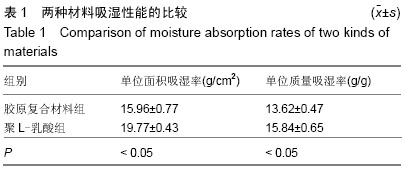
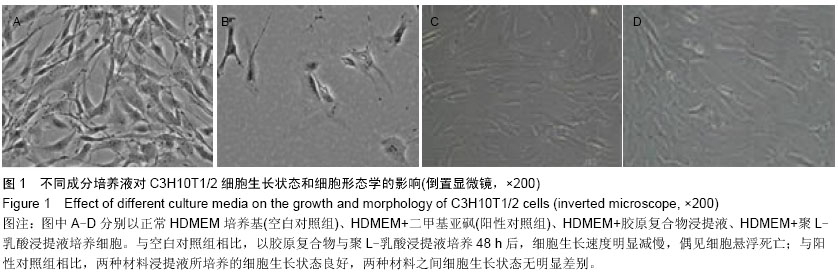
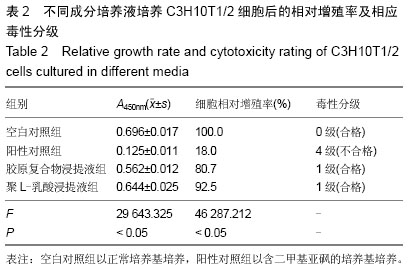
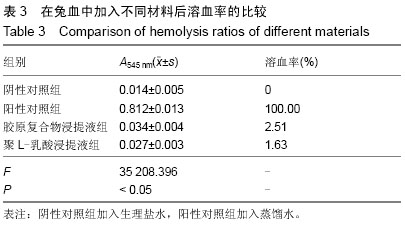
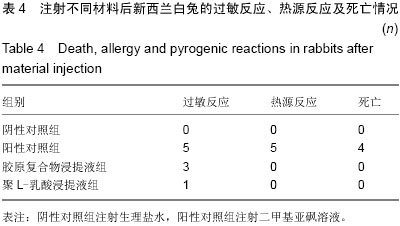
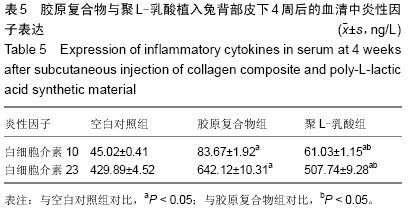
| [1] Li J,Hong J,Zheng Q, et al.Repair of rat cranial bone defects with nHAC/PLLA and BMP-2-related peptide or rhBMP-2.J Orthop Res.2011;29(11):1745-1752.
[2] Yuan Y,Jin X,Fan Z,et al.In vivo degradation of copolymers prepared from L-lactide, 1,3-trimethylene carbonate and glycolide as coronary stent materials. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2015;26(3):139.
[3] Pauck RG,Reddy BD.Computational analysis of the radial mechanical performance of PLLA coronary artery stents.Med Eng Phys.2015;37(1):7-12.
[4] Busch R,Strohbach A,Rethfeldt S,et al.New stent surface materials: the impact of polymer-dependent interactions of human endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, and platelets.Acta Biomater.2014;10(2):688-700.
[5] Inoue M,Sasaki M,Katada Y,et al.Poly-(L-lactic acid) and citric acid-crosslinked gelatin composite matrices as a drug-eluting stent coating material with endothelialization, antithrombogenic, and drug release properties.J Biomed Mater Res A.2013;101(7): 2049-2057.
[6] Flege C,Vogt F,Höges S,et al.Development and characterization of a coronary polylactic acid stent prototype generated by selective laser melting.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2013;24(1): 241-255.
[7] Kim HI,Ishihara K,Lee S,et al. Tissue response to poly (L-lactic acid)-based blend with phospholipid polymer for biodegradable cardiovascular stents.Biomaterials. 2011;32(9):2241-2247.
[8] Bruining N,de Winter S,Roelandt JR,et al.Monitoring in vivo absorption of a drug-eluting bioabsorbable stent with intravascular ultrasound-derived parameters a feasibility study.JACC Cardiovasc Interv.2010;3(4):449-456.
[9] Lewis RA.Ab interno approach to the subconjunctival space using a collagen glaucoma stent. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2014;40(8):1301-1306.
[10] Zhao N,Workman B,Zhu D.Endothelialization of novel magnesium-rare earth alloys with fluoride and collagen coating. Int J Mol Sci.2014;15(4):5263-5276.
[11] Li J,Zhang K,Chen H,et al.A novel coating of type IV collagen and hyaluronic acid on stent material-titanium for promoting smooth muscle cell contractile phenotype. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2014;38:235-243.
[12] Soltysiak P,Höllwarth ME,Saxena AK.Comparison of suturing techniques in the formation of collagen scaffold tubes for composite tubular organ tissue engineering. Biomed Mater Eng.2010;20(1):1-11.
[13] Martínez de Arenaza I,Obarzanek-Fojt M,Sarasua JR,et al. Pyrene-end-functionalized poly(L-lactide) as an efficient carbon nanotube dispersing agent in poly(L-lactide): mechanical performance and biocompatibility study. Biomed Mater. 2015; 10(4):045003.
[14] Cai Q,Shi Y,Shan D,et al.Osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells on poly (l-lactide)/Fe3O4 nanofibers with static magnetic field exposure. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2015; 55:166-173.
[15] Yang DZ,Chen AZ,Wang SB,et al.Preparation of poly(L-lactic acid) nanofiber scaffolds with a rough surface by phase inversion using supercritical carbon dioxide .Biomed Mater.2015; 10(3):035015.
[16] Hu Y,Darcos V,Monge S,et al. Thermo-responsive drug release from self-assembled micelles of brush-like PLA/PEG analogues block copolymers.Int J Pharm.2015;491(1-2): 152-161.
[17] Yang Y,Wu J,Jin G,et al.Research of osteoblastic induced rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells cultured on β-TCP/PLLA porous scaffold. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(3):3202-3209.
[18] Di Bonito P,Petrone L,Casini G,et al.Amino-functionalized poly(l-lactide) lamellar single crystals as a valuable substrate for delivery of HPV16-E7 tumor antigen in vaccine development.Int J Nanomedicine.2015;10:3447-3458.
[19] Yu Y,Lü X,Ding F. microRNA regulatory mechanism by which PLLA aligned nanofibers influence PC12 cell differentiation.J Neural Eng.2015;12(4):046010.
[20] Kowalski W,Dammer M,Bakczewitz F,et al.In-situ investigation of stress conditions during expansion of bare metal stents and PLLA-coated stents using the XRD sin(2)ψ-technique.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2015; 49:23-29.
[21] Lin JH,Chen CK,Wen SP,et al.Poly-L-lactide/sodium alginate/chitosan microsphere hybrid scaffolds made with braiding manufacture and adhesion technique: Solution to the incongruence between porosity and compressive strength. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2015;52:111-120.
[22] Pan P,Han L,Bao J,et al.Competitive Stereocomplexation, Homocrystallization, and Polymorphic Crystalline Transition in Poly(l-lactic acid)/Poly(d-lactic acid) Racemic Blends: Molecular Weight Effects.J Phys Chem B.2015;119(21):6462-6470.
[23] Mashhadikhan M,Soleimani M,Parivar K,et al. ADSCs on PLLA/PCL Hybrid Nanoscaffold and Gelatin Modification: Cytocompatibility and Mechanical Properties. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2015;7(1):32-38.
[24] Liu M,Huang G,Cong Y,et al.The preparation and characterization of micelles from poly(γ-glutamic acid)-graft- poly(L-lactide) and the cellular uptake thereof. J Mater Sci Mater Med.2015;26(5):187.
[25] Wach RA,Adamus A,Kowalska-Ludwicka K,et al.In vivo evaluation of nerve guidance channels of PTMC/PLLA porous biomaterial.Arch Med Sci.2015;11(1):210-219.
[26] Zhang Z,Lv Q,Gao X,et al.pH-Responsive Poly(ethylene glycol)/Poly(L-lactide) Supramolecular Micelles Based on Host-Guest Interaction.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015 ; 7(16): 8404-8411.
[27] Lizundia E,Vilas JL,León LM.Crystallization, structural relaxation and thermal degradation in Poly (L-lactide)/cellulose nanocrystal renewable nanocomposites. Carbohydr Polym.2015;123: 256-265.
[28] Frydrych M,Román S,MacNeil S,et al.Biomimetic poly(glycerol sebacate)/poly(l-lactic acid) blend scaffolds for adipose tissue engineering. Acta Biomater.2015;18:40-49.
[29] Uchida S,Utsunomiya H,Taketa T,et al.Arthroscopic fragment fixation using hydroxyapatite/poly-L-lactate Acid thread pins for treating elbow osteochondritis dissecans.Am J Sports Med. 2015;43(5):1057-1065.
[30] Stein P,Vitavska O,Kind P,et al.The biological basis for poly-L-lactic acid-induced augmentation.J Dermatol Sci.2015; 78(1):26-33. |