中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (48): 7206-7211.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.48.009
• 骨科植入物 orthopedic implant • 上一篇 下一篇
三种内外固定器械固定胫骨骨折的蠕变特性分析
王 刚1,李新颖2,张树泉3,李亚军4
- 1内蒙古民族大学附属医院骨科,内蒙古自治区通辽市 028000;2吉林大学中日联谊医院超声科,吉林省长春市 130031;3天津市南开医院骨科,天津市 300100;4吉林大学数学学院,吉林省长春市 130028
Creep characteristics of tibial fractures with three internal and external fixation devices
Wang Gang1, Li Xin-ying2, Zhang Shu-quan3, Li Ya-jun4
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia University for the Nationalities, Tongliao 028000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Ultrasound, China Japan Union Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130031, Jilin Province, China; 3Department of Orthopedics, Tianjin Nankai Hospital, Tianjin 300100, China; 4School of Mathematics, Jilin University, Changchun 130028, Jilin Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
黏弹性:聚合物在加工过程中通常是从固体变为液体(熔融和流动),再从液体变固体(冷却和硬化),所以加工过程中聚合物在不同条件下会分别表现出固体和液体的性质,即表现出弹性和黏性。但是由于聚合物大分子的长链结构和大分子运动的特殊性质,聚合物的形变和流动不可能是纯弹性和纯黏性的,塑料对应力的响应兼有弹性固体和黏性流体的双重特性称黏弹性。黏弹性使塑料同时具有类似固体的特性(如弹性、强度、因次稳定性)和类似液体的特性(如随时间、温度、负荷大小和速率而变化的流动特性)。黏弹性材料不仅具有弹性,而且具有摩擦。当应力被移除后,一部分功被用于摩擦效应而被转化成热能,这一过程可用应力-应变曲线表示。
蠕变实验:测定金属材料在长时间的恒温和恒应力作用下,发生缓慢的塑性变形现象的一种材料机械性能实验。温度越高或应力越大,蠕变现象越显著。蠕变可在单一应力(拉力、压力或扭力),也可在复合应力下发生。通常的蠕变实验是在单向拉伸条件下进行的。蠕变极限是试样在规定的温度和规定的时间内产生的蠕变变形量或蠕变速度不超过规定值时的最大恒应力。
摘要
背景:模拟胫骨骨折分别以髓内钉、钢板、外固定支架进行固定后的蠕变力学特性罕见报道。
目的:分析3种内外固定器械固定胫骨骨折的蠕变特性,为临床提供生物力学参数。
方法:模拟胫骨骨折分别以髓内钉、钢板、外固定支架进行固定,在电子万能试验机上对3组标本进行轴向压缩蠕变实验。
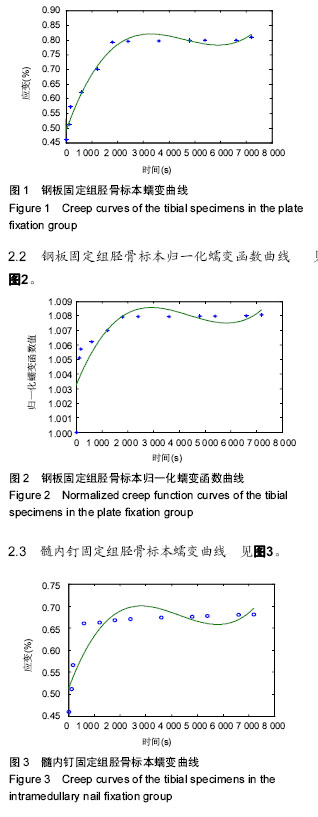
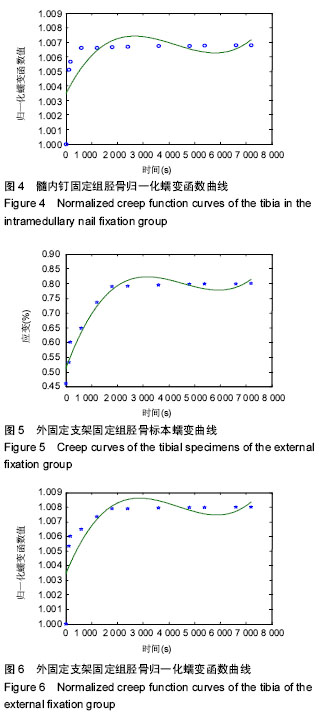
结果与结论:髓内钉固定组7 200 s蠕变量为0.22%,钢板固定组7 200 s蠕变量为0.34%,外固定支架组7 200 s蠕变量为0.42%。外固定支架固定组7 200 s蠕变量大于钢板固定组和髓内钉固定组(P < 0.05),钢板固定组7 200 s蠕变量大于髓内钉固定组(P < 0.05)。结果表明外固定支架、钢板固定、髓内钉固定股骨的蠕变特性均发生了改变,但改变程度不同。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0003-3989-0250(张树泉)
中图分类号:

.jpg)