Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (13): 2076-2081.doi: 10.12307/2024.117
Previous Articles Next Articles
Solute carrier family 2 member 12 intervenes in uric acid-induced renal tubular cell injury
He Yi1, 2, Li Xiaolin1, He Jinke1, Jiang Xiangju1, Liang Meiting1, 2, Chen Wujin2, Cui Yuena2, Sun Yuping2
- 1Xinjiang Second Medical College, Karamay 834000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2School of Basic Medical Sciences, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2022-11-02Accepted:2023-03-14Online:2024-05-08Published:2023-08-28 -
Contact:Sun Yuping, MD, Professor, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:He Yi, Master, Associate professor, Xinjiang Second Medical College, Karamay 834000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; School of Basic Medical Sciences, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Scientific Research Program of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region Universities, No. XJEDU2021Y054 (to HY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
He Yi, Li Xiaolin, He Jinke, Jiang Xiangju, Liang Meiting, Chen Wujin, Cui Yuena, Sun Yuping. Solute carrier family 2 member 12 intervenes in uric acid-induced renal tubular cell injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(13): 2076-2081.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
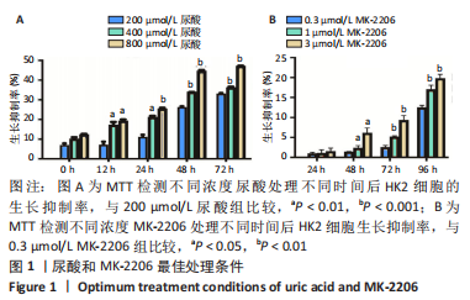
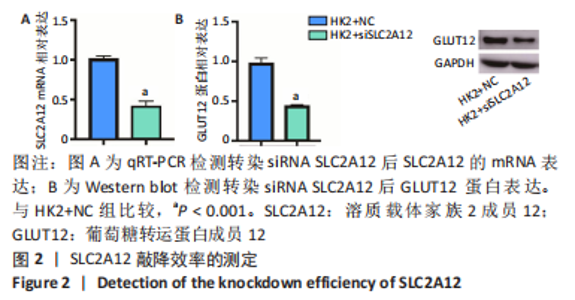
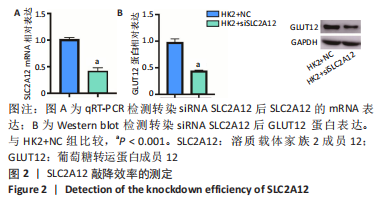
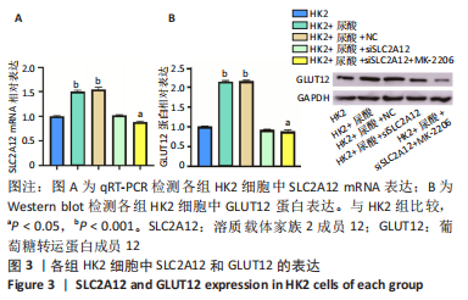
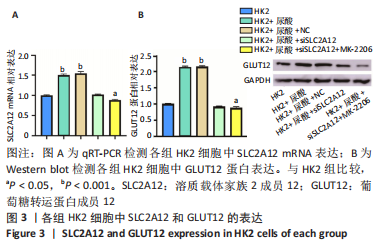
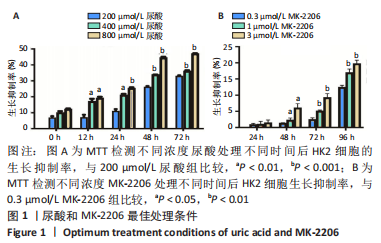
2.1 尿酸促进HK2细胞表达SLC2A12 MTT结果显示尿酸作用时间为48 h时细胞抑制率明趋于平缓,且作用浓度为800 μmol/L时细胞抑制率最大,此条件作为最适处理条件,见图1A,AKT抑制剂MK-2206的最适作用浓度为3 μmol/L,作用时间为48 h,见图1B。此外,qRT-PCR和Western blot检测表明,与转染siRNA NC比较,转染siRNA SLC2A12后细胞中SLC2A12 mRNA表达和GLUT12蛋白表达显著降低,见图2A,B。qRT-PCR检测结果显示,与HK2组比较,HK2+尿酸组SLC2A12 mRNA水平显著增加;与HK2+尿酸组比较,HK2+尿酸+siSLC2A12组SLC2A12 mRNA水平显著降低。HK2+尿酸+siSLC2A12+MK-2206组SLC2A12 mRNA水平低于HK2组,见图3A。Western blot检测结果显示,与HK2组比较,HK2+尿酸组GLUT12蛋白表达显著增加;与HK2+尿酸组比较,HK2+尿酸+siSLC2A12组GLUT12蛋白表达降低。HK2+尿酸+siSLC2A12+MK-2206组GLUT12蛋白水平低于HK2组,见图3B。"
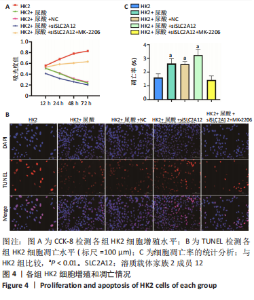
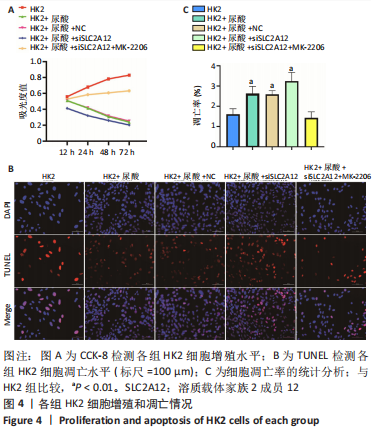
2.2 敲降SLC2A12对尿酸处理的HK2细胞增殖和凋亡的影响 CCK-8检测结果发现与HK2组相比,HK2+尿酸组细胞增殖能力降低,HK2+尿酸+siSLC2A12组细胞增殖能力进一步降低;与HK2+尿酸+siSLC2A12组相比,HK2+尿酸+siSLC2A12+MK-2206组细胞增殖能力明显升高,见图4A。TUNEL染色结果发现与HK2组相比,HK2+尿酸组HK2细胞凋亡数量升高;与HK2+尿酸组相比,HK2+尿酸+siSLC2A12组细胞凋亡数量进一步升高;与HK2+尿酸+siSLC2A12组相比,HK2+尿酸+siSLC2A12+MK-2206组细胞凋亡数量下降,见图4B,C。"
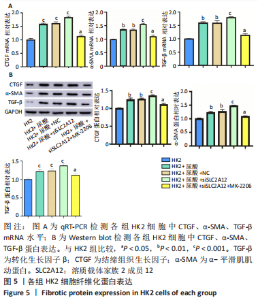
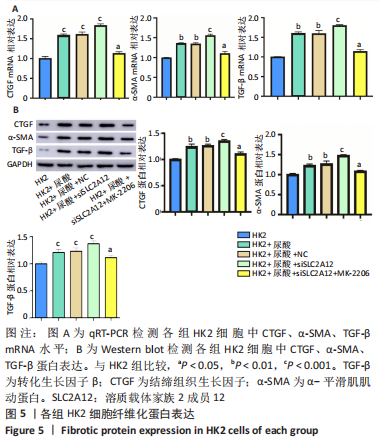
2.3 敲降SLC2A12对尿酸处理后HK2细胞纤维化的影响 qRT-PCR检测结果发现,与HK2组比较,HK2+尿酸组结缔组织生长因子、α-平滑肌肌动蛋白、转化生长因子β mRNA表达显著增加(P < 0.01),HK2+尿酸+siSLC2A12组结缔组织生长因子、α-平滑肌肌动蛋白、转化生长因子β mRNA表达进一步升高(P < 0.001);与HK2+尿酸+siSLC2A12组比较,HK2+尿酸+siSLC2A12+MK-2206组结缔组织生长因子、α-平滑肌肌动蛋白、转化生长因子β mRNA表达下降(P < 0.05),但仍高于HK2组(P < 0.05),见图5A。Western blot检测结缔组织生长因子、α-平滑肌肌动蛋白、转化生长因子β的蛋白水平与mRNA水平相似,见图5B。"
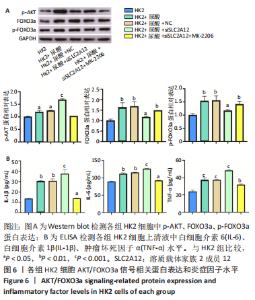
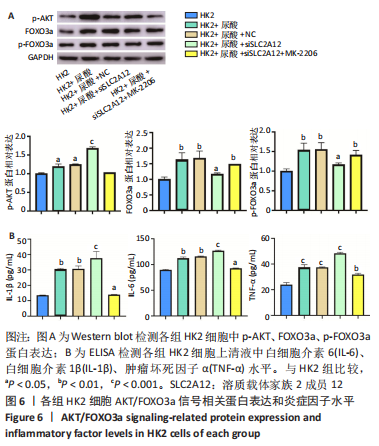
2.4 敲降SLC2A12调控AKT/FOXO3a信号轴 Western blot检测结果显示,与HK2组比较,HK2+尿酸组p-AKT、FOXO3a、p-FOXO3a蛋白表达显著增加(P < 0.05),HK2+尿酸+siSLC2A12组p-AKT水平显著升高,而FOXO3a、p-FOXO3a的增加水平得到缓解,但仍高于对照组(P < 0.05);与HK2+尿酸+siSLC2A12组比较,HK2+尿酸+siSLC2A12+MK-2206组p-AKT蛋白表达下降,FOXO3a、p-FOXO3a蛋白表达升高(P < 0.01),见图6A。 2.5 敲降SLC2A12对尿酸处理后HK2细胞分泌炎症因子水平的影响 与HK2组比较,HK2+尿酸组细胞上清液中白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α水平显著升高(P < 0.01),HK2+尿酸+siSLC2A12组白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α水平进一步升高(P < 0.001);与HK2+尿酸+siSLC2A12组比较,HK2+尿酸+siSLC2A12+MK-2206组细胞上清液中白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α水平显著下降,但仍高于HK2组(P < 0.05),见图6B。"
| [1] YU X, ZHANG L, ZHANG P, et al. Lycium barbarum polysaccharides protect mice from hyperuricaemia through promoting kidney excretion of uric acid and inhibiting liver xanthine oxidase. Pharm Biol. 2020;58(1):944-949. [2] SU HY, YANG C, LIANG D, et al. Research Advances in the Mechanisms of Hyperuricemia-Induced Renal Injury. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:5817348. [3] WANG Y, XU F, ZHANG X, et al. Cross-sectional association between gamma-glutamyl transferase and hyperuricaemia: the China Multi-Ethinic Cohort (CMEC) study. BMJ Open. 2022;12(5):e058793. [4] LUO Q, DING R, CHEN L, et al. The Association Between Spicy Food Intake and Risk of Hyperuricemia Among Chinese Adults. Front Public Health. 2022;10:919347. [5] SANG S, WANG L, LIANG T, et al. Potential role of tea drinking in preventing hyperuricaemia in rats: biochemical and molecular evidence. Chin Med. 2022;17(1):108. [6] WU X, YOU C. The biomarkers discovery of hyperuricemia and gout: proteomics and metabolomics. PeerJ. 2023;11:e14554. [7] TSAI CW, LIN SY, KUO CC, et al. Serum Uric Acid and Progression of Kidney Disease: A Longitudinal Analysis and Mini-Review. PLoS One. 2017;12(1): e0170393. [8] YANG B, XIN M, LIANG S, et al. New insight into the management of renal excretion and hyperuricemia: Potential therapeutic strategies with natural bioactive compounds. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1026246. [9] QIN Y, ZHANG X, TAO H, et al. Ameliorative effect and mechanism of Yi-Suan-Cha against hyperuricemia in rats. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021;35(8):e23859. [10] TOYODA Y, TAKADA T, MIYATA H, et al. Identification of GLUT12/SLC2A12 as a urate transporter that regulates the blood urate level in hyperuricemia model mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(31):18175-18177. [11] NIAN YL, YOU CG. Susceptibility genes of hyperuricemia and gout. Hereditas. 2022;159(1):30. [12] WAHEED Y, YANG F, SUN D. Role of asymptomatic hyperuricemia in the progression of chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular disease. Korean J Intern Med. 2021;36(6):1281-1293. [13] BOHATA J, HORVATHOVA V, PAVLIKOVA M, et al. Circulating microRNA alternations in primary hyperuricemia and gout. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021; 23(1):186. [14] DOBSON M, RAMAKRISHNAN G, MA S, et al. Bimodal regulation of FoxO3 by AKT and 14-3-3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1813(8):1453-1464. [15] LIU L, ZHAO T, SHAN L, et al. Estradiol regulates intestinal ABCG2 to promote urate excretion via the PI3K/Akt pathway. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2021;18(1):63. [16] LEE TH, CHEN JJ, WU CY, et al. Hyperuricemia and Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease: A Review from Physiology and Pathogenesis to the Role of Urate-Lowering Therapy. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021;11(9):1674. [17] LIU N, XU H, SUN Q, et al. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Hyperuricemia and Xanthine Oxidoreductase (XOR) Inhibitors. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021; 2021:1470380. [18] MAIUOLO J, OPPEDISANO F, GRATTERI S, et al. Regulation of uric acid metabolism and excretion. Int J Cardiol. 2016;213: 8-14. [19] BRODERICK L, HOFFMAN HM. IL-1 and autoinflammatory disease: biology, pathogenesis and therapeutic targeting. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(8): 448-463. [20] STANIROWSKI PJ, SZUKIEWICZ D, MAJEWSKA A, et al. Differential Expression of Glucose Transporter Proteins GLUT-1, GLUT-3, GLUT-8 and GLUT-12 in the Placenta of Macrosomic, Small-for-Gestational-Age and Growth-Restricted Foetuses. J Clin Med. 2021;10(24):5 833. [21] CHIBA Y, MURAKAMI R, MATSUMOTO K, et al. Glucose, Fructose, and Urate Transporters in the Choroid Plexus Epithelium. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(19): 7230. [22] NIE S, QIAN X, SHI M, et al. ALDH1A3 Accelerates Pancreatic Cancer Metastasis by Promoting Glucose Metabolism. Front Oncol. 2020;10: 915. [23] DAY RO, KAMEL B, KANNANGARA DR, et al. Xanthine oxidoreductase and its inhibitors: relevance for gout. Clin Sci (Lond). 2016;130(23):2167-2180. [24] NISHINO M, EGAMI Y, KAWANAMI S, et al. Lowering Uric Acid May Improve Prognosis in Patients With Hyperuricemia and Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction. J Am Heart Assoc. 2022;11(19):e026301. [25] RIAZ M, AL KURY LT, ATZAZ N, et al. Carvacrol Alleviates Hyperuricemia-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation by Modulating the NLRP3/NF-κB Pathwayt. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022;16:1159-1170. [26] CHEN Y, YANG Y, ZHONG Y, et al. Genetic risk of hyperuricemia in hypertensive patients associated with antihypertensive drug therapy: A longitudinal study. Clin Genet. 2022;101(4):411-420. [27] LUO Q, XIA X, LI B, et al. Serum uric acid and cardiovascular mortality in chronic kidney disease: a meta-analysis. BMC Nephrol. 2019; 20(1): 18. [28] GHERGHINA ME, PERIDE I, TIGLIS M, et al. Uric Acid and Oxidative Stress-Relationship with Cardiovascular, Metabolic, and Renal Impairment. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(6):3188. [29] MARINKOVIC D, ZHANG X, YALCIN S, et al. Foxo3 is required for the regulation of oxidative stress in erythropoiesis. J Clin Invest. 2007;117(8): 2133-2144. [30] GOMEZ-CABRERA MC, ARC-CHAGNAUD C, SALVADOR-PASCUAL A, et al. Redox modulation of muscle mass and function. Redox Biol. 2020; 35: 101531. [31] MA WG, WANG J, BU XW, et al. Effects of Polygonum cuspidatum on AMPK-FOXO3α Signaling Pathway in Rat Model of Uric Acid-Induced Renal Damage. Chin J Integr Med. 2019;25(3):182-189. [32] ZHANG Y, ZHANG H, HU L, et al. lncRNA TUG1 regulates hyperuricemia-induced renal fibrosis in a rat model. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2022;54(9):1365-1375. [33] SHI Y, XU L, TAO M, et al. Blockade of enhancer of zeste homolog 2 alleviates renal injury associated with hyperuricemia. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019;316(3):F488-F505. [34] XU L, LU LL, GAO JD. Traditional Chinese Herbal Medicine Plays a Role in the Liver, Kidney, and Intestine to Ameliorate Hyperuricemia according to Experimental Studies. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021: 4618352. [35] CRIȘAN TO, CLEOPHAS MC, OOSTING M, et al. Soluble uric acid primes TLR-induced proinflammatory cytokine production by human primary cells via inhibition of IL-1Ra. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(4):755-762. [36] SHEN L, DONG Y, LI M, et al. The relationship between leukocyte level and hypertension in elderly patients with hyperuricemia. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(51):e32327. [37] BAINBRIDGE SA, ROBERTS JM. Uric acid as a pathogenic factor in preeclampsia. Placenta. 2008;29 Suppl A(Suppl A):S67-72. [38] NATSUKO PD, LAURA SC, DENISE CC, et al. Differential gene expression of ABCG2, SLC22A12, IL-1β, and ALPK1 in peripheral blood leukocytes of primary gout patients with hyperuricemia and their comorbidities: a case-control study. Eur J Med Res. 2022;27(1):62. [39] WANG CC, LI YL, CHIU PY, et al. Protective effects of corni fructus extract in mice with potassium oxonate-induced hyperuricemia. J Vet Med Sci. 2022; 84(8):1134-1141. [40] SCANU A, LUISETTO R, RAMONDA R, et al. Anti-Inflammatory and Hypouricemic Effect of Bioactive Compounds: Molecular Evidence and Potential Application in the Management of Gout. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022;44(11):5173-5190. |
| [1] | Yang Yifeng, Ye Nan, Wang Lin, Guo Shuaicheng, Huang Jian. Signaling pathway of dexmedetomidine against ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1464-1469. |
| [2] | Yue Yun, Wang Peipei, Yuan Zhaohe, He Shengcun, Jia Xusheng, Liu Qian, Li Zhantao, Fu Huiling, Song Fei, Jia Menghui. Effects of croton cream on JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1186-1192. |
| [3] | Liu Xin, Hu Man, Zhao Wenjie, Zhang Yu, Meng Bo, Yang Sheng, Peng Qing, Zhang Liang, Wang Jingcheng. Cadmium promotes senescence of annulus fibrosus cells via activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1217-1222. |
| [4] | Wei Juan, Li Ting, Huan Mengting, Xie Ying, Xie Zhouyu, Wei Qingbo, Wu Yunchuan. Mechanism by which static exercise improves insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1271-1276. |
| [5] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [6] | Wei Yuanxun, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Zhang Chi, Pan Chengzhen, Wei Zongbo. The mechanism of Notch signaling pathway in osteoporosis and its prevention and treatment with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 587-593. |
| [7] | Liu Baofang, Xu Bin, Chen Lei. Pueraria decoction in the treatment of osteoarthritis: network pharmacology analysis and animal model validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 193-199. |
| [8] | Zuo Jun, Ma Shaolin. Mechanism of beta-sitosterol on hypertrophic scar fibroblasts: an analysis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 216-223. |
| [9] | Peng Yuanhao, Lyu Dongmei, Zhuang Xinyi, Yu Ting, Cheng Qian. Consistency between two types of cone-beam CT transformed two-dimensional images and traditional lateral cephalometric radiographs for quantitative analysis of cervical vertebral bone age [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(18): 2881-2886. |
| [10] | Zhao Kui, Pan Runsang, Lan Fengjun, Deng Jin, Chen Houping. Molecular mechanisms of autophagy-apoptosis interactions in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(18): 2912-2917. |
| [11] | Yang Yunyun, Chen Qiqing, Zhao Jirong, Zhu Bao, Ma Dong, Huang Junkai, An Dehao, Zou Jipeng, Liu Weihang. Research status of traditional Chinese medicine monomer mediating related signaling pathways in treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(18): 2918-2924. |
| [12] | Chai Shuang, Ma Jiangtao, Yang Yanbing, Su Xiaochuan, Xie Yan, Teng Junyan, Qin Na. The role and mechanism of estrogen receptor in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis by Gushukang [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(16): 2574-2578. |
| [13] | Jiang Jie, Liu Juan, Yu Yanyan, Yang Yue, Wang Qianhui. Mechanism by which moxibustion pretreatment attenuates oxidative stress injury in a rat model of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(16): 2488-2493. |
| [14] | Chang Yu, Li Hui, Zhang Tianshui, Wang Chunyu, Yu Li, Wu Zimei, Li Wen, Wang Zhengdong. Bone morphogenetic protein/Smad signaling pathway involved in chondrodysplasia in the ankle of a rat congenital clubfoot model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(16): 2500-2504. |
| [15] | Xie Wenguan, Liu Yutao, Cui Wenbo, Kuang Mingye. Melatonin inhibits hydrogen peroxide-induced injury of human nucleus pulposus cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2180-2185. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||