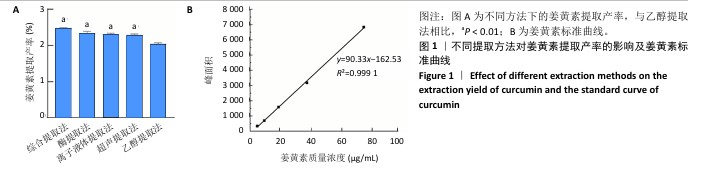
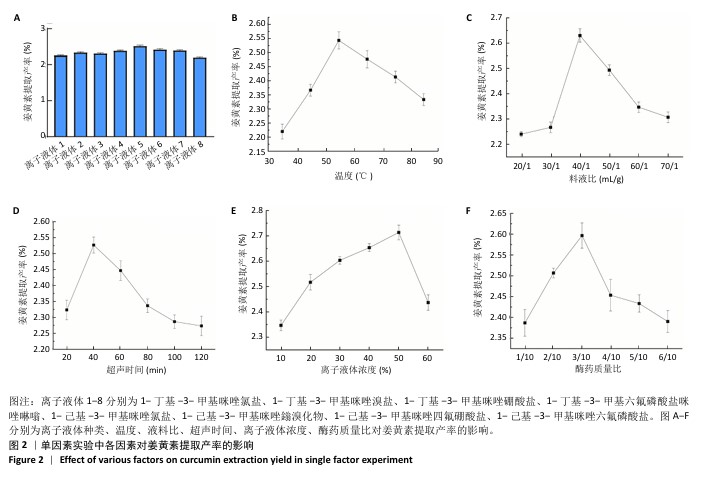
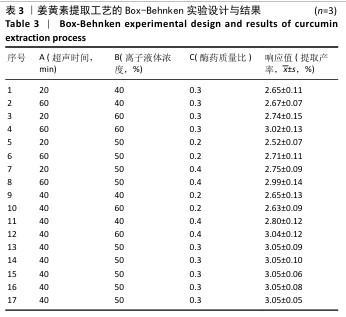
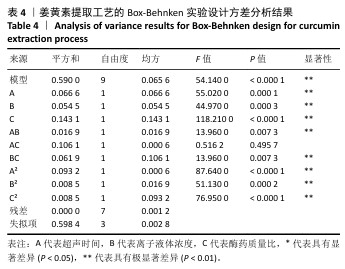
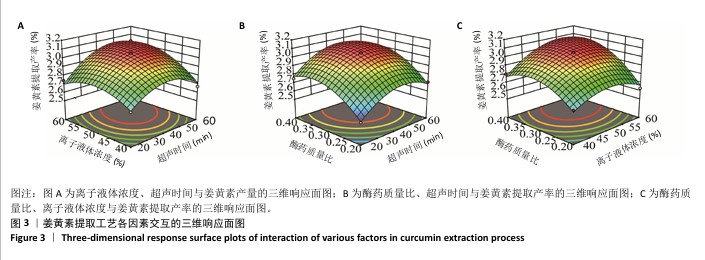
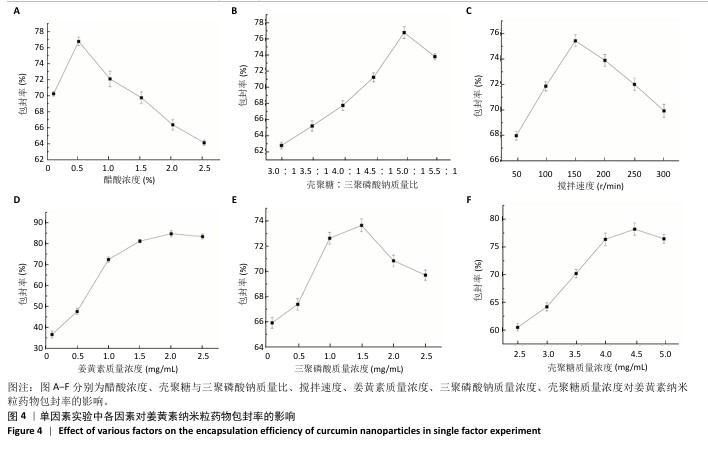
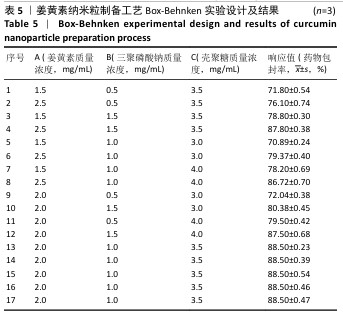
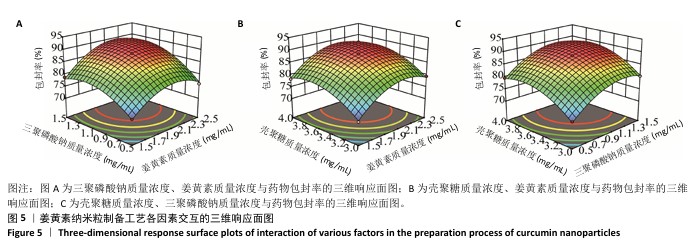
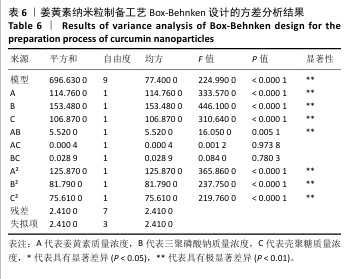
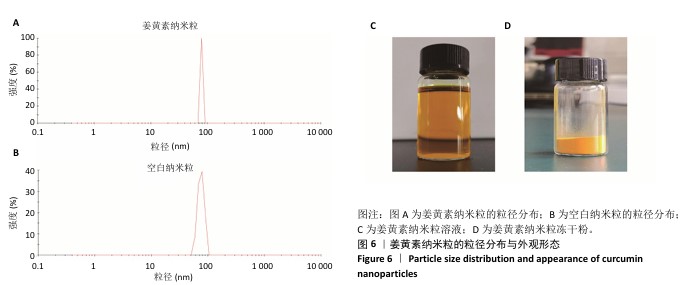
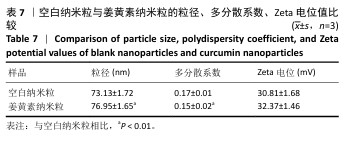
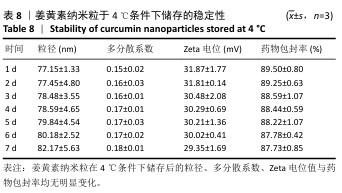
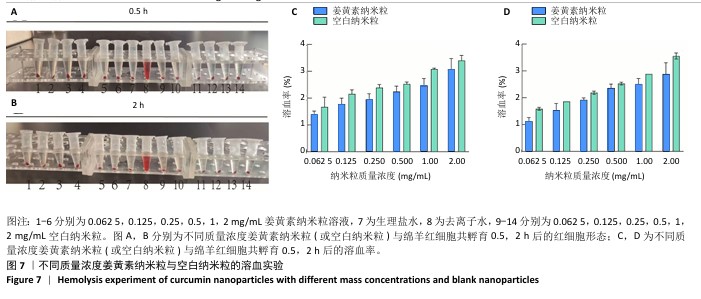
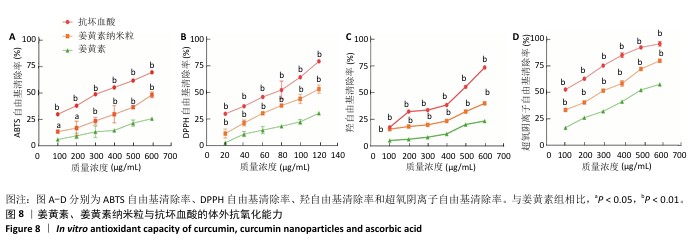
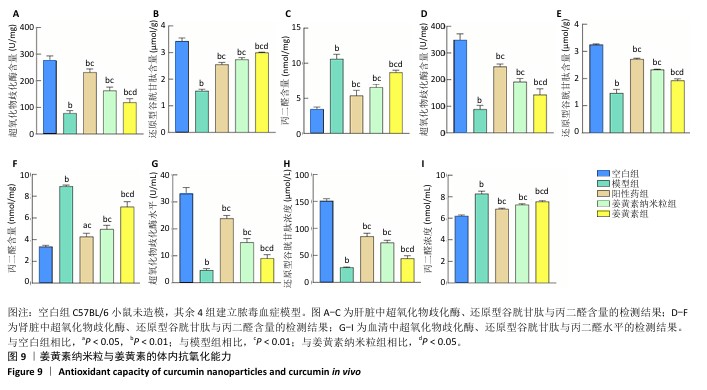
[1] 国家药典委员会.中华人民共和国药典(一部)[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社,2020.
[2] DOS SANTOS PDF, FRANCISCO CRL, COQUEIRO A, et al. The nanoencapsulation of curcuminoids extracted from Curcuma longa L. and an evaluation of their cytotoxic, enzymatic, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Food Funct. 2019;10(2):573-582.
[3] ZHOU H, FENG X, YAN Y, et al. Optimization of an ultrasonic-assisted aqueous two-phase extraction method for four flavonoids from Lysionotus pauciflorus. Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2022;52(7):
770-782.
[4] XU T, ZHANG H, WANG S, et al. A review on the advances in the extraction methods and structure elucidation of Poria cocos polysaccharide and its pharmacological activities and drug carrier applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;217:536-551.
[5] 苏适,于德涵,柴宝丽,等.响应面法优化超声辅助离子液体提取黑豆花青素工艺研究[J].中国调味品,2019,44(7):154-159.
[6] 周龙珠,王朋,董双,等.可溶性膳食纤维的制备及其在畜牧生产中的应用研究进展[J].中国畜牧杂志,2022,58(4):11-15.
[7] 张帅,郭晓雪,任丽琨,等.酶法改性影响膳食纤维的构成及生物作用效果的研究进展[J].食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(4):
1089-1098.
[8] GONG S, SUN M, LEE Y, et al. Bulk‐like Pt (100)‐oriented Ultrathin Surface: Combining the Merits of Single Crystals and Nanoparticles to Boost Oxygen Reduction Reaction. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2023; 135(4):e202214516.
[9] ARDEAN C, DAVIDESCU CM, NEMEŞ NS, et al. Factors influencing the antibacterial activity of chitosan and chitosan modified by functionalization. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(14):7449.
[10] HEJJAJI EM, SMITH AM, MORRIS GA. Evaluation of the mucoadhesive properties of chitosan nanoparticles prepared using different chitosan to tripolyphosphate (CS: TPP) ratios. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;120:1610-1617.
[11] 杨天硕,肖小兰,阮文权,等.响应面法优化负压原位碱度蒸汽汽提脱氨处理兰炭废水的研究[J].煤炭转化,2024,47(4):79-88.
[12] 许珂,缪秉陶,曹洪杰,等.鮟鱇鱼皮活性肽的分离纯化及其对HK-2细胞损伤保护的作用[J].广东海洋大学学报,2024,44(4):1-10.
[13] 李慧卿,曹叶霞,黄坊娇.DPPH·和ABTS+·比较研究毛建草多酚、黄酮和多糖的抗氧化协同作用[J].山西农业大学学报(自然科学版),2022,42(3):98-105.
[14] HOU D, LIAO H, HAO S, et al. Curcumin simultaneously improves mitochondrial dynamics and myocardial cell bioenergy after sepsis via the SIRT1-DRP1/PGC-1α pathway. Heliyon. 2024;10(7):e28501.
[15] JIANG C, SHI Q, YANG J, et al. Ceria nanozyme coordination with curcumin for treatment of sepsis-induced cardiac injury by inhibiting ferroptosis and inflammation. J Adv Res. 2024;63:159-170.
[16] XIAO Z, YU X, ZHANG S, et al. The Expression Levels and Significance of GSH, MDA, SOD, and 8‐OHdG in Osteochondral Defects of Rabbit Knee Joints. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022(1):6916179.
[17] 王月光,穆晓红,蒋昇源,等.急性脊髓损伤患者早期血清标志物与AISA分级的相关性[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(34): 5494-5499.
[18] WU J, SU C, JIANG J, et al. The potential role of serum lipoprotein in children with sepsis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023;102(48):e36311.
[19] TAO H, SHEN L. Research progress of curcumin in the treatment of sepsis. Shock. 2024;61(6):805-816.
[20] SULZBACHER MM, SULZBACHER LM, PASSOS FR, et al.Adapted murine sepsis score: improving the research in experimental sepsis mouse model. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022(1):5700853.
[21] 胡钰,傅纤雯,阙珊奇,等.干燥和提取方式对栀子花成分及抑菌活性的影响[J].食品科技,2024,49(5):200-207.
[22] MOHAMMADPOUR H, SADRAMELI SM, ESLAMI F, et al. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of Moringa peregrina oil with response surface methodology and comparison with Soxhlet method. Ind Crops Prod. 2019;131:106-116.
[23] LIANG H, WANG W, XU J, et al. Optimization of ionic liquid-based microwave-assisted extraction technique for curcuminoids from Curcuma longa L. Food Bioprod Process. 2017;104:57-65.
[24] ALEXANDRE EM, SILVA S, SANTOS SA, et al. Antimicrobial activity of pomegranate peel extracts performed by high pressure and enzymatic assisted extraction. Food Res Int. 2019;115:167-176.
[25] KIM DW, YOUSAF AM, LI DX, et al.Development of RP-HPLC method for simultaneous determination of docetaxel and curcumin in rat plasma: Validation and stability. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2017;12(1):
105-113.
[26] ZHENG S, ZHU Y, JIAO C, et al. Extraction and analysis of gigantol from Dendrobium officinale with response surface methodology. Molecules. 2018;23(4):818.
[27] 郑晓庆,王德达,慕鸿雁.装载鱼油的壳聚糖-三聚磷酸盐复合体系工艺研究[J].食品科技,2022,47(4):267-274.
[28] INDA A, TETTAMANTI CS, MARTINEZ SM, et al. New RP-HPLC method for the simultaneous determination of process yield and percentage of encapsulation of Gallein in albumin nanoparticles. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2024;1240:124161.
[29] 吴瑛,李阳,李凤琴,等.黄芩苷壳聚糖纳米粒的制备及表征[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2014,20(15):15-19.
[30] 李宛蓉,刘佩,余静怡,等.乳清分离蛋白与单宁酸相互作用提高稻米油Pickering乳液的稳定性[J].食品科学,2020,41(18):1-7.
[31] HASSAN S, BILAL N, KHAN TJ, et al. Bioinspired chitosan based functionalization of biomedical implant surfaces for enhanced hemocompatibility, antioxidation and anticoagulation potential: an in silico and in vitro study. RSC Adv. 2024;14(29):20691-20713.
[32] GUO X, LI W, WANG H, et al. Preparation, characterization, release and antioxidant activity of curcumin-loaded amorphous calcium phosphate nanoparticles. J Non Cryst Solids. 2018;500:317-325.
[33] 赵彩云,高文静,吴斌,等.杏干多酚的提取工艺及体外抗氧化活性研究[J].保鲜与加工,2024,24(5):61-68.
[34] 余青松,马欣龙,陈玉霞,等.茯苓菌固态发酵香菇柄基质的酶活力、营养成分及抗氧化活性变化[J].华中农业大学学报,2024,43(4): 230-238.
[35] 刘燕,马雪萍,史玉柱,等.滨蒿提取物对脂多糖诱导小鼠急性肺损伤的保护作用及抗氧化活性[J].中药药理与临床,2024,40(4): 78-82.
[36] WANG G, MA X, HUANG W, et al. Macrophage biomimetic nanoparticle-targeted functional extracellular vesicle micro-RNAs revealed via multiomics analysis alleviate sepsis-induced acute lung injury. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024;22(1):362.
[37] WANG J, WEI L, LIU C, et al. Taurine treatment alleviates intestinal mucositis induced by 5-fluorouracil in mice. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2022;77(3):399-404.
[38] AIMAIER S, TAO Y, LEI F, et al. Protective effects of the Terminalia bellirica tannin-induced Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in rats with high-altitude pulmonary hypertension. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023;23(1):150.
[39] ZHANG L, FAN G, KHAN MA, et al. Ultrasonic-assisted enzymatic extraction and identification of anthocyanin components from mulberry wine residues. Food Chem. 2020;323:126714.
[40] TSAI WH, YU KH, HUANG YC, et al. EGFR-targeted photodynamic therapy by curcumin-encapsulated chitosan/TPP nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13:903-916.
[41] DU Z, LIU J, ZHANG T, et al. A study on the preparation of chitosan-tripolyphosphate nanoparticles and its entrapment mechanism for egg white derived peptides. Food Chem. 2019;286:530-536.
[42] 管庆霞,林泽榆,夏昭睿,等.马钱子碱聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物纳米粒表征及体内药动学评价[J].吉林中医药,2023,43(10): 1193-1198.
[43] WEI ZZ, ZHOU TQ, XIA ZM, et al. Four organosulfur compounds from the seeds of Capsella bursa-pastoris and their anti-inflammatory activities. Nat Prod Res. 2023;37(16):2688-2696.
[44] HCINI K, BAHI A, ZARROUG MB, et al. Polyphenolic profile of tunisian thyme (Thymbra capitata L.) post-distilled residues: evaluation of total phenolic content and phenolic compounds and their contribution to antioxidant activity. Molecules. 2022;27(24):8791.
[45] KAŹMIERCZAK-BARAŃSKA J, BOGUSZEWSKA K, ADAMUS-GRABICKA A, et al. Two faces of vitamin C—antioxidative and pro-oxidative agent. Nutrients. 2020;12(5):1501.
[46] JIE Z, LIU J, SHU M, et al. Detection strategies for superoxide anion: A review. Talanta. 2022;236: 122892.
[47] SANDHU S K, RAUT J, KUMAR S, et al. Nanocurcumin and viable Lactobacillus plantarum based sponge dressing for skin wound healing. Int J Pharm. 2023;643:123187.
[48] LI Q, DING J, XIA B, et al. L-theanine alleviates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing oxidative stress and apoptosis through activation of the JAK2/STAT3 pathway in mice. Mol Med. 2024;30(1):98.
[49] ABDELNASER M, ALAAELDIN R, ATTYA ME, et al. Modulating Nrf-2/HO-1, apoptosis and oxidative stress signaling pathways by gabapentin ameliorates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024;397(2):947-958.
[50] 赵蝴蝶,易帆,马越,等.天然姜黄色素的应用及性能改善研究进展[J].印染助剂,2023,40(11):1-9.
[51] 郭玉,任迪峰,郭子烟,等.姜黄素增溶技术研究进展[J].食品与发酵工业,2024,50(14):342-348.
[52] 张欣,孙敬蒙,贾珍珍,等.叶黄素复合纳米颗粒的制备工艺优化及其稳定性和抗氧化活性分析[J].食品工业科技,2024,45(16): 102-113.
[53] FAN Y, YI J, ZHANG Y, et al. Fabrication of curcumin-loaded bovine serum albumin (BSA)-dextran nanoparticles and the cellular antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2018;239: 1210-1218.
[54] 陈煜淳,林勇,刘勇,等.姜黄素的应用、制备及改性研究进展[J].现代食品科技,2024,40(6):327-335.
[55] KHAN A, WANG C, SUN X, et al. Physicochemical and microstructural properties of polymerized whey protein encapsulated 3, 3′-Diindolylmethane nanoparticles. Molecules. 2019;24(4):702.
[56] YEDGAR S, BARSHTEIN G, GURAL A. Hemolytic activity of nanoparticles as a marker of their hemocompatibility. Micromachines (Basel). 2022; 13(12):2091.
[57] NAMGOONG JW, KIM HM, KIM SH, et al. Synthesis and characterization of metal phthalocyanine bearing carboxylic acid anchoring groups for nanoparticle dispersion and their application to color filters. Dyes Pigm. 2021;184:108737.
[58] TIAN Z, MAI Y, MENG T, et al. Nanocrystals for improving oral bioavailability of drugs: intestinal transport mechanisms and influencing factors. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2021;22(5):179.
[59] 向晓燕,余忠姝,谢佳希,等.壳聚糖杂化吴茱萸碱复合纳米粒的药动学研究[J].医药导报,2021,40(8):1022-1025.
[60] 杨晓宇,罗寒,盛剑勇,等.配体修饰的口服纳米载药系统的研究进展[J].医药导报,2020,39(9):1234-1239. |