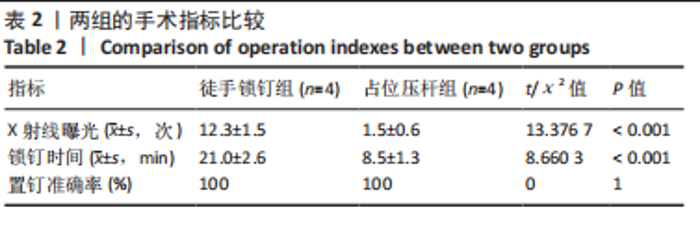
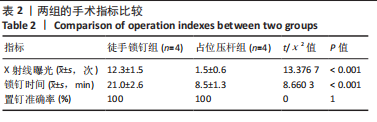
[1] 陈彦震,叶森,赖晓榕,等.顺势双反牵引器联合超声在股骨干骨折交锁髓内钉内固定术中的应用[J].中华创伤杂志,2019,35(7): 644-646.
[2] 袁野,黄文良,徐林,等.侧卧位牵引架闭合复位髓内钉固定治疗股骨干骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(12):1847-1852.
[3] 夏西尚,方宣城,邱新建,等.股骨大粗隆入钉点与梨状窝入钉点交锁髓内钉内固定治疗股骨干骨折的疗效对比研究[J].创伤外科杂志,2020,22(2):129-132.
[4] 桂鹏,邹毅,冷华伟,等.闭合与开放髓内钉治疗股骨干骨折比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(22):2027-2031.
[5] 毛国庶,周敏,李晓明,等.第三骨块对股骨干骨折髓内钉固定后骨愈合效果的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(15):2405-2409.
[6] 戴海,黄宗贵,吴永祥,等.数字化仿真技术在股骨干骨折髓内钉固定术中的应用[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2020,38(3):327-330.
[7] 桂景雄,邓志成,朱小华,等.有限切开复位在髓内钉治疗股骨干骨折中的应用评价[J].中国医师进修杂志,2020(3):265-270.
[8] 陈勋,喻姿瑞,王宇飞,等.稳定股骨粗隆间骨折Gamma髓内钉内固定术中远端锁钉与否对疗效的影响[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2020,35(4):378-380.
[9] WU KJ, LI SH, YEH KT, et al. The risk factors of nonunion after intramedullary nailing fixation of femur shaft fracture in middle age patients. Medicine(Baltimore). 2019;98(29):e16559.
[10] 王士进,史静,陈元振,等.InterTan髓内钉治疗股骨转子间骨折45例经验[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(18):1725-1726.
[11] 陈孝均,茶晓锋,蒋川锋,等.一种股骨髓内钉远端精准锁定装置[P].中国专利:2020200980180,2020-10-09.
[12] 冉小烽.在闭合复位髓内钉固定中不同的体位牵引方法治疗股骨干骨折的效果[J].骨科临床与研究杂志,2020,5(6):335-339.
[13] 陈志达,蔡弢艺,丁真奇,等.股骨髓内钉芯钻瞄准系统与体外瞄准架系统的远端锁定效果比较[J].骨科,2020,11(1):23-29.
[14] 张楠,杨杰,翁润民.闭合复位交锁髓内钉治疗股骨干骨折术中操作困难的原因及对策[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2019,41(11):1163-1166.
[15] 王臣,肖万军.Sureshot远端瞄准系统进行股骨髓内钉远端锁钉操作的临床应用价值分析[J].创伤外科杂志,2017,19(8):578-582.
[16] GAO H, LIU Z, WANG G, et al. A New Accurate, Simple and Less Radiation Exposure Device for Distal Locking of Femoral Intramedullary Nails. Int J Gen Med. 2021;14:4145-4153.
[17] 张浩东,张峰峰,孙立宁.基于增强现实技术髓内钉远端锁孔导航[J].哈尔滨工程大学学报,2022,43(4):458-464.
[18] 戴能,刘拴,张明勇,等.关节镜下股骨髓内钉经骨窗压杆远端锁定技术[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2021,29(16):1501-1504.
[19] 茶晓锋,谢霁,蒋川锋,等.一种新型股骨髓内钉远端定位架的研制[J].医疗装备,2021,34(18):1-2.
[20] 邱海滨,张衡,徐建彪.下肢骨干骨折髓内钉内固定术中远端锁钉放置困难的关键原因及其处理[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2018, 33(4):440-441.
[21] KIM KK, RYU SK, LEE SW, et al. Is Full-Length Intramedullary Nail Necessary for Atypical Subtrochanteric Femoral Fracture Associated with Bisphosphonate? J Bone Metab. 2020;27(2):133-142.
[22] DAVIDSON A, HOURI SS, COHEN J, et al. Initial definitive treatment of open femoral shaft fractures with retrograde nailing - is it safe? A retrospective analysis comparing antegrade to retrograde nailing. Injury. 2021;53(3):1231-1236.
[23] 严怀宁,张晓峰,叶荣,等.股骨髓内钉扩髓偏离股骨中心线对远端锁钉锁定的影响[J].武警医学,2017,28(8):826-828.
[24] 张道虎,帅敏,李东,等.微调瞄准架校准中心定位杆法在股骨交锁髓内钉远端锁钉植入中的应用[J].中外医疗,2015,34(30):56-58.
[25] DUNLEAVY ML, BURTON A, REID JS, et al. Surgical management of angulated femoral intramedullary nails associated with closed fractures: A systematic review of the literature. J Orthop. 2020;21: 314-320.
[26] 莫楚鸿,唐灿锐,李国兴.无X线暴露探针技术在股骨髓内钉远端锁钉置入困难中的应用[J].广州医科大学学报,2019,47(5):78-80.
[27] 李运美,邢宝瑞,郭东辉,等.自制微调装置在股骨交锁髓内钉远端锁钉过程中的应用[J].中国骨伤,2019,32(2):161-165.
[28] 谈应东,张浩,申国庆,等.下肢髓内钉远端锁钉可调式显影瞄准器临床应用研究[J].中国社区医师,2019,35(10):61+63.
[29] 王栋,章小军.闭合复位顺行髓内钉固定治疗股骨干骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2020,23(2):256-258.
[30] 李军,詹俊锋,许新忠,等.一种新型导航系统在胫骨髓内钉远端锁钉应用中的评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(27):4342-4347.
[31] 王晓飞.磁力导航髓内钉内固定治疗股骨干骨折患者的短期随访研究[J].中国药物与临床,2020,20(6):943-945.
[32] 陈军辉.可视化磁力导航髓内钉联合捆绑带治疗股骨干骨折的效果[J].实用临床医学,2020,21(5):43-45.
[33] WONG TH, LEE MS, WU SY, et al. Novel Passive Two-Stage Magnetic Targeting Devices for Distal Locking of Interlocking Nails. J Healthc Eng. 2017;2017:3619403.
[34] KUBICEK J, TOMANEC F, CERNY M, et al. Recent Trends, Technical Concepts and Components of Computer-Assisted Orthopedic Surgery Systems: A Comprehensive Review. Sensors (Basel). 2019;19(23): 5199.
[35] CHOI J, KIM J, HWANG JY, et al. A novel smart navigation system for intramedullary nailing in orthopedic surgery. PLoS One. 2017;12(4): e0174407.
[36] 蔡弢艺,陈志达,黄国锋,等.由内向外芯钻髓内钉技术治疗股骨干骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(18):1643-1647.
[37] 陶勇,江渟,田克超.芯钻远端锁定系统在髓内钉治疗股骨干骨折中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(36):5800-5805.
[38] 鲁成,仲文军,杨劲松,等.改进定位器械提高交锁髓内钉远端锁钉置入准确率的临床研究[J].中华全科医学,2018,16(8):1293-1295+1307.
[39] BÄCKER HC, HEYLAND M, WU CH, et al. Breakage of intramedullary femoral nailing or femoral plating: how to prevent implant failure. EurJ Med Res. 2022;27(1):7.
[40] 赵晶焱.直视下安置定位杆解决股骨交锁髓内钉远端锁钉困难[J].云南医药,2009,30(3):392-393.
[41] 蒙剑德,廖志峰,钟玫.“胫骨远端双柱压杆瞄准器”在胫骨干骨折交锁钉手术中的应用研究[J].微创医学,2019,14(2):157-159.
[42] 金宝城,王友,王建祥,等.可调式交锁髓内钉定位杆在股骨干骨折手术中的应用[J].河北医学,2013,19(01):137-139.
[43] 孔祥颖,夏阳,秦泗峰.闭合复位国产改进型交锁髓内钉内固定治疗股骨干骨折疗效观察[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2020,35(4): 390-391.
[44] 李英超.阻挡钉技术在髓内钉治疗股骨及胫骨干骨折的应用[D].长春:吉林大学,2018.
[45] 陈立军,庞清江,余霄,等.股骨交锁髓内钉远端锁钉体外透视定位器的研制及临床应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(8):757-761.
|