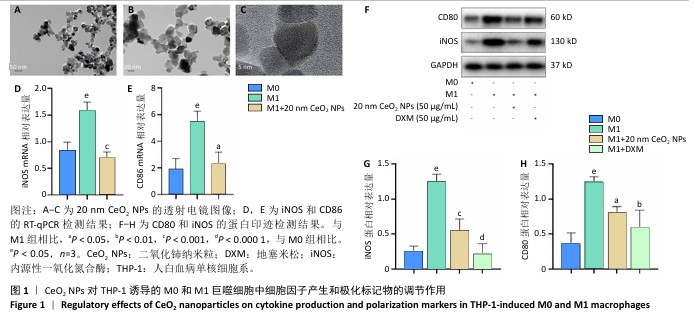
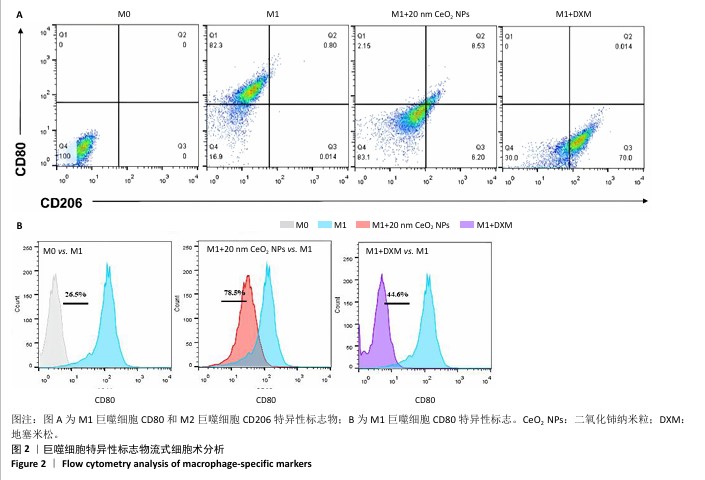
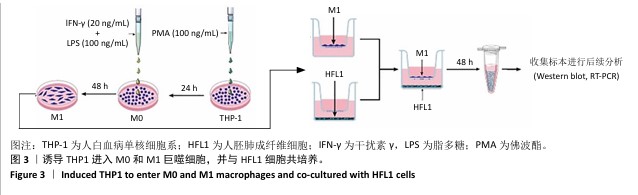
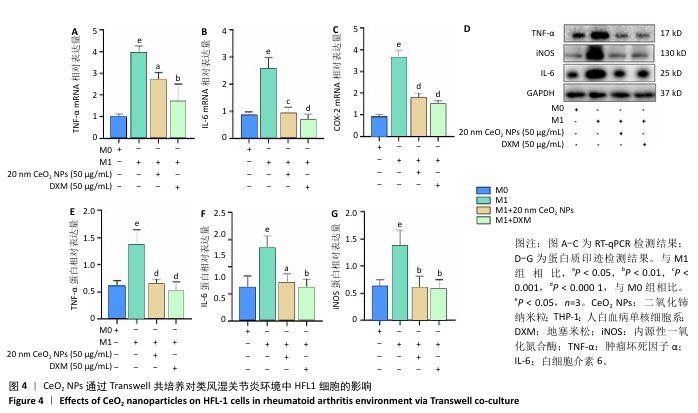
[1] 王俊伟, 李伟, 耿兴超.类风湿关节炎发病机制研究进展[J].风湿病与关节炎,2024,13(8):67-72.
[2] FINCKH A, GILBERT B, HODKINSON B, et al. Global epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022;18(10):591-602.
[3] CUSH JJ. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Early Diagnosis and Treatment. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2022;48(2):537-547.
[4] KOMATSU N, TAKAYANAGI H. Mechanisms of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis-immune cell-fibroblast-bone interactions. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(7):415-429.
[5] RODRÍGUEZ-UBREVA J, DE LA CALLE-FABREGAT C, LI T, et al. Inflammatory cytokines shape a changing DNA methylome in monocytes mirroring disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(11):1505-1516.
[6] KUROWSKA-STOLARSKA M, ALIVERNINI S. Synovial tissue macrophages in joint homeostasis, rheumatoid arthritis and disease remission. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(7):384-397.
[7] CUTOLO M, CAMPITIELLO R, GOTELLI E, et al. The Role of M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovitis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:867260.
[8] SMOLEN JS, ALETAHA D, MCINNES IB. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2016;388(10055):2023-2038.
[9] HUMAIRA, BUKHARI SAR, SHAKIR HA, et al. Biosynthesized Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles CeO2NPs: Recent Progress and Medical Applications. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2023;24(6):766-779.
[10] LORD MS, BERRET JF, SINGH S, et al. Redox Active Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles: Current Status and Burning Issues. Small (Weinheim an Der Bergstrasse, Germany). 2021;17(51):e2102342.
[11] LI M, LIU J, LUO X, et al. Monoclonal Antibody-Guided Tumor-Targeted Hollow Virus-Like Cerium Oxide with Oxygen Self-Supply for Intensifying Photodynamic Therapy. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(8):e2202418.
[12] MENG L, TANG L, GAO F, et al. Hollow CeO2-Based Nanozyme with Self-Accelerated Cascade Reactions for Combined Tumor Therapy. Chemistry. 2024;30(49):e202401640.
[13] SANMUGAM A, ABBISHEK S, KUMAR SL, et al. Synthesis of chitosan based reduced graphene oxide-CeO2 nanocomposites for drug delivery and antibacterial applications. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2023;145:106033.
[14] ERNST LM, PUNTES V. How Does Immunomodulatory Nanoceria Work? ROS and Immunometabolism. Front Immunol. 2022;13:750175.
[15] BYUN SY, HAN AR, KIM KM, et al. Antibacterial properties of mesoporous silica coated with cerium oxide nanoparticles in dental resin composite. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):18014.
[16] HE J, MENG X, MENG C, et al. Layer-by-Layer Pirfenidone/Cerium Oxide Nanocapsule Dressing Promotes Wound Repair and Prevents Scar Formation. Molecules. 2022;27(6):1830.
[17] YU D, CHEN L, YAN T, et al. Enhancing Infected Diabetic Wound Healing through Multifunctional Nanocomposite-Loaded Microneedle Patch: Inducing Multiple Regenerative Sites. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13(20): e2301985.
[18] VANDEWALLE J, LUYPAERT A, DE BOSSCHER K, et al. Therapeutic Mechanisms of Glucocorticoids. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2018; 29(1):42-54.
[19] CRUZ-TOPETE D, CIDLOWSKI JA. One hormone, two actions: anti- and pro-inflammatory effects of glucocorticoids. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2015;22(1-2):20-32.
[20] QUAN L, ZHANG Y, CRIELAARD BJ, et al. Nanomedicines for inflammatory arthritis: head-to-head comparison of glucocorticoid-containing polymers,micelles,and liposomes.ACS Nano. 2014;8(1): 458-466.
[21] JANG S, KWON EJ, LEE JJ. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Pathogenic Roles of Diverse Immune Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(2):905.
[22] YUNNA C, MENGRU H, LEI W, et al. Macrophage M1/M2 polarization. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;877:173090.
[23] LI Y, LIANG Q, ZHOU L, et al. An ROS-responsive artesunate prodrug nanosystem co-delivers dexamethasone for rheumatoid arthritis treatment through the HIF-1α/NF-κB cascade regulation of ROS scavenging and macrophage repolarization. Acta Biomater. 2022;152:406-424.
[24] KIM J, KIM HY, SONG SY, et al. Synergistic Oxygen Generation and Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging by Manganese Ferrite/Ceria Co-decorated Nanoparticles for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment. ACS Nano. 2019;13(3):3206-3217.
[25] PAOLINO S, CUTOLO M, PIZZORNI C. Glucocorticoid management in rheumatoid arthritis: morning or night low dose? Reumatologia. 2017;55(4):189-197.
[26] SAIFI MA, SEAL S, GODUGU C. Nanoceria, the versatile nanoparticles: Promising biomedical applications. J Control Release. 2021;338: 164-189.
[27] FU X, LI P, CHEN X, et al. Ceria nanoparticles: biomedical applications and toxicity. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2024;25(5):361-388.
[28] MIRAN HA, JAF ZN, ALTARAWNEH M,et al. An Insight into Geometries and Catalytic Applications of CeO2 from a DFT Outlook. Molecules. 2021;26(21):6485.
[29] MENG X, WANG WD, LI SR, et al.Harnessing cerium-based biomaterials for the treatment of bone diseases. Acta Biomater. 2024;183:30-49.
[30] GIRIGOSWAMI A, ADHIKESAVAN H, MUDENKATTIL S, et al. Role of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles and Doxorubicin in Improving Cancer Management: A Mini Review.Curr Pharm Des. 2023;29(33):
2640-2654.
[31] SAIF-ELNASR M, SAMY EM, ABDEL-KHALEK AF. Cerium oxide nanoparticles display antioxidant and antiapoptotic effects on gamma irradiation-induced hepatotoxicity. Cell Biochem Funct. 2024; 42(5):e4092.
[32] ALVANDI M, SHAGHAGHI Z, FARZIPOUR S, et al. Radioprotective Potency of Nanoceria. Curr Radiopharm. 2024;17(2):138-147.
[33] YANG L, RAN H, YIN Y, et al. Mitochondrial Targeted Cerium Oxide Nanoclusters for Radiation Protection and Promoting Hematopoiesis. International Journal of Nanomedicine. 2024;19:6463-6483.
[34] YANG J, XIAO S, DENG J, et al. Oxygen vacancy-engineered cerium oxide mediated by copper-platinum exhibit enhanced SOD/CAT-mimicking activities to regulate the microenvironment for osteoarthritis therapy. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024;22(1):491.
[35] SANDOVAL C, REYES C, ROSAS P, et al. Effectiveness of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Evolution Using In Vivo and In Vitro Studies: A Systematic Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2023; 24(21):15728.
[36] SUN Y, SUN X, LI X, et al. A versatile nanocomposite based on nanoceria for antibacterial enhancement and protection from aPDT-aggravated inflammation via modulation of macrophage polarization. Biomaterials. 2021;268:120614.
[37] HUSSAIN S, AL-NSOUR F, RICE AB, et al. Cerium dioxide nanoparticles induce apoptosis and autophagy in human peripheral blood monocytes. ACS Nano. 2012;6(7):5820-5829.
[38] MA JY, ZHAO H, MERCER RR, et al. Cerium oxide nanoparticle-induced pulmonary inflammation and alveolar macrophage functional change in rats. Nanotoxicology. 2011;5(3):312-325.
[39] PARK EJ, CHOI J, PARK YK, et al. Oxidative stress induced by cerium oxide nanoparticles in cultured BEAS-2B cells. Toxicology. 2008; 245(1-2):90-100.
[40] HUSSAIN S, AL-NSOUR F, RICE AB, et al. Cerium dioxide nanoparticles induce apoptosis and autophagy in human peripheral blood monocytes. ACS Nano. 2012;6(7):5820-5829.
[41] KALASHNIKOVA I, CHUNG SJ, NAFIUJJAMAN M, et al. Ceria-based nanotheranostic agent for rheumatoid arthritis. Theranostics. 2020; 10(26):11863-11880. |