够通过抑制皮瓣组织的炎症反应,来提高移植皮瓣的存活率[62-64]。 众所周知,外泌体具有间充质干细胞相似的功能,能够促进细胞的增殖、迁移以及血管形成能力。陶苏皖[65]发现外泌体/水凝胶复合材料能够通过持续有效地释放外泌体,增强外泌体的作用效力,促进损伤组织的修复和再生。凌华军等[66]在负载外泌体水凝胶的研究中发现,负载外泌体的水凝胶不仅可以增加损伤组织的外泌体的数量和保留时间,还可以促进成纤维细胞的迁移,诱导血管新生,增加毛细血管数量,促进组织的修复和再生。甲壳素纳米纤维的多孔结构模拟了天然细胞外基质的纤维结构,是一种很好的伤口敷料材料,促进细胞播种,允许养分、氧气和废物扩散,并能吸收伤口分泌物,防止伤口过度脱水和细菌感染。LIU等[67]发现脂肪间充质干细胞负载的β-甲壳素纳米纤维水凝胶激活了转化生长因子β/smad信号通路,降低了Smad的磷酸化以及基质金属蛋白酶抑制剂1、血管内皮生长因子R和α平滑肌蛋白的表达,显著促进血管生成,进而促进损伤组织的愈合和修复。 除了常用的水凝胶外,其他一些生物支架的作用也非常显著。鱼鳞支架通过脱细胞脱钙过程获得,通过脱细胞脱钙过程,残留的各种生物活性物质被很好地保存在鱼鳞支架中,而且鱼鳞脱钙后表面保留了定向胶原纳米纤维,为细胞定向生长提供了适宜的环境。这些特性明显由于水凝胶可能成为一种优秀的3D组织工程支架。LIN等[68]研究发现,装载间充质干细胞的鱼鳞支架能有效促进血管生成,调节巨噬细胞向M2表型的极化,减轻皮瓣周围和坏死区域的炎症反应,从而提高随机皮瓣的存活率。 上述的实验研究表明,利用生物材料封装间充质干细胞移植到损伤组织,可以显著提高间充质干细胞在促进血管新生和抑制炎症反应中的作用,具有极大的应用前景。然而目前间充质干细胞大多都在2D培养,与传统的2D培养相比,间充质干细胞在3D培养支架中的生长状态接近于自然生长状态,间充质干细胞在形态学、功能结构、基因表达等方面的表现更加优异,治疗效果也会更好,因此日后应着重对3D生物材料研发和应用。 文章总结了生物材料封装间充质干细胞的研究进展[61-68],见表5。"
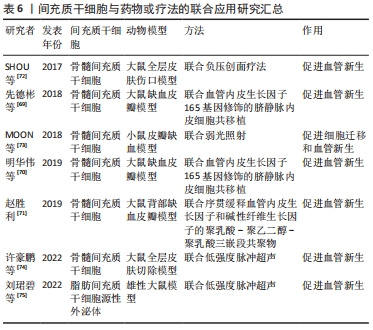
2.4 联合疗法 除了上述的方法外,间充质干细胞和一些药物或治疗方法等的联合应用也是治疗皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤、提高移植皮瓣存活率常用的方法。间充质干细胞能够自己旁分泌促血管新生因子,骨髓间充质干细胞与血管内皮生长因子165基因修饰的脐静脉内皮细胞共移植,可以显著上调血管内皮生长因子蛋白表达,增加毛细血管的数量和密度,促进血管新生,改善微循环,提高缺血皮瓣存活率,且共移植的促血管生成能力强于单独移植[69-70]。而骨髓间充质干细胞与碱性成纤维细胞生长因子联用同样也能促进血管新生,赵胜利[71]研究发现,将骨髓间充质干细胞与序贯缓释血管内皮生长因子和碱性成纤维细胞生长因子的聚乳酸-聚乙二醇-聚乳酸三嵌段共聚物三者联合应用不仅可以促进缺血的皮瓣组织血管新生,改善微循环,还能刺激骨髓间充质干细胞向内皮样细胞分化,促进缺血皮瓣组织的修复,提高皮瓣的存活率。 负压创面疗法因能促进损伤组织的微循环而被广泛用于损伤组织的修复和皮肤移植中。SHOU 等[72]在体内实验中发现,骨髓间充质干细胞联合负压创面疗法可以显著上调缺血皮肤组织中血管内皮生长因子、NG2和CD31的表达,促进皮肤组织的血管新生,改善微循环,提高了损伤皮肤组织的修复和再生。众所周知,低水平的可见光或近红外光可以减轻疼痛、炎症和水肿,促进伤口、深层组织和神经的愈合,并防止组织损伤。既往研究表明,低强度光照射对血管生成和血管生成均有重要影响。MOON等[73]研究发现骨髓间充质干细胞联合低强度光照射不仅可以促进骨髓间充质干细胞迁移还可以促进缺血的皮瓣组织血管新生,增加毛细血管数量,进而提高移植皮瓣的存活率。低强度超声是一种新型的治疗方式,具有微创、安全和使用便捷等特点,不仅低强度超声预处理间充质干细胞可以促进损伤皮肤组织的修复,低强度超声和间充质干细胞的联用同样也能通过促进血管的新生来促进缺血组织的修复。许豪鹏等[74]发现低强度超声联合骨髓间充质干细胞同样能够显著促进血管新生,而且能够缩短大鼠皮肤愈合增殖期。刘珺碧等[75]在低强度超声联合脂肪间充质干细胞外泌体的研究中发现,低强度超声可以提高外泌体中血管内皮生长因子的功能表达以及增加人脐静脉内皮细胞内一氧化氮合酶的活性,提高一氧化氮水平,进而促进血管内皮细胞增殖和迁移并促进血管新生,而且联用的治疗效果远高于单独使用。 间充质干细胞和其他药物或疗法的联合应用虽然显著提高了间充质干细胞在促进血管新生方面的作用,提高了其治疗效果,是一种更有效、安全、简单、经济及灵活的促皮瓣成活方法。 然而目前关于联合应用的最佳方式、使用剂量、使用时间及不良反应等方面研究甚少,用于联合应用的药物研究也很少,而且目前联合应用的作用主要在促进血管新生,关于抑制炎症反应、促进细胞增殖及迁移等作用尚未发现,因此日后研究者们还需要投入更多的研究和实验去探索和挖掘。 文章总结了间充质干细胞与药物或疗法的联合应用研究进展[69-75],见表6。"
| [1] USLU AB. Effect of dipyridamole on random pattern skin flap viability in rats. J Plast Surg Hand Surg. 2020;54(4):240-247. [2] BOSCÁ MM, ALÓS R, MAROTO N, et al. Recommendations of the Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis Spanish Working Group (GETECCU) for the treatment of perianal fistulas of Crohn’s disease. Recomendaciones del Grupo Español de Trabajo de Enfermedad de Crohn y Colitis Ulcerosa (GETECCU) para el tratamiento de las fístulas perianales de la enfermedad de Crohn. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;43(3):155-168. [3] ELLABBAN MA, FATTAH IOA, KADER GA, et al. The effects of sildenafil and/or nitroglycerin on random-pattern skin flaps after nicotine application in rats. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):3212. [4] LEE W, OH W, OH SM, et al. Comparative effectiveness of different interventions of perivascular hyaluronidase. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020;145(4):957-964. [5] GIATSIDIS G, CHENG L, HADDAD A, et al. Noninvasive induction of angiogenesis in tissues by external suction: sequential optimization for use in reconstructive surgery. Angiogenesis. 2018;21(1):61-78. [6] GIATSIDIS G, CHENG L, FACCHIN F, et al. Moderate-intensity intermittent external volume expansion optimizes the soft-tissue response in a murine model. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;139(4):882-890. [7] LAVRENTIEVA A, HATLAPATKA T, NEUMANN A, et al. Potential for osteogenic and chondrogenic differentiation of MSC. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2013;129:73-88. [8] EKRAM S, KHALID S, SALIM A, et al. Regulating the fate of stem cells for regenerating the intervertebral disc degeneration. World J Stem Cells. 2021; 13(12):1881-1904. [9] LEE DE, AYOUB N, AGRAWAL DK. Mesenchymal stem cells and cutaneous wound healing: novel methods to increase cell delivery and therapeutic efficacy. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7:37. [10] KHAYAMBASHI P, IYER J, PILLAI S, et al. Hydrogel encapsulation of mesenchymal stem cells and their derived exosomes for tissue engineering. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(2):684. [11] TSIAPALIS D, O’DRISCOLL L. Mesenchymal stem cell derived extracellular vesicles for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications. Cells. 2020; 9(4):991. [12] 冯亮,樊力.骨髓间充质干细胞通过增加血管生成和血管内皮生长因子表达影响大鼠随意型皮瓣存活实验研究[J].陕西医学杂志,2022,51(3):298-302. [13] NIU Q, YANG Y, LI D, et al. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells alleviate ischemia-reperfusion injury and promote survival of skin flaps in rats. Life (Basel). 2022;12(10):1567. [14] FENG CJ, PERNG CK, LIN CH, et al. Intra-arterial injection of human adipose-derived stem cells improves viability of the random component of axial skin flaps in nude mice. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2020;73(3):598-607. [15] DING JP, CHEN B, QIAN WJ, et al. Effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on perforator skin flap survival area in rats. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020; 58(6):669-674. [16] NAKAGAWA T, SASAKI M, KATAOKA-SASAKI Y, et al. Intravenous infusion of mesenchymal stem cells promotes the survival of random pattern flaps in rats. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2021;148(4):799-807. [17] HUANG P, WANG L, LI Q, et al. Atorvastatin enhances the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes in acute myocardial infarction via up-regulating long non-coding RNA H19. Cardiovasc Res. 2020;116(2):353-367. [18] XUAN W, KHAN M, ASHRAF M. Extracellular vesicles from notch activated cardiac mesenchymal stem cells promote myocyte proliferation and neovasculogenesis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:11. [19] FATHY M, OKABE M, M OTHMAN E, et al. Preconditioning of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem-like cells with eugenol potentiates their migration and proliferation in vitro and therapeutic abilities in rat hepatic fibrosis. Molecules. 2020;25(9):2020. [20] CHEN W, ZHUO Y, DUAN D, et al. Effects of hypoxia on differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;15(4):332-339. [21] ZHENG J, LI H, HE L, et al. Preconditioning of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells by rapamycin increases cell migration and ameliorates liver ischaemia/reperfusion injury in mice via the CXCR4/CXCL12 axis. Cell Prolif. 2019;52(2): e12546. [22] ISIK B, THALER R, GOKSU BB, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning induces epigenetic changes and modifies swine mesenchymal stem cell angiogenesis and senescence in experimental atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):240. [23] ONG ALC, LEE SH, AUNG SW, et al. 5-Azacytidine pretreatment confers transient upregulation of proliferation and stemness in human mesenchymal stem cells. Cells Dev. 2021;165:203659. [24] AMIRI F, JAHANIAN-NAJAFABADI A, ROUDKENAR MH. In vitro augmentation of mesenchymal stem cells viability in stressful microenvironments: in vitro augmentation of mesenchymal stem cells viability. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2015; 20(2):237-251. [25] FARAHPOUR MR, SHEIKH S, KAFSHDOOZ E, et al. Accelerative effect of topical Zataria multiflora essential oil against infected wound model by modulating inflammation, angiogenesis, and collagen biosynthesis. Pharm Biol. 2021;59(1):1-10. [26] ELBIALY ZI, ASSAR DH, ABDELNABY A, et al. Healing potential of Spirulina platensis for skin wounds by modulating bFGF, VEGF, TGF-ß1 and α-SMA genes expression targeting angiogenesis and scar tissue formation in the rat model. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;137:111349. [27] SONG Y, DOU H, LI X, et al. Exosomal miR-146a contributes to the enhanced therapeutic efficacy of interleukin-1β-primed mesenchymal stem cells against sepsis. Stem Cells. 2017;35(5):1208-1221. [28] KAO AP, WANG KH, LONG CY, et al. Interleukin-1β induces cyclooxygenase-2 expression and promotes the invasive ability of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from ovarian endometrioma. Fertil Steril. 2011;96(3):678-684.e1. [29] 刘流,刘琳,梁力川,等.IL-1β预处理脂肪间充质干细胞促进VEGF蛋白分泌和巨噬细胞M_2型极化的研究[J].四川大学学报(医学版),2019,50(2):171-176. [30] MA T, WANG X, JIAO Y, et al. Interleukin 17 (IL-17)-induced mesenchymal stem cells prolong the survival of allogeneic skin grafts. Ann Transplant. 2018;23:615-621. [31] MA TX, XU YW, JIANG DY. Effects and mechanism of interleukin-17-modified mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on rejection reaction of allogeneic skin transplantation in mice. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2020;36(3):234-243. [32] 郝艺. TNF-α诱导的脐带间充质干细胞外泌体对修复细胞及创面愈合的影响研究[D].遵义:遵义医科大学,2021. [33] 陈自力,曹宁,徐萌,等.肿瘤坏死因子α预处理人脐带间充质干细胞的生物学特征分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(24):3780-3787. [34] CHEN L, XU Y, ZHAO J, et al. Conditioned medium from hypoxic bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells enhances wound healing in mice [published correction appears in PLoS One. PLoS One. 2014;9(4):e96161. [35] KIM YS, NOH MY, CHO KA, et al. Hypoxia/reoxygenation-preconditioned human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells rescue ischemic rat cortical neurons by enhancing trophic factor release. Mol Neurobiol. 2015;52(1):792-803. [36] KHEIRANDISH M, GAVGANI SP, SAMIEE S. The effect of hypoxia preconditioning on the neural and stemness genes expression profiling in human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells. Transfus Apher Sci. 2017;56(3):392-399. [37] 郜敏,张杰,王际壮,等.低氧预处理大鼠脂肪源性间充质干细胞条件培养基对大鼠全层皮肤缺损创面愈合的影响[J].中华烧伤杂志,2020,36(9):803-812. [38] 胡玄.低氧预处理脂肪干细胞-胞外囊泡促进皮瓣移植后血管新生的实验研究[D].南昌:南昌大学,2020. [39] WU S, HU X, WANG ZH, et al. Extracellular vesicles isolated from hypoxia-preconditioned adipose-derived stem cells promote hypoxia-inducible factor 1α-mediated neovascularization of random skin flap in rats. Ann Plast Surg. 2022; 89(2):225-229. [40] 侯婧瑛,于萌蕾,郭天柱,等.缺氧预处理激活HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞生存和血管再生[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(7): 985-990. [41] 侯婧瑛,郭天柱,于萌蕾,等.预处理通过激活MALAT1靶向抑制miR-195促进骨髓间充质干细胞的生存和血管形成[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(7): 1005-1011. [42] 唐建宏,张霓霓,黄桂林,等.不同体积分数氧气预处理人羊膜间充质干细胞的生物学特性[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(15):2318-2324. [43] 梁东兰,黄宏,荆昭,等.低浓度过氧化氢预处理骨髓间充质干细胞对创面愈合的促进作用[J].感染、炎症、修复,2016,17(3):131-135,128. [44] BAI Y, HAN YD, YAN XL, et al. Adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes stimulated by hydrogen peroxide enhanced skin flap recovery in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;500(2):310-317. [45] ARIYANTI AD, ZHANG J, MARCELINA O, et al. Salidroside-pretreated mesenchymal stem cells enhance diabetic wound healing by promoting paracrine function and survival of mesenchymal stem cells under hyperglycemia. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8(4):404-414. [46] 杨金龙,张荣明,魏巍,等.红景天苷预处理脂肪干细胞促进糖尿病大鼠皮肤创面愈合的作用及机制[J].实用医学杂志,2021,37(3):308-313. [47] 梁至洁,黄东琳,朱丹丹,等.淫羊藿苷优化大鼠脂肪干细胞促进超长随意皮瓣存活的实验研究[J].中国临床新医学,2022,15(12):1140-1146. [48] 许豪鹏.低强度超声预处理骨髓间充质干细胞促进皮肤创伤快速高质量修复的研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2022. [49] ASHINA K, TSUBOSAKA Y, KOBAYASHI K, et al. VEGF-induced blood flow increase causes vascular hyper-permeability in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;464(2):590-595. [50] AKIMOTO M, TAKEDA A. Reply: effects of CB-VEGF-A injection in rat flap models for improved survival. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014;133(3):424e-425e. [51] 郑岩,易成刚,郭树忠,等.转基因的骨髓间充质干细胞治疗大鼠缺血皮瓣[J].中华实验外科杂志,2007,24(3):339-342. [52] 金文虎,周爱婷,吴中桓,等.血管内皮生长因子基因修饰人羊膜间充质干细胞利于超长随意皮瓣的成活[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(21):3349-3356. [53] 尹朝奇,周建大,罗成群,等.转染TGF-β1的骨髓间充质干细胞移植对预构皮瓣存活影响的实验研究[J].中国普通外科杂志,2016,25(6):875-881. [54] 陈勇,范龙坤.miR-126调节骨髓间充质干细胞对游离皮瓣组织学活性的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(36):5332-5337. [55] 张赛圣,程丽霞.骨髓间充质干细胞miR-126高表达在游离皮瓣移植后皮瓣血管新生中的促进作用及机制研究[J].现代医学,2018,46(2):126-130. [56] LENG X, FAN Y, WANG Y, et al. Treatment of ischemia-reperfusion injury of the skin flap using human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hUC-MSCs) transfected with “F-5” gene. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:2751-2764. [57] 张月,韩飞,何亭,等.肝细胞生长因子修饰人脂肪间充质干细胞对糖尿病大鼠全层皮肤缺损创面愈合的影响及其机制[J].中华烧伤杂志,2021,37(9): 860-868. [58] 曹涛,肖丹,计鹏,等.肝细胞生长因子修饰的人脂肪间充质干细胞外泌体对糖尿病小鼠全层皮肤缺损的作用[J].中华烧伤与创面修复杂志,2022, 38(11):1004-1013. [59] TONG X, YANG F. Sliding hydrogels with mobile molecular ligands and crosslinks as 3D stem cell niche. Adv Mater. 2016;28(33):7257-7263. [60] AKBARI A, JABBARI N, SHARIFI R, et al. Free and hydrogel encapsulated exosome-based therapies in regenerative medicine. Life Sci. 2020;249:117447. [61] 孙晓明. 水凝胶基生物支架促进缺血性任意皮瓣血管化研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2017. [62] 徐晓明,陈艳,宋倩,等.人胎盘间充质干细胞凝胶促进SD大鼠放射性皮肤损伤的愈合[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(25):3976-3980. [63] 田凯.加载干细胞和去铁胺的复合丝蛋白水凝胶促进狭长窄蒂皮瓣血管化和功能化修复的研究[D].苏州:苏州大学,2021. [64] 唐晓铎.面向复杂皮肤创面修复的多功能水凝胶材料[D].长春:吉林大学, 2022. [65] 陶苏皖.脂肪间充质干细胞外泌体/壳聚糖水凝胶复合敷料促进皮肤伤口修复[D].武汉:武汉科技大学,2022. [66] 凌华军,崔瑞文,王其友.负载外泌体的3D明胶细胞外基质水凝胶促进皮肤损伤愈合[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(12):1900-1905. [67] LIU Y, LIU Y, WU M, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell-loaded β-chitin nanofiber hydrogel promote wound healing in rats. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2022;33(2):12. [68] LIN X, KONG B, ZHU Y, et al. Bioactive fish scale scaffolds with MSCs-loading for skin flap regeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(21):e2201226. [69] 先德彬,明华伟,徐荣胜,等.骨髓间充质干细胞与血管内皮生长因子165基因转染人脐静脉内皮细胞共移植促进缺血皮瓣血管的生成[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(1):46-52. [70] 明华伟,何芸,付光新,等.BMSCs与VEGF 165-HUVEC局部皮下组织层共移植大鼠缺血皮瓣存活率观察[J].山东医药,2019,59(15):37-41. [71] 赵胜利.序贯缓释VEGF和bFGF的PELA混合微囊联合骨髓间充质干细胞修复大鼠背部缺血皮瓣的实验研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2019. [72] SHOU K, NIU Y, ZHENG X, et al. Enhancement of bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell angiogenic capacity by NPWT for a combinatorial therapy to promote wound healing with large defet. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:7920265. [73] MOON JH, RHEE YH, AHN JC, et al. Enhanced survival of ischemic skin flap by combined treatment with bone marrow-derived stem cells and low-level light irradiation. Lasers Med Sci. 2018;33(1):1-9. [74] 许豪鹏,唐义林,夏怡,等.低强度超声联合骨髓间充质干细胞缩短大鼠皮肤愈合增殖期的研究[J].中国超声医学杂志,2022,38(4):449-453. [75] 刘珺碧,蒋日月,王浩,等.低强度脉冲超声联合脂肪间充质干细胞源性外泌体促进内皮细胞血管生成的实验研究[J].临床超声医学杂志,2022,24(1):1-5. |
| [1] | Chen Kaijia, Liu Jingyun, Cao Ning, Sun Jianbo, Zhou Yan, Mei Jianguo, Ren Qiang. Application and prospect of tissue engineering in treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1450-1456. |
| [2] | Bai Chen, Yang Wenqian, Meng Zhichao, Wang Yuze. Strategies for repairing injured anterior cruciate ligament and promoting graft healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1457-1463. |
| [3] | Yang Yifeng, Ye Nan, Wang Lin, Guo Shuaicheng, Huang Jian. Signaling pathway of dexmedetomidine against ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1464-1469. |
| [4] | Yue Yun, Wang Peipei, Yuan Zhaohe, He Shengcun, Jia Xusheng, Liu Qian, Li Zhantao, Fu Huiling, Song Fei, Jia Menghui. Effects of croton cream on JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1186-1192. |
| [5] | Lou Guo, Zhang Yan, Fu Changxi. Role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in exercise preconditioning-induced improvement of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1283-1288. |
| [6] | Xu Canli, He Wenxing, Wang Lei, Wu Fangting, Wang Jiahui, Duan Xuelin, Zhao Tiejian, Zhao Bin, Zheng Yang. Bibliometric analysis of researches on liver organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1099-1104. |
| [7] | Liu Hanfeng, Wang Jingjing, Yu Yunsheng. Artificial exosomes in treatment of myocardial infarction: current status and prospects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1118-1123. |
| [8] | Ma Shuwei, He Sheng, Han Bing, Zhang Liaoyun. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of animals with acute liver failure: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1137-1142. |
| [9] | Sun Yukang, Song Lijuan, Wen Chunli, Ding Zhibin, Tian Hao, Ma Dong, Ma Cungen, Zhai Xiaoyan. Visualization analysis of stem cell therapy for myocardial infarction based on Web of Science in recent ten years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1143-1148. |
| [10] | Feng Ruiqin, Han Na, Zhang Meng, Gu Xinyi, Zhang Fengshi. Combination of 1% platelet-rich plasma and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves the recovery of peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 985-992. |
| [11] | Wang Wen, Zheng Pengpeng, Meng Haohao, Liu Hao, Yuan Changyong. Overexpression of Sema3A promotes osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells and MC3T3-E1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 993-999. |
| [12] | Qiu Xiaoyan, Li Bixin, Li Jingdi, Fan Chuiqin, Ma Lian, Wang Hongwu. Differentiation of insulin-producing cells from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells infected by MAFA-PDX1 overexpressed lentivirus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1000-1006. |
| [13] | Liu Qiwei, Zhang Junhui, Yang Yuan, Wang Jinjuan. Role and mechanism of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on polycystic ovary syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1015-1020. |
| [14] | Wang Shanshan, Shu Qing, Tian Jun. Physical factors promote osteogenic differentiation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1083-1090. |
| [15] | Pan Xiaolong, Fan Feiyan, Ying Chunmiao, Liu Feixiang, Zhang Yunke. Effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine on inhibiting the aging of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1091-1098. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||