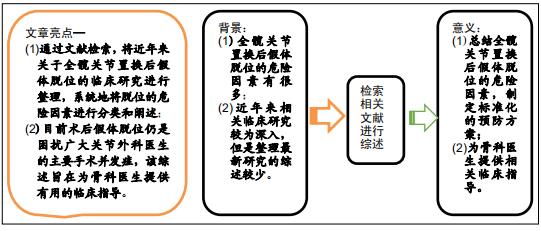
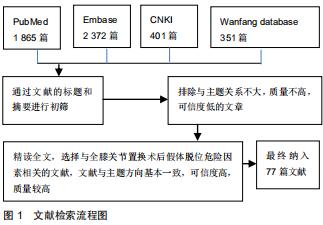
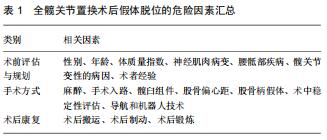
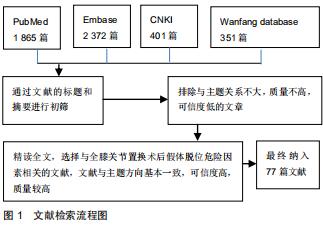
|
[1] SU W, ZENG M, HU Y, et al. Cup revision involving retention of a fixed but malpositioned acetabular component in patients with poor general conditions. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(46): e8622.
[2] GRAVES SE, DE STEIGER R, DAVIDSON D, et al. The use of femoral stems with exchangeable necks in primary total hip arthroplasty increases the rate of revision. Bone Joint J. 2017; 99-b(6):766-773.
[3] EKMAN E, NURMI H, REITO A, et al. Complications Following 250 Cemented Modular Hip Hemiarthroplasties. Scand J Surg. 2018:1457496918812226.
[4] HADDAD FS. Even the winners are losers. Bone Joint J. 2017; 99-b(5):561-562.
[5] BERRY DJ, VON KNOCH M, SCHLECK CD, et al. The cumulative long-term risk of dislocation after primary Charnley total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86(1):9-14.
[6] INACIO MC, AKE CF, PAXTON EW, et al. Sex and risk of hip implant failure: assessing total hip arthroplasty outcomes in the United States. JAMA Intern Med.2013;173(6):435-441.
[7] JORGENSEN CC, KJAERSGAARD-ANDERSEN P, SOLGAARD S, et al. Hip dislocations after 2,734 elective unilateral fast-track total hip arthroplasties: incidence, circumstances and predisposing factors. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(11): 1615-1622.
[8] FESSY MH, PUTMAN S, VISTE A, et al. What are the risk factors for dislocation in primary total hip arthroplasty? A multicenter case-control study of 128 unstable and 438 stable hips. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2017;103(5):663-668.
[9] KOBAYASHI S, KUBO T, IWAMOTO Y, et al. Nationwide multicenter follow-up cohort study of hip arthroplasties performed for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Int Orthop. 2018;42(7): 1661-1668.
[10] LUBBEKE A. Obesity in total hip arthroplasty-does it really matter? Acta Orthop. 2012;83(1): 99-100.
[11] WAGNER ER, KAMATH AF, FRUTH KM, et al. Effect of Body Mass Index on Complications and Reoperations After Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016;98(3):169-179.
[12] QUEALLY JM, ABDULKARIM A, MULHALL KJ. Total hip replacement in patients with neurological conditions. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009;91(10):1267-1273.
[13] MOON AS, PINTO MC, CICHOS KH, et al. Total Joint Arthroplasty in Patients With Cerebral Palsy. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2019.
[14] JÄMSEN E, PELTOLA M2, PUOLAKKA T, et al. Surgical outcomes of hip and knee arthroplasties for primary osteoarthritis in patients with Alzheimer's disease: a nationwide registry-based case-controlled study. Bone Joint J. 2015;97-b(5):654-661.
[15] PIERREPONT J, HAWDON G, MILES BP, et al. Variation in functional pelvic tilt in patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-b(2):184-191.
[16] STEFL M, LUNDERGAN W, HECKMANN N, et al. Spinopelvic mobility and acetabular component position for total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-b(1 Supple A):37-45.
[17] ESPOSITO CI, MILLER TT, KIM HJ, et al. Reply to the Letter to the Editor: Does Degenerative Lumbar Spine Disease Influence Femoroacetabular Flexion in Patients Undergoing Total Hip Arthroplasty? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(8):1881.
[18] BUCKLAND AJ, PUVANESARAJAH V, VIGDORCHIK J, et al. Dislocation of a primary total hip arthroplasty is more common in patients with a lumbar spinal fusion. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-b(5): 585-591.
[19] PUTNIS SE, WARTEMBERG GK, KHAN WS, et al. A literature review of total hip arthroplasty in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: perioperative considerations and outcome. Open Orthop J. 2015;9:483-488.
[20] ZHENG GQ, ZHANG YG, CHEN JY, et al. Decision making regarding spinal osteotomy and total hip replacement for ankylosing spondylitis: experience with 28 patients. Bone Joint J. 2014;96-b(3):360-365.
[21] WYLES CC, HEIDENREICH MJ, JENG J, et al. The john charnley award: redefining the natural history of osteoarthritis in patients with hip dysplasia and impingement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017; 475(2):336-350.
[22] BERGH C, FENSTAD AM, FURNES O, et al. Increased risk of revision in patients with non-traumatic femoral head necrosis. Acta Orthop. 2014;85(1):11-17.
[23] MU W, YANG D, XU B, et al. Midterm Outcome of Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty in Crowe IV-Hartofilakidis Type III Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(3): 668-675.
[24] SHOJI T, YAMASAKI T, IZUMI S, et al. Factors affecting the potential for posterior bony impingement after total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-b(9):1140-1146.
[25] LANGTON DJ, JAMESON SS, JOYCE TJ, et al. Accelerating failure rate of the ASR total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(8):1011-1016.
[26] RAVI B, JENKINSON R, AUSTIN PC, et al. Relation between surgeon volume and risk of complications after total hip arthroplasty: propensity score matched cohort study. BMJ. 2014; 348:g3284.
[27] HEDLUNDH U, AHNFELT L, HYBBINETTE CH, et al. Surgical experience related to dislocations after total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996;78(2):206-209.
[28] MALKANI AL, ONG KL, LAU E, et al. Early- and late-term dislocation risk after primary hip arthroplasty in the Medicare population. J Arthroplasty. 2010;25(6 Suppl):21-25.
[29] KANEKO T, HIRAKAWA K, FUSHIMI K. Relationship between peri-operative outcomes and hospital surgical volume of total hip arthroplasty in Japan. Health Policy. 2014;117(1): 48-53.
[30] MIRIC A, KAHN B, WALDMAN B, et al. Characteristics and natural history of transient postoperative pseudosubluxation after total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2000;15(6):736-743.
[31] JINNAH AH, SMITH BP, PERRICELLI BC. Comparison of two multimodal pain regimens used for postoperative pain control in total joint arthroplasty patients. J Surg Orthop Adv. 2016;25(4): 209-214.
[32] MASONIS JL, BOURNE RB. Surgical approach, abductor function, and total hip arthroplasty dislocation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;(405):46-53.
[33] PETIS S, HOWARD JL, LANTING BL, et al. Surgical approach in primary total hip arthroplasty: anatomy, technique and clinical outcomes. Can J Surg. 2015;58(2):128-139.
[34] 王岳桂,胡波涌,陆细红,等.人工全髋关节置换术后脱位的原因分析及防治对策探讨[J].中国医药科学,2018,8(16):205-207.
[35] 殷勇,谢成,杨静,等.不同手术入路行全髋关节置换术对髋臼假体位置及术后早期髋关节功能影响的临床研究[J].创伤外科杂志,2019, 21(5):362-366.
[36] ZIJLSTRA WP, DE HARTOG B, VAN STEENBERGEN LN, et al. Effect of femoral head size and surgical approach on risk of revision for dislocation after total hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2017;88(4):395-401.
[37] JAMESON SS, LEES D, JAMES P, et al. Lower rates of dislocation with increased femoral head size after primary total hip replacement: a five-year analysis of NHS patients in England. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(7):876-880.
[38] AMLIE E, HOVIK O, REIKERAS O. Dislocation after total hip arthroplasty with 28 and 32-mm femoral head. J Orthop Traumatol. 2010;11(2):111-115.
[39] HOWIE DW, HOLUBOWYCZ OT, MIDDLETON R. Large femoral heads decrease the incidence of dislocation after total hip arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(12):1095-102.
[40] BROOKS PJ. Hip resurfacing: a large, US single-surgeon series. Bone Joint J. 2016;98-b(1 Suppl A):10-13.
[41] HAUGHOM BD, PLUMMER DR, MORIC M, et al. Is There a Benefit to Head Size Greater Than 36 mm in Total Hip Arthroplasty? J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(1):152-155.
[42] LUO Y, SUN XF, CHEN J, et al. Could larger diameter of 4th generation ceramic bearing increase the rate of squeaking after THA?: A retrospective study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(52): e13977.
[43] LEWINNEK GE, LEWIS JL, TARR R, et al. Dislocations after total hip-replacement arthroplasties. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1978;60(2): 217-220.
[44] BEVERLAND DE, O'NEILL CK, RUTHERFORD M, et al. Placement of the acetabular component. Bone Joint J. 2016;98-b (1 Suppl A):37-43.
[45] SEAGRAVE KG, TROELSEN A, MALCHAU H, et al. Acetabular cup position and risk of dislocation in primary total hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2017;88(1):10-17.
[46] ESPOSITO CI, GLADNICK BP, LEE YY, et al. Cup position alone does not predict risk of dislocation after hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(1):109-113.
[47] PARVIZI J, WADE FA, RAPURI V, et al. Revision hip arthroplasty for late instability secondary to polyethylene wear. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;447:66-69.
[48] SHAH SM, WALTER WL, TAI SM, et al. Late Dislocations After Total Hip Arthroplasty: Is the Bearing a Factor? J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(9):2852-2856.
[49] 胥伯勇,郭文涛,穆文博,等.限制性内衬翻修治疗髋关节置换术后反复脱位的7例报道[J].新疆医科大学学报,2018,41(6):697-701.
[50] 排祖拉·阿不都吉力力.运用限制性内衬治疗反复人工髋关节脱位[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2014.
[51] 郑鸿,谭宏昌,钟环,等.仿生双动全髋置换术治疗CroweⅢ型成人髋关节发育不良[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(1):87-89.
[52] FORDE B, ENGELN K, BEDAIR H, et al. Restoring femoral offset is the most important technical factor in preventing total hip arthroplasty dislocation. J Orthop. 2018;15(1):131-133.
[53] YANG C, ZHANG L, CHEN S, et al. [Effect of Jumbo cups for total hip arthroplasty revision on femoral offset and hip center of rotation]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017; 31(2):139-143.
[54] JINNO T, KOGA D, ASOU Y, et al. Intraoperative evaluation of the effects of femoral component offset and head size on joint stability in total hip arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2017;25(1): 2309499016684298.
[55] COLAS S, ALLALOU A, POICHOTTE A, et al. Exchangeable Femoral Neck (Dual-Modular) THA Prostheses Have Poorer Survivorship Than Other Designs: A Nationwide Cohort of 324,108 Patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;475(8):2046-2059.
[56] HAYASHI S, NISHIYAMA T, FUJISHIRO T, et al. Excessive femoral offset does not affect the range of motion after total hip arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2013;37(7):1233-1237.
[57] NOBLE PC, ALEXANDER JW, LINDAHL LJ, et al. The anatomic basis of femoral component design. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1988; (235):148-65.
[58] OPPERER M, LEE YY, NALLY F, et al. A critical analysis of radiographic factors in patients who develop dislocation after elective primary total hip arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2016;40(4): 703-708.
[59] NAM D, SALIH R, NAHHAS CR, et al. Is a modular dual mobility acetabulum a viable option for the young, active total hip arthroplasty patient? Bone Joint J. 2019;101-b(4):365-371.
[60] MALIK A, MAHESHWARI A, DORR LD. Impingement with total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(8):1832-1842.
[61] SCULCO PK, COTTINO U, ABDEL MP, et al. Avoiding hip instability and limb length discrepancy after total hip arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am. 2016;47(2):327-334.
[62] NAITO M, OGATA K, ASAYAMA I. Intraoperative limb length measurement in total hip arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 1999;23(1): 31-33.
[63] DOMB BG, EL BITAR YF, SADIK AY, et al. Comparison of robotic-assisted and conventional acetabular cup placement in THA: a matched-pair controlled study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(1): 329-336.
[64] ELSON L, DOUNCHIS J, ILLGEN R, et al. Precision of acetabular cup placement in robotic integrated total hip arthroplasty. Hip Int. 2015;25(6):531-536.
[65] ILLGEN RLN, BUKOWSKI BR, ABIOLA R, et al. Robotic-assisted total hip arthroplasty: outcomes at minimum two-year follow-up. Surg Technol Int. 2017;30:365-372.
[66] BARGAR WL, BAUER A, BORNER M. Primary and revision total hip replacement using the Robodoc system. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;(354):82-91.
[67] PONGKUNAKORN A, CHATMAITRI S, DIEWWATTANAWIWAT K. Use of smartphone to improve acetabular component positioning in total hip athroplasty: A comparative clinical study. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2019;27(1):2309499019825578.
[68] TIMPERLEY AJ, BIAU D, CHEW D, et al. Dislocation after total hip replacement - there is no such thing as a safe zone for socket placement with the posterior approach. Hip Int. 2016;26(2): 121-127.
[69] GROMOV K, TROELSEN A, OTTE KS, et al. Removal of restrictions following primary THA with posterolateral approach does not increase the risk of early dislocation--reply. Acta Orthop. 2015;86(4): 518-519.
[70] SMITH TO, SACKLEY CM. UK survey of occupational therapist's and physiotherapist's experiences and attitudes towards hip replacement precautions and equipment. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17:228.
[71] JORGENSEN CC, KEHLET H. Fall-related admissions after fast-track total hip and knee arthroplasty - cause of concern or consequence of success? Clin Interv Aging. 2013;8:1569-1577.
[72] VERVERELI PA, LEBBY EB, TYLER C, et al. Evaluation of reducing postoperative hip precautions in total hip replacement: a randomized prospective study. Orthopedics. 2009;32(12):889.
[73] LEE GRH, BERSTOCK JR, WHITEHOUSE MR, et al. Recall and patient perceptions of hip precautions 6 weeks after total hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2017;88(5):496-499.
[74] KORNUIJT A, DAS D, SIJBESMA T, et al. The rate of dislocation is not increased when minimal precautions are used after total hip arthroplasty using the posterolateral approach: a prospective, comparative safety study. Bone Joint J. 2016;98-b(5):589-594.
[75] VAN DER WEEGEN W, KORNUIJT A, DAS D. Do lifestyle restrictions and precautions prevent dislocation after total hip arthroplasty? A systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. Clin Rehabil. 2016;30(4):329-339.
[76] ALLEGRA PR, NUNO AU, BARRERA CM, et al. MRI Evaluation of Posterior Capsular Dehiscence After Posterior Approach Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2019;27(23): e1052-e1058.
[77] TOHIDI M, BROGLY SB, LAJKOSZ K, et al. Ten-year risk of complication and mortality after total hip arthroplasty in morbidly obese patients: a population study. Can J Surg. 2019;62(6): 442-449.
|