Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (24): 3908-3913.doi: 10.12307/2022.575
Previous Articles Next Articles
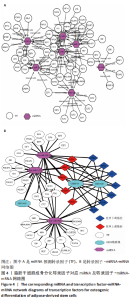
Transcription factor-miRNA-mRNA network analysis of osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells
Yu Chunbo, Li Dayu, Fan Fang, Li Changfu
- School of Basic Medicine, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2021-08-30Accepted:2021-10-11Online:2022-08-28Published:2022-01-24 -
Contact:Li Changfu, Master, Professor, School of Basic Medicine, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Yu Chunbo, Master, Experimentalist, School of Basic Medicine, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Zunyi City School Joint Fund, No. Zunyi Kehe HZ (2020)87 (to YCB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yu Chunbo, Li Dayu, Fan Fang, Li Changfu. Transcription factor-miRNA-mRNA network analysis of osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3908-3913.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
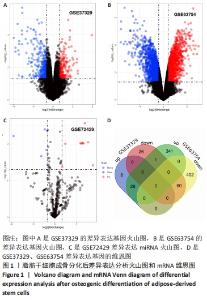
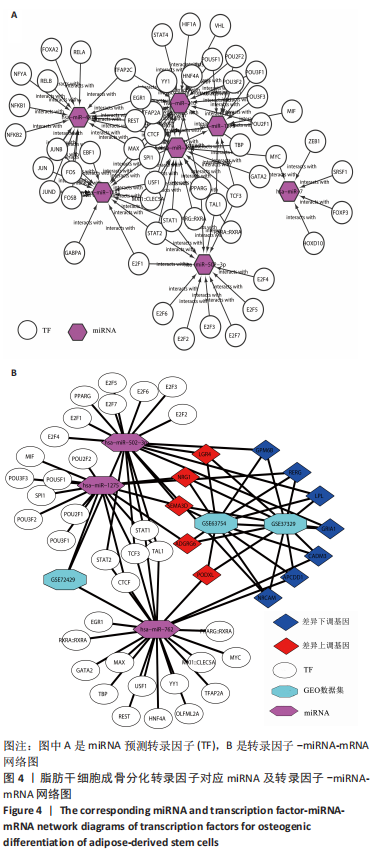
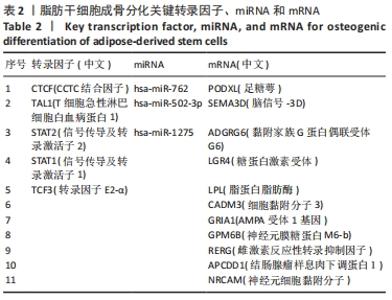
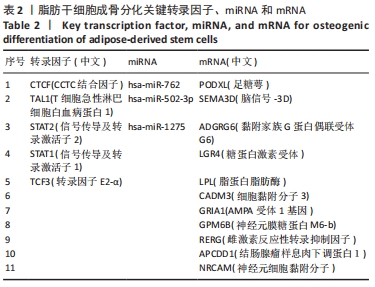
2.1 差异表达分析 通过GEO 检索筛选得到3张数据芯片,见表1。其脂肪干细胞组和成骨分化组来自于人脂肪来源的干细胞,通过GEO2R在线分析得到火山图,以|log2FC|≥2、P < 0.05筛选GSE37329得到121个差异表达基因(34个在成骨分化组上调,87个下调),见图1A;GSE63754得到830个差异表达基因(368个上调,462个下调),见图1B;以|log2FC|≥1、P < 0.05筛选GSE72429得到16个差异表达miRNA (10个上调,下调6个),见图1C;利用维恩图对GSE37329、GSE63754差异表达基因去交集,得到共同上调基因26个,共同下调基因60个,见图1D。"

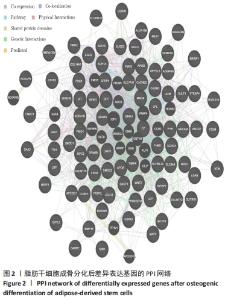
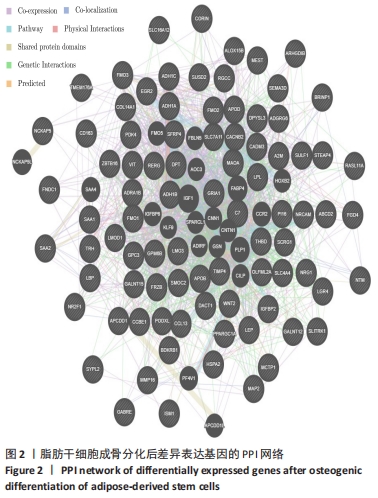
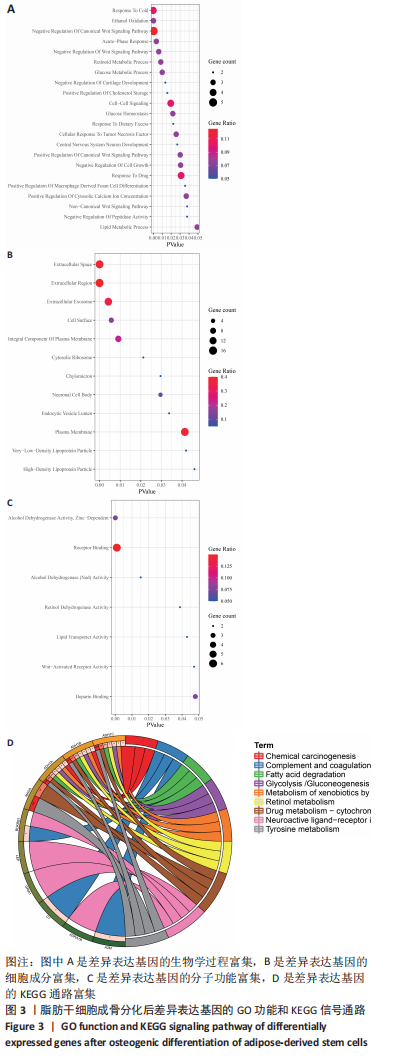
2.3 差异表达基因富集分析 通过DAVID富集分析发现,生物学过程富集在对寒冷的反应、乙醇氧化、经典 Wnt 信号通路的负调控、非经典Wnt信号途径、软骨发育的负调控、中枢神经系统神经元发育、细胞对肿瘤坏死因子的反应、细胞间信号转导及葡萄糖、脂质、维甲酸代谢过程等,见图3A;细胞成分富集在细胞外空间、胞外区、胞外外泌体、细胞表面、胞质核糖体、乳糜微粒、神经元细胞体、内吞囊泡管腔、质膜、极低密度脂蛋白颗粒、高密度脂蛋白颗粒等等,见图3B;分子功能主要表现在酒精脱氢酶活性,锌依赖、受体结合、酒精脱氢酶(Nad)活性、视黄醇脱氢酶活性、脂质转运蛋白活性、Wnt 激活的受体活性、肝素结合等,见图3C。KEGG信号通路主要表现在酪氨酸代谢、药物代谢-细胞色素 P450、脂肪酸降解、视黄醇代谢、糖酵解/糖异生、补体和凝血级联、细胞色素 P450 对异生物质的代谢、神经活性配体-受体相互作用、化学致癌等信号途径,见图3D。"
| [1] ZHAO X, LIANG M, LI X, et al. Identification of key genes and pathways associated with osteogenic differentiation of adipose stem cells. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(12):9777-9785. [2] 李兴艳,杨业静,黄家志,等.脂肪干细胞成骨分化的潜在关键基因与信号通路[J].广西医学,2021,43(1):70-73. [3] QUAN L, WANG Y, LIANG J, et al. Screening for genes, transcription factors and miRNAs associated with the myogenic and osteogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Int J Mol Med. 2016;38(6):1839-1849. [4] WARDE-FARLEY D, DONALDSON SL, COMES O, et al. The GeneMANIA prediction server: biological network integration for gene prioritization and predicting gene function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38(Web Server issue):W214-W220. [5] HUANG DAW, SHERMAN BT, LEMPICKI RA. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 2009;4(1):44-57. [6] LIU ZP, WU C, MIAO H, et al. RegNetwork: an integrated database of transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulatory networks in human and mouse. Database (Oxford). 2015;2015:bav095. [7] TOKAR T, PASTRELLO C, ROSSOS AEM, et al. mirDIP 4.1-integrative database of human microRNA target predictions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(D1):D360-D370. [8] 陈火. PODXL在胃癌转移中的作用及机制研究[D].苏州:苏州大学,2016. [9] 胡雪晴,林芙君,吴伟斌,等. Podocalyxin基因沉默对足细胞结构和功能的影响[J].肾脏病与透析肾移植杂志,2018,27(6):538-543. [10] YUAN WH, XIE QQ, WANG KP, et al. Screening of osteoarthritis diagnostic markers based on immune-related genes and immune infiltration. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):7032. [11] RYYN NEN J, KRIEBITZSCH C, MEYER MB, et al. Class 3 semaphorins are transcriptionally regulated by 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) in osteoblasts. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017;173:185-193. [12] SUN P, HE L, JIA K, et al. Regulation of body length and bone mass by Gpr126/Adgrg6. Sci Adv. 2020;6(12):eaaz0368. [13] YU WJ, ZHANG Z, FU W Z, et al. Association between LGR4 polymorphisms and peak bone mineral density and body composition. J Bone Miner Metab. 2020;38(5):658-669. [14] LUO J, YANG Z, MA Y, et al. LGR4 is a receptor for RANKL and negatively regulates osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption. Nat Med. 2016;22(5):539-546. [15] 王斌. Wnt/β-catenin、BMP-2/Runx2/Osterix、LGR4/RANKL/RANK通路的关键因子在骨质疏松性骨折端的表达分析[D].广州:广州医科大学,2019. [16] CHANG L, GARCIA-ARCOS I, NYR NR, et al. Lipoprotein Lipase Deficiency Impairs Bone Marrow Myelopoiesis and Reduces Circulating Monocyte Levels. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018;38(3):509-519. [17] 张晓萌. GPM6B在平滑肌细胞分化中的作用和机制研究[D].西安: 中国人民解放军空军军医大学,2018. [18] GHARIBI B, GHUMAN MS, CAMA G, et al. Site-specific differences in osteoblast phenotype, mechanical loading response and estrogen receptor-related gene expression. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2018;477: 140-147. [19] 史亚茹,杨威利,杨俊英,等. APCDD1对骨髓基质干细胞成脂分化及脂质合成的影响[J].山东医药,2018,58(37):1-5. [20] RAN S, PEI YF, LIU YJ, et al. Bivariate genome-wide association analyses identified genes with pleiotropic effects for femoral neck bone geometry and age at menarche. PloS One. 2013;8(4):e60362. [21] 李强.人大肠癌HT-29细胞系Livin基因相关miRNAs的筛选[D].南昌:南昌大学,2014. [22] 任梦迪,宁玉烨,黎明,等.细粒棘球蚴病患者外周血微小RNA的差异表达分析及其特异性诊断标志物的筛选[J].中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志,2017,35(5):423-428. [23] GAO J, GAO L, LI R, et al. Integrated analysis of microRNA-mRNA expression in A549 cells infected with influenza A viruses (IAVs) from different host species. Virus Res. 2019;263:34-46. [24] JOERGER M, BATY F, FR HM, et al. Circulating microRNA profiling in patients with advanced non-squamous NSCLC receiving bevacizumab/erlotinib followed by platinum-based chemotherapy at progression (SAKK 19/05). Lung Cancer. 2014;85(2):306-313. [25] 王庆辉,钱惠忠,张媛媛,等.基于GEO数据库对慢性乙型肝炎中关键miRNAs筛选及其生物信息学分析[J].山东医药,2020,60(26): 19-23. [26] RECHSTEINER T, SCHWARZ E, BROCK M, et al. The micro-RNA hsa-miR-502-3p is down-regulated in the plasma of obstructive sleep apnea patients after 2 weeks of continuous positive airway pressure therapy withdrawal: Data from a randomized controlled trial. Eur Respir J. 2014; 44:P2201. [27] 荆琳,单鹏程,张洪美,等.膝骨关节炎患者软骨组织与血浆中miRNA表达变化及意义[J].山东医药,2016,56(37):61-63. [28] OZDOGAN H, GUR DEDEOGLU B, OZTEMUR ISLAKOGLU Y, et al. DICER1 gene and miRNA dysregulation in mesenchymal stem cells of patients with myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloblastic leukemia. Leuk Res. 2017;63:62-71. [29] YANG JR, SHI MX, ZENG Y. LncRNA HAND2-AS1 inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of chronic myeloid leukemia cells by sponging with micRNA-1275. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(5):2103-2111. [30] MUJAHED H, MILIARA S, NEDDERMEYER A, et al. AML displays increased CTCF occupancy associated with aberrant gene expression and transcription factor binding. Blood. 2020;136(3):339-352. [31] FAN J, DU W, ZHANG H, et al. Transcriptional downregulation of miR-127-3p by CTCF promotes prostate cancer bone metastasis by targeting PSMB5. FEBS Lett. 2020;594(3):466-476. [32] PORCHER C, CHAGRAOUI H, KRISTIANSEN M S. SCL/TAL1: a multifaceted regulator from blood development to disease. Blood. 2017;129(15):2051-2060. [33] DEY S, CURTIS D J, JANE S M, et al. The TAL1/SCL transcription factor regulates cell cycle progression and proliferation in differentiating murine bone marrow monocyte precursors. Mol Cell Biol. 2010;30(9): 2181-2192. [34] 冯欣,李垚. STAT-1对白介素1β诱导的关节软骨细胞衰老的影响及其可能机制研究[J].中国全科医学,2016,19(11):1310-1313. [35] YI T, LEE D S, JEON M S, et al. Gene expression profile reveals that STAT2 is involved in the immunosuppressive function of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Gene. 2012;497(2):131-139. [36] HEATH H, BRITTON G, KUDO H, et al. Stat2 loss disrupts damage signalling and is protective in acute pancreatitis. J Pathol. 2020;252(1): 41-52. [37] 谢雪,石毓君,刘玉萍.肝细胞肝癌中TCF3表达及与预后的关系[J].临床与实验病理学杂志,2020,36(9):1036-1042. [38] HE B, CHEN J, LIU L, et al. Knockdown of Tcf3 enhances the wound healing effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in rats. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(8):BSR20180369. [39] GUO Q, LIU Y, SUN R, et al. Mechanical stimulation induced osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs through TWIST/E2A/p21 axis. Biosci Rep. 2020; 40(5):BSR20193876. |
| [1] | Zhou Hongqin, Wu Dandan, Yang Kun, Liu Qi. Exosomes that deliver specific miRNAs can regulate osteogenesis and promote angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112. |
| [2] | Gao Yujin, Peng Shuanglin, Ma Zhichao, Lu Shi, Cao Huayue, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. Osteogenic ability of adipose stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 999-1004. |
| [3] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [4] | Xu Jing, Yan Yongmin, Cai Mengjie . miR-373 inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation by downregulating transforming growth factor beta type II receptor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 756-761. |
| [5] | Chen Chichi, Zhang Yu, He Jiachen, Shi Qin. Osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in obese mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3846-3851. |
| [6] | You Wulin, Huang Guicheng, Wang Jianwei. Osteogenic differentiation potential of microencapsulated transgenic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells cocultured with osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3852-3857. |
| [7] | Cui Yinpeng, Guo Ai, Ma Lifeng, Liu Zhenjiang. Ouabain induces in vitro differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3796-3801. |
| [8] | Wu Siyi, Wu Qiong. Effect of adipose-derived stem cell transplantation on the immune microenvironment of adipose tissue in aged mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3773-3778. |
| [9] | Jin Ke, Wu Xiaoling, Luo Xiaoling, Xu Pengfei, Xu Xiaomei. Osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells under estrogen and crosstalk between the two pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3886-3891. |
| [10] | Gu Xiaodong, Li Fei, Che Xianda, Li Pengcui. Relationship between apoptosis of osteoarthritis chondrocytes and reduction of histone deacetylase 4 content [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(20): 3147-3151. |
| [11] | Feng Dongfei, He Hongxu, Xie Qi, Zhang Lili, Zhou Hui, Li Wei. Selection of key genes related to biological functions and regulation pathway in periodontal reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 253-259. |
| [12] | Cao Wei, Mao Furong, Hu Xiaohua, Yang Xiaohong. N-6 methyladenosine RNA methylation regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 266-270. |
| [13] | Zhang Jinming, Tian Yingzhou, Zhao Ling, Xiong Lihua, Wang Qiuping, Song Wei, Wen Jianxuan. Icariin alleviates osteoporosis by promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 2991-2996. |
| [14] | Chen Siming, Hu Jiawei, Li Lili, Wu Yongqiang, Peng Weijie. Comparison of biological characteristics of two kinds of primary isolated human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells under three-dimensional culture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 2997-3003. |
| [15] | Wan Zhe, Du Jun, He Jing, Hu Yang. Effect of Gushukang on osteogenic differentiation in a Beagle dog model during orthodontic root resorption and its mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(17): 2654-2659. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||