中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (3): 471-477.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.03.026
• 骨与关节循证医学 evidence-based medicine of the bone and joint • 上一篇 下一篇
关节镜下前交叉韧带重建保留残端与否干预膝关节本体感觉功能恢复的Meta分析
张太良1,张 磊2,廉志明1,杨广忠1
- 1新疆医科大学第一附属医院,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830054;2新疆武警兵团指挥部医院,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830002
Effect of remnant preservation on recovery of knee proprioception in arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a meta-analysis
Zhang Tai-liang1, Zhang Lei2, Lian Zhi-ming1, Yang Guang-zhong1
- 1First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Hospital Affiliated to Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps Headquarters of Chinese People’s Armed Police Forces, Urumqi 830002, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
前交叉韧带重建:前交叉韧带损伤初期膝关节剧烈疼痛、肿胀、软弱无力、皮下瘀斑等,后期出现膝关节错动感,肌肉萎缩,肌力及运动能力下降等,若不积极治疗极易出现膝关节不稳和退行性改变,严重影响患者的日常生活和运动功能。因其很难自愈,为了最大限度的恢复膝关节的结构和功能,减少膝关节的进一步损伤,手术重建已成为前交叉韧带损伤治疗的优选方式。与传统的不保留残端重建相比,保留残端重建前交叉韧带也引起了较大关注,具体效果如何仍然存在争议。
膝关节的本体感觉:为一种特殊的感觉形式,包括关节的运动觉和关节位置觉,包含3个方面的功能:关节位置的静态感知能力,关节的运动和加速度感知能力,启动神经-肌肉反射的回馈系统并调节肌张力。前交叉韧带重建术后本体感觉的恢复在很大程度上影响了膝关节的功能,与韧带的力学稳定性相比,术后良好的本体感觉是决定术后患者膝关节功能满意度的主要因素。
摘要
背景:对于前交叉韧带严重损伤或断裂的患者,膝关节镜下前交叉韧带重建是目前常规手术修复方案,而对于术中前交叉韧带残端的保留问题,目前众说纷纭,其对膝关节本体感觉的影响也越来越受到人们的关注。
目的:通过Meta分析比较关节镜下保留残端与不保留残端重建前交叉韧带对其本体感觉功能恢复的效果差异。
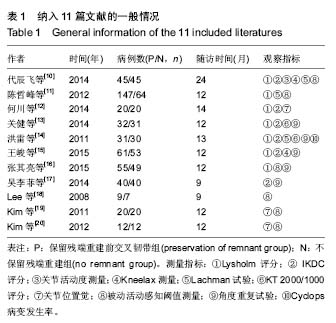
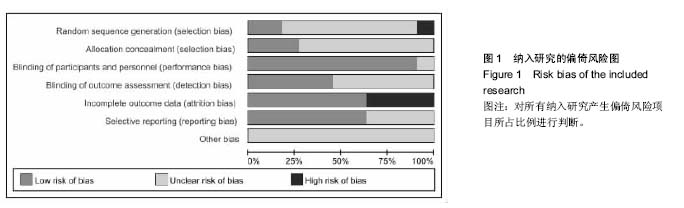
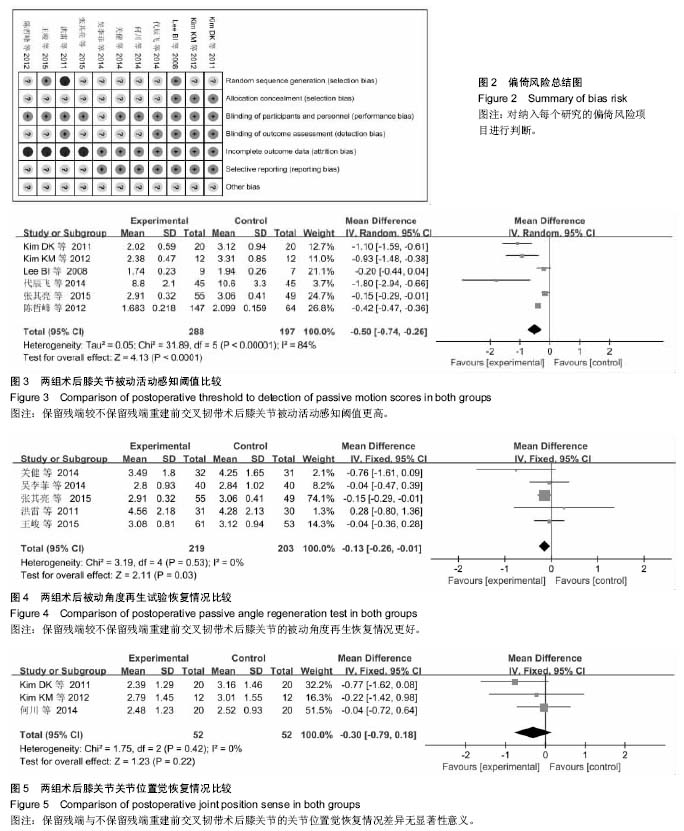
方法:检索从 2001 至 2016 年关于采用关节镜下保留残端与不保留残端重建前交叉韧带的临床对照研究文献,采用 Meta 分析方法对采用这两种手术患者的术后膝关节被动活动感知阈值、被动角度再生试验、关节位置觉及KT 1000/2000评分、IKDC评分、Lysholm评分等进行比较。
结果与结论:①共纳入11篇文献;②Meta分析结果:与重建前交叉韧带不保留残端相比,保留残端在膝关节被动活动感知阈值[OR=-0.50,95%CI(-0.74,-0.26),P < 0.000 1]、膝关节被动角度再生试验[OR=-0.13,95%CI(-0.26,-0.01),P=0.03< 0.05]、Lysholm评分[OR=1.25,95%CI(0.63,2.06),P=0.000 2]、IKDC评分[OR=1.28,95%CI(0.27,2.28),P=0.01]等方面更具优势;而在膝关节关节位置觉[OR=-0.30,95%CI(-0.79,0.18),P=0.22]、KT 1000/2000评分[OR=-0.05,95%CI(-0.13,0.03),P=0.24]方面两者差异无显著性意义;③结果提示,重建前交叉韧带保留残端比不保留残端更有益于膝关节本体感觉的恢复,但仍需前瞻性大样本长期的随机对照试验来验证。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-8511-2076(杨广忠)
中图分类号:

.jpg)