中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (4): 633-640.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.04.024
• 组织构建学术探讨 tissue construction academic discussion • 上一篇 下一篇
基于文献计量学心肌梗死模型大鼠血清代谢组学的特点
伍新诚1,郑景辉2,马晓聪1,卓小媛1,张新春1
- 1广西中医药大学研究生院,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530001;2广西中医药大学附属瑞康医院心血管内科,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530001
Metabolomics characteristics in a rat model of myocardial infarction based on bibiometrics analyses
Wu Xin-cheng1, Zheng Jing-hui2, Ma Xiao-cong1, Zhuo Xiao-yuan1, Zhang Xin-chun1
- 1Graduate School of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Cardiovasology, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
代谢组学:是继基因组学和蛋白质组学之后新近发展起来的一门学科,是系统生物学的重要组成部分。之后得到迅速发展并渗透到多项领域,比如疾病诊断、医药研制开发、营养食品科学、毒理学、环境学,植物学等与人类健康护理密切相关的领域。基因组学和蛋白质组学分别从基因和蛋白质层面探寻生命的活动,而实际上细胞内许多生命活动是发生在代谢物层面的,如细胞信号释放(cell signaling),能量传递,细胞间通信等都是受代谢物调控的。
转运蛋白:是膜蛋白的一大类,介导生物膜内外的化学物质以及信号交换。脂质双分子层在细胞或细胞器周围形成了一道疏水屏障, 将其与周围环境隔绝起来。尽管有一些小分子可以直接渗透通过膜,但是大部分的亲水性化合物,如糖,氨基酸,离子,药物等等,都需要特异的转运蛋白的帮助来通过疏水屏障。因此,转运蛋白在营养物质摄取,代谢产物释放以及信号转导等广泛的细胞活动中起着重要的作用。
文题释义:
代谢组学:是继基因组学和蛋白质组学之后新近发展起来的一门学科,是系统生物学的重要组成部分。之后得到迅速发展并渗透到多项领域,比如疾病诊断、医药研制开发、营养食品科学、毒理学、环境学,植物学等与人类健康护理密切相关的领域。基因组学和蛋白质组学分别从基因和蛋白质层面探寻生命的活动,而实际上细胞内许多生命活动是发生在代谢物层面的,如细胞信号释放(cell signaling),能量传递,细胞间通信等都是受代谢物调控的。
转运蛋白:是膜蛋白的一大类,介导生物膜内外的化学物质以及信号交换。脂质双分子层在细胞或细胞器周围形成了一道疏水屏障, 将其与周围环境隔绝起来。尽管有一些小分子可以直接渗透通过膜,但是大部分的亲水性化合物,如糖,氨基酸,离子,药物等等,都需要特异的转运蛋白的帮助来通过疏水屏障。因此,转运蛋白在营养物质摄取,代谢产物释放以及信号转导等广泛的细胞活动中起着重要的作用。
.jpg) 文题释义:
代谢组学:是继基因组学和蛋白质组学之后新近发展起来的一门学科,是系统生物学的重要组成部分。之后得到迅速发展并渗透到多项领域,比如疾病诊断、医药研制开发、营养食品科学、毒理学、环境学,植物学等与人类健康护理密切相关的领域。基因组学和蛋白质组学分别从基因和蛋白质层面探寻生命的活动,而实际上细胞内许多生命活动是发生在代谢物层面的,如细胞信号释放(cell signaling),能量传递,细胞间通信等都是受代谢物调控的。
转运蛋白:是膜蛋白的一大类,介导生物膜内外的化学物质以及信号交换。脂质双分子层在细胞或细胞器周围形成了一道疏水屏障, 将其与周围环境隔绝起来。尽管有一些小分子可以直接渗透通过膜,但是大部分的亲水性化合物,如糖,氨基酸,离子,药物等等,都需要特异的转运蛋白的帮助来通过疏水屏障。因此,转运蛋白在营养物质摄取,代谢产物释放以及信号转导等广泛的细胞活动中起着重要的作用。
文题释义:
代谢组学:是继基因组学和蛋白质组学之后新近发展起来的一门学科,是系统生物学的重要组成部分。之后得到迅速发展并渗透到多项领域,比如疾病诊断、医药研制开发、营养食品科学、毒理学、环境学,植物学等与人类健康护理密切相关的领域。基因组学和蛋白质组学分别从基因和蛋白质层面探寻生命的活动,而实际上细胞内许多生命活动是发生在代谢物层面的,如细胞信号释放(cell signaling),能量传递,细胞间通信等都是受代谢物调控的。
转运蛋白:是膜蛋白的一大类,介导生物膜内外的化学物质以及信号交换。脂质双分子层在细胞或细胞器周围形成了一道疏水屏障, 将其与周围环境隔绝起来。尽管有一些小分子可以直接渗透通过膜,但是大部分的亲水性化合物,如糖,氨基酸,离子,药物等等,都需要特异的转运蛋白的帮助来通过疏水屏障。因此,转运蛋白在营养物质摄取,代谢产物释放以及信号转导等广泛的细胞活动中起着重要的作用。摘要
背景:研究证实,代谢组学可以从一个总体轮廓上对大鼠心肌梗死病理代谢产物进行分析,从全面总体的角度对大鼠心肌梗死机制进行观察。
目的:进一步分析大鼠心肌梗死模型血清代谢组生物信息学通路。
方法:从中国知网、万方数据库、维普数据库、Embase、PubMed数据库中检索大鼠心肌梗死的实验研究。对纳入研究代谢产物进行汇总。信号通路分析采用KEGG,代谢产物分子注释、相关的酶或转运蛋白及其相关性质分析采用HMDB,代谢产物路径可视化采用metPA网络软件。
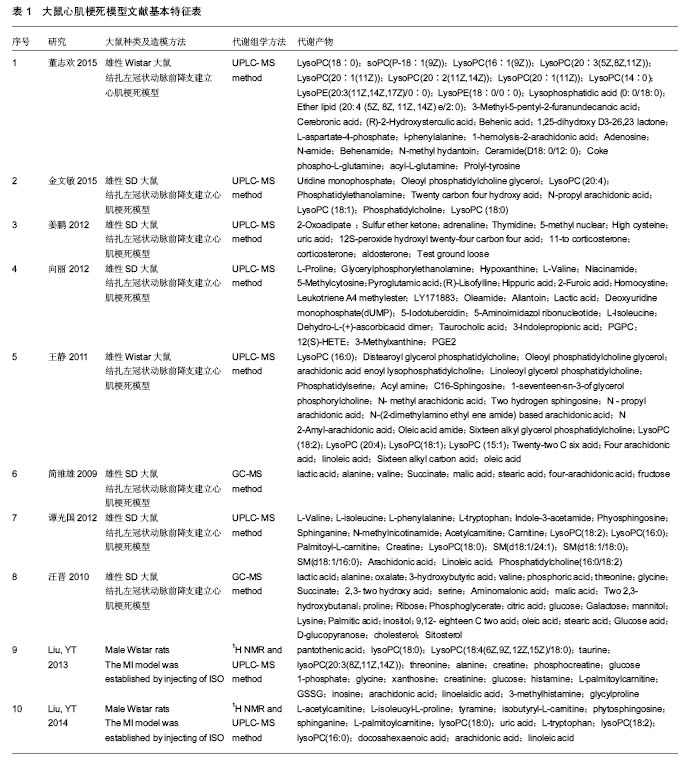
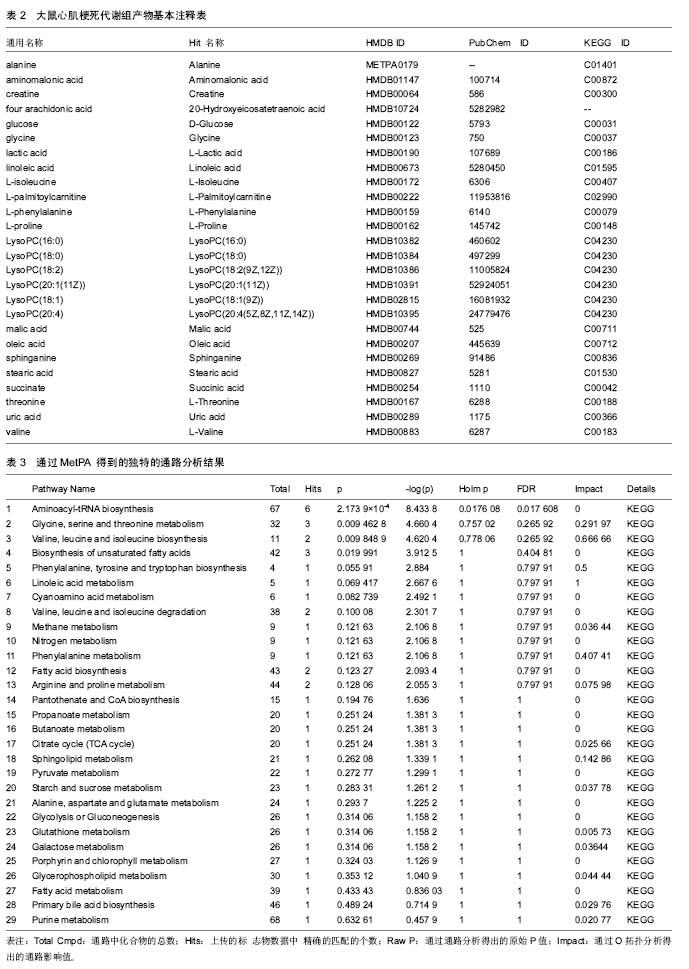
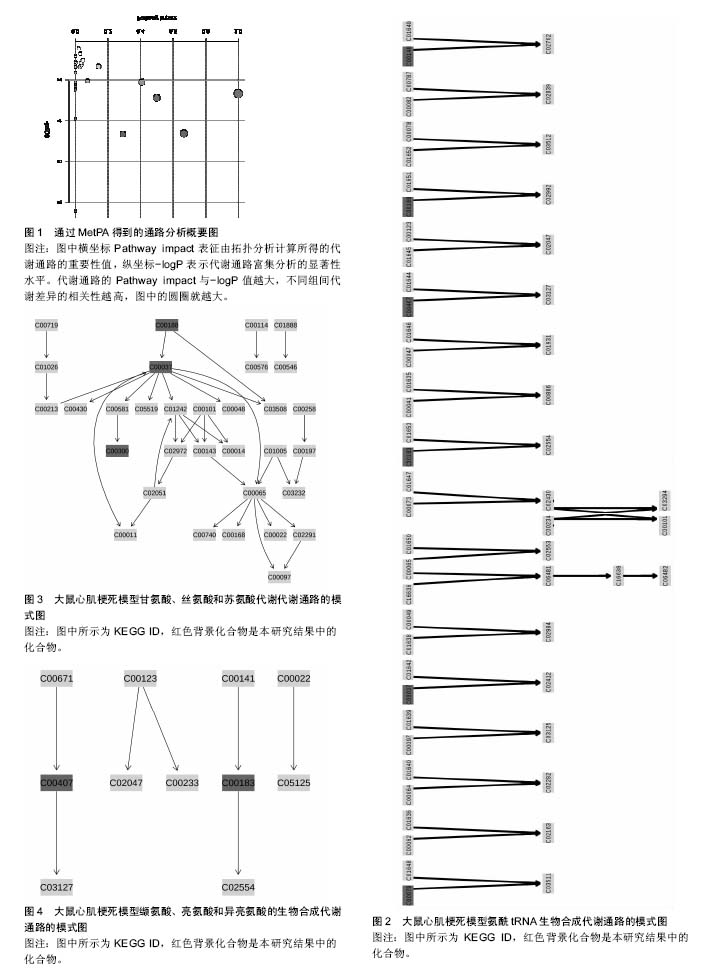
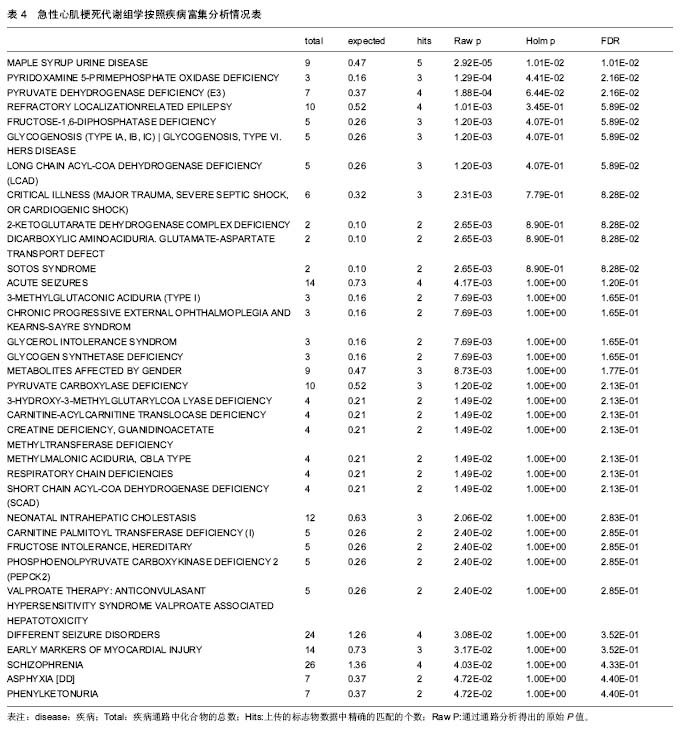
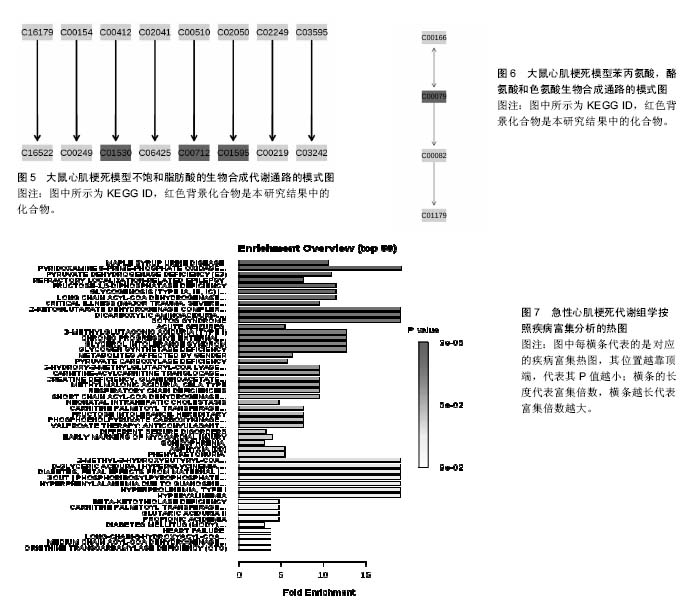
结果与结论:①共有10篇文献纳入分析,有26个代谢产物在这些文献中重复出现,主要参与了29条代谢路径;②通过通路拓扑分析选出了5条代谢通路作为大鼠心肌梗死代谢通路,分别是:氨酰tRNA生物合成、甘氨酸、丝氨酸和苏氨酸代谢、缬氨酸、亮氨酸和异亮氨酸的生物合成、不饱和脂肪酸的生物合成、苯丙氨酸,酪氨酸和色氨酸生物合成;③大鼠心肌梗死代谢组生物信息分析显示心肌梗死发病机制涉及到糖类、脂肪、蛋白质、RNA等物质代谢及其代谢通路。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-9710-3732(伍新诚)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
代谢组学:是继基因组学和蛋白质组学之后新近发展起来的一门学科,是系统生物学的重要组成部分。之后得到迅速发展并渗透到多项领域,比如疾病诊断、医药研制开发、营养食品科学、毒理学、环境学,植物学等与人类健康护理密切相关的领域。基因组学和蛋白质组学分别从基因和蛋白质层面探寻生命的活动,而实际上细胞内许多生命活动是发生在代谢物层面的,如细胞信号释放(cell signaling),能量传递,细胞间通信等都是受代谢物调控的。
转运蛋白:是膜蛋白的一大类,介导生物膜内外的化学物质以及信号交换。脂质双分子层在细胞或细胞器周围形成了一道疏水屏障, 将其与周围环境隔绝起来。尽管有一些小分子可以直接渗透通过膜,但是大部分的亲水性化合物,如糖,氨基酸,离子,药物等等,都需要特异的转运蛋白的帮助来通过疏水屏障。因此,转运蛋白在营养物质摄取,代谢产物释放以及信号转导等广泛的细胞活动中起着重要的作用。
文题释义:
代谢组学:是继基因组学和蛋白质组学之后新近发展起来的一门学科,是系统生物学的重要组成部分。之后得到迅速发展并渗透到多项领域,比如疾病诊断、医药研制开发、营养食品科学、毒理学、环境学,植物学等与人类健康护理密切相关的领域。基因组学和蛋白质组学分别从基因和蛋白质层面探寻生命的活动,而实际上细胞内许多生命活动是发生在代谢物层面的,如细胞信号释放(cell signaling),能量传递,细胞间通信等都是受代谢物调控的。
转运蛋白:是膜蛋白的一大类,介导生物膜内外的化学物质以及信号交换。脂质双分子层在细胞或细胞器周围形成了一道疏水屏障, 将其与周围环境隔绝起来。尽管有一些小分子可以直接渗透通过膜,但是大部分的亲水性化合物,如糖,氨基酸,离子,药物等等,都需要特异的转运蛋白的帮助来通过疏水屏障。因此,转运蛋白在营养物质摄取,代谢产物释放以及信号转导等广泛的细胞活动中起着重要的作用。