| [1] Moya-Angeler J, Gianakos AL, Villa JC, et al. Current concepts on osteonecrosis of the femoral head. World J Orthop 2015;6(8):590-601. [2] Motomura G, Yamamoto T, Yamaguchi R, et al. Morphological analysis of collapsed regions in osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(2):184-187. [3] Gou WL, Lu Q, Wang X, et al. Key pathway to prevent the collapse of femoral head in osteonecrosis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015;19(15):2766-2774. [4] Zhou GQ, Pang ZH, Chen QQ, et al. Reconstruction of the biomechanical transfer path of femoral head necrosis: a subject-specific finite element investigation. Comput Biol Med. 2014;52(3):96-101. [5] Zhou G, Ying Z, Zeng L, et al. Should thorough Debridement be used in Fibular Allograft with impaction bone grafting to treat Femoral Head Necrosis: a biomechanical evaluation. Bmc Musculoskeletal Disorder. 2014;16(1):1-9. [6] Ueo T, Tsutsumi S, Yamamuro T, et al. Biomechanical aspects of the development of aseptic necrosis of the femoral head. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1985;104(3):145-149. [7] Yang JW, Koo KH, Lee MC, et al. Mechanics of femoral head osteonecrosis using three-dimensional finite element method. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2002;122(2):88-92. [8] Yu T. Research Progress on role of sclerosis band in the collapse of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Medical Recapitulate. 2015;21(1):84-86.[9] Shi J, Chen J, Wu J, et al. Evaluation of the 3D finite element method using a tantalum rod for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Med Sci Monit. 2013;20(4):2556-2564. [10] Penix AR, Cook SD, Skinner HB, et al. Femoral head stresses following cortical bone grafting for aseptic necrosis. A finite element study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983;(173): 159-165. [11] Xiao D, Ye M, Li X et al. Development of femoral head interior supporting device and 3d finite element analysis of its application in the treatment of femoral head avascular necrosis. Med Sci Monit. 2015;21(7):1520-1526. [12] Volokh KY, Yoshida H, Leali A, et al. Prediction of femoral head collapse in osteonecrosis. J Biomech Eng. 2006; 128(3): 467-470. [13] Li XL, Lv ZP and Liu YJ. Constructing a finite element model of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;30: 5522-5525.[14] Pang ZH, Wei QS, Zhou GQ, et al. Establishment and application of subject-specific three-dimensional finite element mesh model for osteonecrosis of femoral head. Shengwu Yixue Gongchengxue Zazhi. 2012;2:251-255. [15] Liu ZH, Li ZR, Sun W, et al. Risk factors for collapse inpatients with osteonecrosis of bilateral femoral heads: Retrospectiveanalysis based on MRI and CT. J Clin Rehabil Tissue Eng Res. 2008;22:4249-4252.[16] Hofstaetter JG, Wang J, Yan J, et al. Changes in bonemicroarchitecture and bone mineral density following experimental osteonecrosis of the hip in rabbits. Cells Tissues Organs. 2006;184(3-4):138-147. [17] Yu T, Xie L, Zhang Z, et al. Prediction of osteonecrosis collapse of the femoral head based on the proportion of the proximal sclerotic rim. Int Orthop. 2015;39(3):1045-1050. [18] Yu T, Xie L, Chu F. A sclerotic rim provides mechanical support for the femoral head in osteonecrosis. Orthopedics. 2015;38(5):e374-e379.[19] Chen ZP, Xu Y, Qi XQ. The formation and function of the sclerosis rim in the femoral head: a biomechanical point of view. Med Eng Phys. 2015;(15):1-8. [20] Karasuyama K, Yamamoto T, Motomura G, et al. The role of sclerotic changes in the starting mechanisms of collapse: a histomorphometric and FEM study on the femoral head of osteonecrosis. Bone. 2015:644-648. [21] Mont MA, Zywiel MG, Marker DR, et al. The natural history of untreated asymptomatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a systematic literature review. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(12):2165-2170. [22] Sakagoshi D, Kabata T, Umemoto Y, et al. A mechanical analysis of femoral resurfacing implantation for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Arthrop. 2010;25(8): 1282-1289. [23] Aruwajoye OO, Kim HKW, Aswath PB. Bone Apatite Composition of Necrotic Trabecular Bone in the Femoral Head of Immature Piglets. Calcif Tissue Int. 2015;96(4): 324-334. [24] Fang B, He W, Zhan L, et al. Finite element analysis of stress distribution over femoral head necrosis zones in different necrosis areas. Zhong Yi Zheng Gu. 2012;10: 10-15. [25] Omran AA. Multiple drilling compared with standard core decompression for avascular necrosis of the femoral head in sickle cell disease patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013; 133(5):609-613. [26] Kang P, Pei F, Shen B, et al. Are the results of multiple drilling and alendronate for osteonecrosis of the femoral head better than those of multiple drilling? A pilot study. Joint Bone Spine. 2012;79(1):67-72. [27] Floerkemeier T, Lutz A, Nackenhorst U, et al. Core decompression and osteonecrosis intervention rod in osteonecrosis of the femoral head: clinical outcome and finite element analysis. Int Orthop. 2010;35(10):1461-1466. [28] Marker DR, Seyler TM, Ulrich SD, et al. Do Modern techniques improve core decompression outcomes for hip osteonecrosis? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(5): 1093-1103. [29] Bae JY, Kwak DS, Park KS, et al. Finite element analysis of the multiple drilling technique for early osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Ann Biomed Eng. 2013;41(12):2528-2537. [30] Tran TN, Warwas S, Haversath M, et al. Experimental and computational studies on the femoral fracture risk for advanced core decompression. Clin Biomech. 2014;29(4): 412-417. [31] Shi J, Chen J, Wu J, et al. Evaluation of the 3D finite element method using a tantalum rod for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Med Sci Monit. 2014;20:2556-2564. [32] Lutz A, Nackenhorst U, von Lewinski G, et al. Numerical studies on alternative therapies for femoral head necrosis. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2011;10(5):627-640. [33] Sardana V, Philippon MJ, de Sa D, et al. Revision hip arthroscopy indications and outcomes: a systematic review. Arthroscopy. 2015;31(10):2047-2055. [34] Marshall DA, Pykerman K, Werle J, et al. Hip resurfacing versus total hip arthroplasty: a systematic review comparing standardized outcomes. Clin Orthop Relate Res. 2014; 472(7):2217-2230. [35] Marshall DA, Pykerman K, Werle J, et al. Hip resurfacing versus total hip arthroplasty: a systematic review comparing standardized outcomes. Clin Orthop Relate Res. 2014; 472(7):2217-2230. [36] Tai CL, Chen YC, Hsieh PH. The effects of necrotic lesion size and orientation of the femoral component on stress alterations in the proximal femur in hip resurfacing-a finite element simulation. BMC Musculoskel Disord. 2014;15(10): 1092-1096. [37] Sakagoshi D, Kabata T, Umemoto Y, et al. A Mechanical Analysis of Femoral Resurfacing Implantation for Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. J Arthrop. 2010;25(8): 1282-1289. [38] Zhou JW, Wu JG, Zhang MC, et al. Balloon inflating and cement filling for treatment of avascular necrosis of the femoral head: a three-dimensional infinite-element study. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2011;10:1724-1728. [39] Pang ZH, He Wei. Clinical application of a new technique based on three-dimensional reconstruction and finite element analysis for osteonecrosis of femoral head in peri-collapse stage. Chin J Joint Surg (Electronic Edition). 2013;3:301-308. [40] Moya-Angeler J, Gianakos AL, Villa JC, et al. Current concepts on osteonecrosis of the femoral head. World J Orthop. 2015;6(8):590-601. |
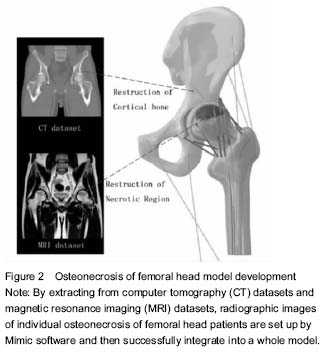
.jpg)

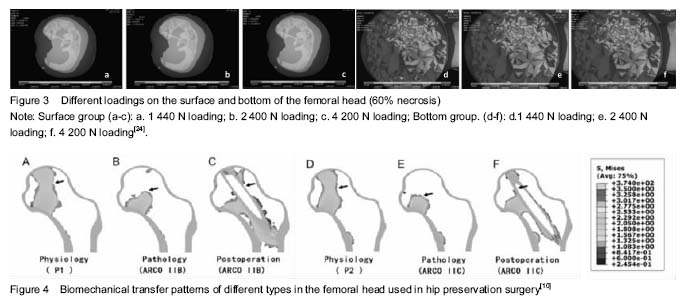
.jpg)