中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (4): 580-585.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.04.015
• 口腔组织构建 oral tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
血管内皮细胞生长因子与碱性成纤维细胞生长因子联合应用对 鼠牙周膜成纤维细胞增殖与碱性磷酸酶活性的影响
曹 宇1,王莉莉2
- 1沈阳市第六人民医院口腔科,辽宁省沈阳市 110000;2锦州医科大学附属口腔医院修复科,辽宁省锦州市 121004
Effects of vascular endothelial growth factor combined with basic fibroblast growth factor on periodontal ligament fibroblast proliferation and alkaline phosphatase activity in rats
Cao Yu1, Wang Li-li2
- 1Department of Stomatology, the Sixth People’s Hospital of Shenyang, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China; 2 Department of Prosthodontics, the Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou 121004, Liaoning Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
牙周组织工程:是将种子细胞在体外进行培养扩增,将扩增的细胞与具有良好生物相容性、可降解性和可吸收的生物材料(支架)按一定的比例混合,形成细胞-材料复合物,将此复合物植入机体牙周病损区,以达到修复创伤和重建功能的目的。
生长因子:是一类通过与特异的、高亲和的细胞膜受体结合,调节细胞生长与其他细胞功能等多效应的多肽类物质。存在于血小板和各种成体与胚胎组织及大多数培养细胞中,对不同种类细胞具有一定的专一性。
文题释义:
牙周组织工程:是将种子细胞在体外进行培养扩增,将扩增的细胞与具有良好生物相容性、可降解性和可吸收的生物材料(支架)按一定的比例混合,形成细胞-材料复合物,将此复合物植入机体牙周病损区,以达到修复创伤和重建功能的目的。
生长因子:是一类通过与特异的、高亲和的细胞膜受体结合,调节细胞生长与其他细胞功能等多效应的多肽类物质。存在于血小板和各种成体与胚胎组织及大多数培养细胞中,对不同种类细胞具有一定的专一性。
.jpg) 文题释义:
牙周组织工程:是将种子细胞在体外进行培养扩增,将扩增的细胞与具有良好生物相容性、可降解性和可吸收的生物材料(支架)按一定的比例混合,形成细胞-材料复合物,将此复合物植入机体牙周病损区,以达到修复创伤和重建功能的目的。
生长因子:是一类通过与特异的、高亲和的细胞膜受体结合,调节细胞生长与其他细胞功能等多效应的多肽类物质。存在于血小板和各种成体与胚胎组织及大多数培养细胞中,对不同种类细胞具有一定的专一性。
文题释义:
牙周组织工程:是将种子细胞在体外进行培养扩增,将扩增的细胞与具有良好生物相容性、可降解性和可吸收的生物材料(支架)按一定的比例混合,形成细胞-材料复合物,将此复合物植入机体牙周病损区,以达到修复创伤和重建功能的目的。
生长因子:是一类通过与特异的、高亲和的细胞膜受体结合,调节细胞生长与其他细胞功能等多效应的多肽类物质。存在于血小板和各种成体与胚胎组织及大多数培养细胞中,对不同种类细胞具有一定的专一性。摘要
背景:碱性成纤维细胞生长因子可以提高成纤维细胞的增殖及胶原的沉积能力,血管内皮细胞生长因子可改善病变组织的血流灌注和新陈代谢水平,且两者在适当的浓度、时间作用下,均可增强碱性磷酸酶的活性。
目的:观察血管内皮细胞生长因子与碱性成纤维细胞生长因子联合应用对鼠牙周膜成纤维细胞增殖与碱性磷酸酶活性的影响。
方法:①体外培养大鼠牙周膜成纤维细胞并鉴定其胚胎来源,第4代细胞用于实验;②检测不同浓度血管内皮细胞生长因子、碱性成纤维细胞生长因子对大鼠牙周膜成纤维细胞增殖的影响,并从中确定显效浓度及最大效应浓度;③将细胞分为5组,分别为A组:对照组,为含体积分数2%胎牛血清的DMEM;B组:血管内皮细胞生长因子最大效应浓度组;C组:碱性成纤维细胞生长因子最大效应浓度组;D组:血管内皮细胞生长因子显效浓度与碱性成纤维细胞生长因子显效浓度联合应用;E组:血管内皮细胞生长因子最大效应浓度与碱性成纤维细胞生长因子最大效应浓度联合应用。于3,7,14 d后,测定5组细胞的碱性磷酸酶活性。
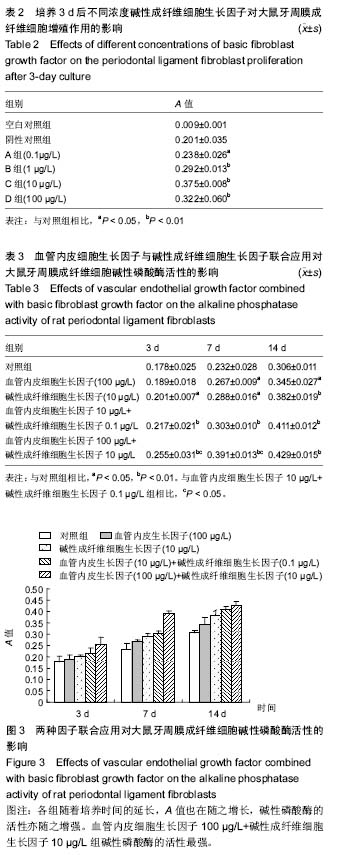
结果与结论:①培养的大鼠牙周膜成纤维细胞生长状态良好,来源于中胚层;②随着血管内皮细胞生长因子、碱性成纤维细胞生长因子质量浓度的增加,大鼠牙周膜成纤维细胞增殖能力也随之提高(P < 0.01)。血管内皮细胞生长因子的显效浓度为10 μg/L,最大效应浓度为100 μg/L;碱性成纤维细胞生长因子的显效浓度为 0.1 μg/L,最大效应浓度为10 μg/L;③当血管内皮细胞生长因子、碱性成纤维细胞生长因子联合作用于大鼠牙周膜成纤维细胞时,实验各组A值均高于对照组。④在应用3 d和7 d时,但D组A值显著低于E组(P < 0.05),14 d时2组差异无显著性意义。⑤结果说明,在一定作用时间内,最大效应浓度联合应用对碱性磷酸酶的活性能起到明显的协同作用,但超过某一时间,显效浓度同最大效应浓度对于牙周膜成纤维细胞碱性磷酸酶活性没有差异。这可能与两因子的作用时效及牙周膜细胞的受体有关。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-1451-9087(曹宇)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
牙周组织工程:是将种子细胞在体外进行培养扩增,将扩增的细胞与具有良好生物相容性、可降解性和可吸收的生物材料(支架)按一定的比例混合,形成细胞-材料复合物,将此复合物植入机体牙周病损区,以达到修复创伤和重建功能的目的。
生长因子:是一类通过与特异的、高亲和的细胞膜受体结合,调节细胞生长与其他细胞功能等多效应的多肽类物质。存在于血小板和各种成体与胚胎组织及大多数培养细胞中,对不同种类细胞具有一定的专一性。
文题释义:
牙周组织工程:是将种子细胞在体外进行培养扩增,将扩增的细胞与具有良好生物相容性、可降解性和可吸收的生物材料(支架)按一定的比例混合,形成细胞-材料复合物,将此复合物植入机体牙周病损区,以达到修复创伤和重建功能的目的。
生长因子:是一类通过与特异的、高亲和的细胞膜受体结合,调节细胞生长与其他细胞功能等多效应的多肽类物质。存在于血小板和各种成体与胚胎组织及大多数培养细胞中,对不同种类细胞具有一定的专一性。