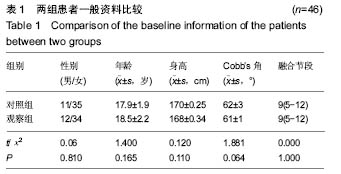
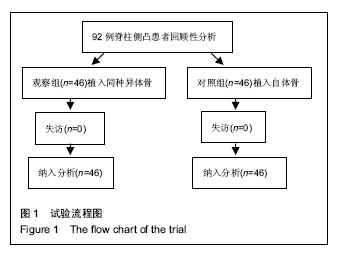
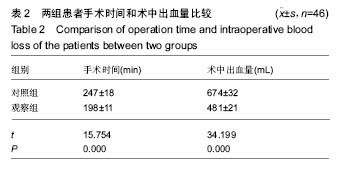
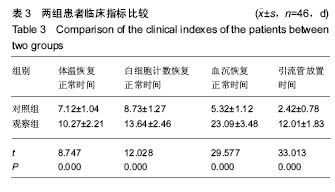
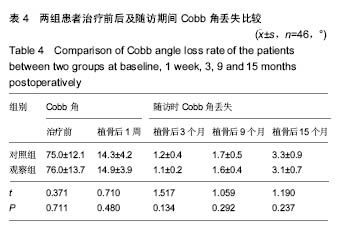
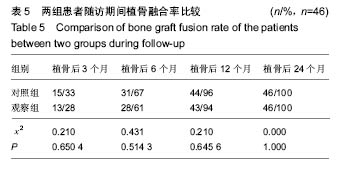
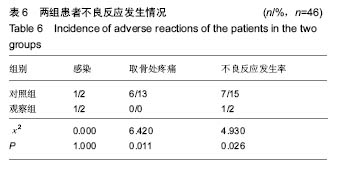
| [1]张鹏,陈东,刘国辉. 青少年特发性脊柱侧凸病因学研究进展[J]. 临床骨科杂志,2008,11(1):85-87.[2]Miller NH. Cause and natural history of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Orthop Clin North Am. 1999;30(3): 343-352. [3]Ovadia D. Classification of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS). J Child Orthop. 2013;7(1):25-28.[4]Ehrler DM, Vaccaro AR. The use of allograft bone in lumbar spine surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;(371):38-45.[5]Prolo DJ, Rodrigo JJ. Contemporary bone graft physiology and surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985;(200):322-342.[6]Boden SD. Bone repair and enhancement clinical trial design. Spine applications. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;(355 Suppl): S336-346. [7]邱勇, 刘臻, 王斌, 等.脊柱前路手术髂前嵴取骨并发症相关分析[J] .中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2007, 17(8):584-587.[8]Delawi D, Dhert WJ, Castelein RM, et al. The incidence of donor site pain after bone graft harvesting from the posterior iliac crest may be overestimated: a study on spine fracture patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(17):1865-1868.[9]Fernyhough JC, Schimandle JJ, Weigel MC, et al. Chronic donor site pain complicating bone graft harvesting from the posterior iliac crest for spinal fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1992;17(12):1474-1480.[10]Sawin PD, Traynelis VC, Menezes AH. A comparative analysis of fusion rates and donor-site morbidity for autogeneic rib and iliac crest bone grafts in posterior cervical fusions. J Neurosurg. 1998;88(2):255-265.[11]Summers BN, Eisenstein SM. Donor site pain from the ilium. A complication of lumbar spine fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1989;71(4):677-680.[12]Nkenke E, Weisbach V, Winckler E, et al. Morbidity of harvesting of bone grafts from the iliac crest for preprosthetic augmentation procedures: a prospective study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004;33(2):157-163.[13]楼肃亮,郑杰,杨永宏,等. 后路半椎体切除内固定治疗先天性脊柱侧凸[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2010,20(5):435-436.[14]张菁,陈海霞. 不同骨移植在脊柱侧凸矫形术中的作用[J].中国康复,2010,25(6):460-461.[15]Khan SN, Sandhu HS, Parvataneni HK, et al. Bone graft substitutes in spine surgery.Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 2000;59(1):5-10.[16]Grogan DP, Kalen V, Ross TI, et al. Use of allograft bone for posterior spinal fusion in idiopathic scoliosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;(369):273-278.[17]黄锐,高峰,王宇,等.脊椎弹性内固定治疗脊柱侧凸的临床疗效[J].中国老年学杂志,2015,35(2):481-482.[18]闵理,刘立岷,宋跃明,等.不同种类骨移植在青少年特发性脊柱侧凸后路矫形术中的中长期疗效评价[J].中国骨与关节外科,2012, 5(5):382-388.[19]Theologis AA, Tabaraee E, Lin T, et al. Type of bone graft or substitute does not affect outcome of spine fusion with instrumentation for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(17):1345-1351.[20]Nakazawa T, Takaso M, Imura T, et al. Autogenous iliac crest bone graft versus banked allograft bone in scoliosis surgery in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Int Orthop. 2010; 34(6):855-861.[21]Violas P, Chapuis M, Bracq H. Local autograft bone in the surgical management of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(2):189-192.[22]张质钢,王小虎,张秋宁.国内系统评价纳入标准对随机试验的界定差异有可能导致偏倚[J].中国循证医学杂志, 2013,13(6): 764-767.[23]Bridwell KH, O'Brien MF, Lenke LG, et al. Posterior spinal fusion supplemented with only allograft bone in paralytic scoliosis. Does it work. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994;19(23): 2658-2666.[24]Schwartz CE, Martha JF, Kowalski P, et al. Prospective evaluation of chronic pain associated with posterior autologous iliac crest bone graft harvest and its effect on postoperative outcome. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2009; 7:49.[25]田敏,邹强,孙磊,等. 同种异体骨与自体骨移植治疗青少年脊柱侧凸的比较研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2007,15(23): 1792-1794.[26]Martinez V, Ben Ammar S, Judet T, et al. Risk factors predictive of chronic postsurgical neuropathic pain: the value of the iliac crest bone harvest model. Pain. 2012;153(7): 1478-1483.[27]Shi J, Wang Z, Wang P, et al. Application and comparison of allograft and autograft bone for interbody fusion in cervical tuberculosis. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2011;25(11):1290-1293.[28]张大伟,李真慧,裴国献,等.复合环孢素同种异体骨与冻干同种异体骨移植后免疫学比较[J].解放军医学院学报,2014,35(3): 266-269.[29]Betz RR, Lavelle WF, Mulcahey MJ, et al. Histology of a fusion mass augmented with demineralized bone matrix for congenital scoliosis. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2011;20(1):37-40.[30]Betz RR, Petrizzo AM, Kerner PJ, et al. Allograft versus no graft with a posterior multisegmented hook system for the treatment of idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(2):121-127.[31]Knapp DR Jr, Jones ET, Blanco JS, et al. Allograft bone in spinal fusion for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005;18 Suppl:S73-76.[32]Jones KC, Andrish J, Kuivila T, et al. Radiographic outcomes using freeze-dried cancellous allograft bone for posterior spinal fusion in pediatric idiopathic scoliosis. J Pediatr Orthop. 2002;22(3):285-289.[33]Watkins RG 4th, Hussain N, Freeman BJ, et al. Anterior instrumentation for thoracolumbar adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: do structural interbody grafts preserve sagittal alignment better than morselized rib autografts. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(20):2337-2342.[34]宋其韬,杨建平,王林森,等. 螺旋 CT三维重建在小儿髋臼发育不良中的作用[J].中华骨科杂志,2003,23(2):92-95.[35]夏榕圻,楼跃,杨渭川,等. 螺旋CT和三维重建技术在髋关节发育不良手术治疗中的应用[J].中华小儿外科杂志, 2003,24(1): 35-37. |
.jpg)
.jpg)