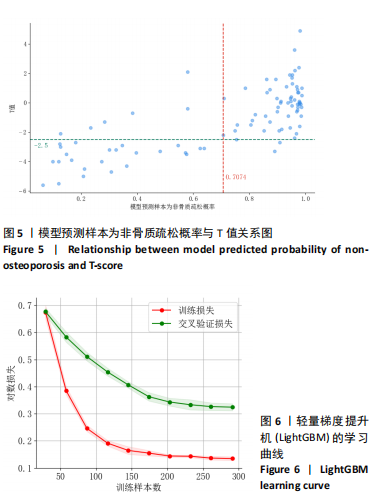
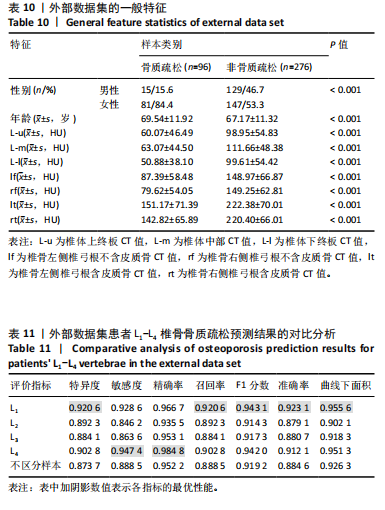
[1] SONG S, GUO Y, YANG Y, et al. Advances in pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies for osteoporosis. Pharmacol Ther. 2022;237:108168.
[2] RACHNER TD, KHOSLA S, HOFBAUER LC. Osteoporosis: now and the future. Lancet. 2011;377(9773):1276-1287.
[3] LÖFFLER MT, JACOB A, SCHARR A, et al. Automatic opportunistic osteoporosis screening in routine CT: improved prediction of patients with prevalent vertebral fractures compared to DXA. Eur Radiol. 2021;31(8):6069-6077.
[4] 孟凡,董敏洁,郭瑾,等.区老年人骨质疏松患病情况及全科防控策略[J]. 中国全科医学,2023,26(22):2778-2784.
[5] 朱洁云,高敏,宋秋韵,等.中国老年人骨质疏松症患病率的Meta分析[J].中国全科医学,2022,25(3):346-353.
[6] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会,章振林.原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2022)[J].中国全科医学,2023,26(14):1671-1691.
[7] 国家统计局,国务院第七次全国人口普查领导小组办公室.第七次全国人口普查公报(第五号):人口年龄构成情况[J].中国统计,2021(5):10-11.
[8] WANG L, YU W, YIN X, et al. Prevalence of Osteoporosis and Fracture in China: The China Osteoporosis Prevalence Study. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(8):e2121106.
[9] SI L, WINZENBERG TM, JIANG Q, et al. Projection of osteoporosis-related fractures and costs in China: 2010-2050. Osteoporos Int. 2015;26(7):1929-1937.
[10] ZENG Q, LI N, WANG Q, et al. The Prevalence of Osteoporosis in China, a Nationwide, Multicenter DXA Survey. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34(10):1789-1797.
[11] 中国健康促进基金会基层医疗机构骨质疏松症诊断与治疗专家共识委员会.基层医疗机构骨质疏松症诊断和治疗专家共识(2021)[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2021,27(7):937-944.
[12] PICKHARDT PJ, CORREALE L, HASSAN C. AI-based opportunistic CT screening of incidental cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis, and sarcopenia: cost-effectiveness analysis. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2023;48(3):1181-1198.
[13] GAO L, MOODIE M, WATTS JJ, et al. Cost-Effectiveness of Osteoporosis Opportunistic Screening Using Computed Tomography in China. Value Health Reg Issues. 2023;38:38-44.
[14] SHIM JG, KIM DW, RYU KH, et al. Application of machine learning approaches for osteoporosis risk prediction in postmenopausal women. Arch Osteoporos. 2020;15(1):169.
[15] BUI HM, HA MH, PHAM HG, et al. Predicting the risk of osteoporosis in older Vietnamese women using machine learning approaches. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1): 20160.
[16] OU YANG WY, LAI CC, TSOU MT, et al. Development of Machine Learning Models for Prediction of Osteoporosis from Clinical Health Examination Data. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(14):7635.
[17] PARK HW, JUNG H, BACK KY, et al. Application of Machine Learning to Identify Clinically Meaningful Risk Group for Osteoporosis in Individuals Under the Recommended Age for Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry. Calcif Tissue Int. 2021;109(6):645-655.
[18] NAM KH, SEO I, KIM DH, et al. Machine Learning Model to Predict Osteoporotic Spine with Hounsfield Units on Lumbar Computed Tomography. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2019;62(4):442-449.
[19] 凯依塞尔·阿布都克力木,麦麦提敏·阿卜力米提,李磊,等.女性腰椎退行性病变患者腰椎CT值对骨质疏松症的诊断作用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2024,28(6):945-949.
[20] 王晓文,招文华,颜先伟,等.腰椎椎弓根对应横断面椎体松质骨CT值与BMD值、T值的相关性[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(10):1465-1471.
[21] HAN K, YOU ST, LEE HJ, et al. Hounsfield unit measurement method and related factors that most appropriately reflect bone mineral density on cervical spine computed tomography. Skeletal Radiol. 2022;51(10):1987-1993.
[22] SCHREIBER JJ, ANDERSON PA, HSU WK. Use of computed tomography for assessing bone mineral density. Neurosurg Focus. 2014;37(1):E4.
[23] 杨思德.椎体松质骨CT值与双能X线骨密度值的相关性研究[D].桂林:桂林医学院,2023.
[24] XU F, ZOU D, LI W, et al. Hounsfield units of the vertebral body and pedicle as predictors of pedicle screw loosening after degenerative lumbar spine surgery. Neurosurg Focus. 2020;49(2):E10.
[25] KE G, MENG Q, FINLEY T, et al. Lightgbm: A highly efficient gradient boosting decision tree. 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA. 2017.
[26] LUNDBERG S, LEE SI. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst. 2017;30:4765-4774.
[27] DEO RC. Machine Learning in Medicine. Circulation. 2015;132(20):1920-1930.
[28] ALI MM, PAUL BK, AHMED K, et al. Heart disease prediction using supervised machine learning algorithms: Performance analysis and comparison. Comput Biol Med. 2021;136:104672.
[29] MARCOS-ZAMBRANO LJ, KARADUZOVIC-HADZIABDIC K, LONCAR TURUKALO T, et al. Applications of Machine Learning in Human Microbiome Studies: A Review on Feature Selection, Biomarker Identification, Disease Prediction and Treatment. Front Microbiol. 2021;12:634511.
[30] KAVITHA C, MANI V, SRIVIDHYA SR, et al. Early-Stage Alzheimer’s Disease Prediction Using Machine Learning Models. Front Public Health. 2022;10:853294.
[31] AZMI J, ARIF M, NAFIS MT, et al. A systematic review on machine learning approaches for cardiovascular disease prediction using medical big data. Med Eng Phys. 2022;105:103825.
[32] CHEN Y, MAO Q, WANG B, et al. Privacy-Preserving Multi-Class Support Vector Machine Model on Medical Diagnosis. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2022;26(7): 3342-3353.
[33] UDDIN S, HAQUE I, LU H, et al. Comparative performance analysis of K-nearest neighbour (KNN) algorithm and its different variants for disease prediction. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):6256.
[34] GUAN X, DU Y, MA R, et al. Construction of the XGBoost model for early lung cancer prediction based on metabolic indices. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2023;23(1):107.
[35] BUDHOLIYA K, SHRIVASTAVA SK, SHARMA V. An optimized XGBoost based diagnostic system for effective prediction of heart disease. J King Saud Univ Comput Inf Sci. 2022;34(7):4514-4523.
[36] HU J, SZYMCZAK S. A review on longitudinal data analysis with random forest. Brief Bioinform. 2023;24(2):bbad002.
[37] SINGH LK, KHANNA M, SINGH R. Artificial intelligence based medical decision support system for early and accurate breast cancer prediction. Adv Eng Softw. 2023;175:103338.
[38] AZAD C, BHUSHAN B, SHARMA R, et al. Prediction model using SMOTE, genetic algorithm and decision tree (PMSGD) for classification of diabetes mellitus. Multimedia Syst. 2022;28(4):1289.
[39] SHEHAB M, ABUALIGAH L, SHAMBOUR Q, et al. Machine learning in medical applications: A review of state-of-the-art methods. Comput Biol Med. 2022;145: 105458.
[40] DONG Z, WANG Q, KE Y, et al. Prediction of 3-year risk of diabetic kidney disease using machine learning based on electronic medical records. J Transl Med. 2022;20(1):143.
[41] PENG X, LI L, WANG X, et al. A Machine Learning-Based Prediction Model for Acute Kidney Injury in Patients With Congestive Heart Failure. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:842873.
[42] SUN Y, DING S, ZHANG Z, et al. An improved grid search algorithm to optimize SVR for prediction. Soft Computing. 2021;25:5633-5644.
[43] FLUSS R, FARAGGI D, REISER B. Estimation of the Youden Index and its associated cutoff point. Biom J. 2005;47(4):458-472.
[44] GUGLIELMI G, LANG TF. Quantitative computed tomography. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2002;6(3):219-227.
[45] LEE SJ, BINKLEY N, LUBNER MG, et al. Opportunistic screening for osteoporosis using the sagittal reconstruction from routine abdominal CT for combined assessment of vertebral fractures and density. Osteoporos Int. 2016;27(3):1131-1136.
[46] KARA K, SIVRIOGLU AK, ARIBAL S, et al. The diagnosis of osteoporosis by measuring lumbar vertebrae density with MDCT: a comparative study with quantitative computerized tomography (QCT). Acta Medica Mediterr. 2013;29:775-779.
[47] PU X, WANG D, GU S. Advances in Hounsfield units value for predicting cage subsidence on spinal interbody fusion surgery. Eur Spine J. 2023;32(9):3149-3157.
[48] ZOU D, MUHEREMU A, SUN Z, et al. Computed tomography Hounsfield unit-based prediction of pedicle screw loosening after surgery for degenerative lumbar spine disease. J Neurosurg Spine. 2020;32(5):716-721.
[49] ZOU D, SUN Z, ZHOU S, et al. Hounsfield units value is a better predictor of pedicle screw loosening than the T-score of DXA in patients with lumbar degenerative diseases. Eur Spine J. 2020;29(5):1105-1111. |