| [1] 李斐,蒋李园.丹参酮ⅡA对慢性脑缺血大鼠脑组织的保护机制[J].中医临床研究,2011,3(20):50-51.
[2] 刘俊.丹参酮结合血塞通治疗社区脑梗死临床效果分析[J].中国农村卫生,2015,13(16):14-15.
[3] Huang BQ, Qian JY, Ma JY, et al. Myocardial transfection of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and co-transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells enhance cardiac repair in rats with experimental myocardial infarction. Stem cell Res Ther. 2014;5(1):22.
[4] Zhang RP, Zhang K, Li JD, et al. In vivo tracking of neuronal-like cells by magnetic resonance in rabbit models of spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2013; 8(36):3373-3381.
[5] 温雅,祝春华,王力娜,等.丹参酮ⅡA 保护脑梗死大鼠血脑屏障的机制研究[J].河北医科大学学报,2014,36(8): 869-872.
[6] 李春雷,张峰.丹参酮ⅡA磺酸钠注射液治疗脑梗死的疗效及对血清中Fibulin-5、vWF和P-选择素的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2015,35(9):2406-2408.
[7] 谢旭芳,刘诗英,金光华,等.自体骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗脑梗死的临床分析[J].检验医学与临床,2014,11(21): 2955-2957.
[8] Guo HD, Cui GH, Tian JX, et al. Transplantation of salvianolic acid B pretreated mesenchymal stem cells improves cardiac function in rats with myocardial infarction through angiogenesis and paracrine mechanisms. Int J Cardiol. 2014;177(2): 538-542.
[9] 朱士光,杨荣礼,耿德勤,等.局灶性脑缺血大鼠z-Longa评分的MRI研究[J].国际老年医学杂志,2012,33(5): 199-201.
[10] 杨冰,张秀清,唐吉友,等.电刺激对脑梗死大鼠运动功能恢复及Nogo-A、NgR 表达的影响[J].山东大学学报(医学版),2008,46(10):931-935.
[11] Garikipati VN, Jadhav S, Pal L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells from fetal heart attenuate myocardial injury after infarction: an in vivo serial pinhole gated SPECT-CT study in rats. PLoS One. 2014;9(6): e100982.
[12] 张洪连,吴晓牧.骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗脑梗死及存在问题[J].中华脑血管病杂志(电子版),2010,4(4):300- 307.
[13] 张涓,张恩户.丹参酮ⅡA与丹皮酚配伍对大鼠脑缺血的保护作用[J].中国医院药学杂志,2013,33(6):458-460.
[14] 承宏伟.社区医院丹参酮治疗急性脑梗死临床应用研究[J].中国社区医师,2014,30(19):100-101.
[15] Tang J, Wang J, Zheng F, et al. Combination of chemokine and angiogenic factor genes and mesenchymal stem cells could enhance angiogenesis and improve cardiac function after acute myocardial infarction in rats. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010;339(1/2): 107-118.
[16] 李军,杜金荣,戴艳萍.骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗大鼠脑梗死的研究[J].黑龙江医学,2011,35(9):663-664.
[17] Zheng SX, Weng YL, Zhou CQ, et al. Comparison of cardiac stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells transplantation on the cardiac electrophysiology in rats with myocardial infarction. Stem Cell Rev. 2013;9(3): 339-349.
[18] 邹锡良.丹参酮ⅡA磺酸钠对急性脑梗死患者血白细胞介素6和神经功能的影响[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2015, 18(4):72-73.
[19] 董平剑,蒋国衡,吝忞,等.丹参酮ⅡA磺酸钠治疗老年急性脑梗死的临床分析[J].中国继续医学教育,2014,(2):55-56.
[20] Liu Y, Li Z, Liu T,et al.Impaired cardioprotective function of transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells from patients with diabetes mellitus to rats with experimentally induced myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2013;12:40.
[21] 周国庆,金怡,张鹏.沉默RhoA基因对骨髓间充质干细胞静脉移植治疗脑梗死大鼠的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,14(45):8416-8420.
[22] Kurihara Y, Takei K.LOTUS, a potent blocker of Nogo receptor-1 causing inhibition of axonal growth. Neural Regen Res. 2015; 10(1): 46-48
[23] Xie XX, Sun AJ, Zhu WQ, et al. Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells preconditioned with hydrogen sulfide enhances repair of myocardial infarction in rats. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2012;226(1):29-36.
[24] Zhang JS, He QY, Huang T, et al. Effects of panax notoginseng saponins on homing of C-kit+ bone mesenchymal stem cells to the infarction heart in rats. J Tradit Chin Med. 2011;31(3):203-208.
[25] 陈兵.用丹参酮ⅡA璜酸钠注射液治疗脑梗死的疗效探讨[J].当代医药论丛,2015,(9):212-212,213.
[26] 刘玲玲,刘红,尹君玲,等.丹参酮ⅡA对局灶性脑缺血大鼠急性期脑保护作用的相关研究[J].中国卒中杂志,2014, 9(1):20-25.
[27] Cui X, Wang H, Guo H, et al. Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells preconditioned with diazoxide, a mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium channel opener, promotes repair of myocardial infarction in rats. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2010;220(2): 139-147.
[28] Mao Y, Li SN, Mao XB, et al. Therapeutic effect of transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells over-expressing Cx43 on heart failure in post-infarction rats. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011;91(28):1982-1986.
[29] 刘荣启.丹参酮ⅡA璜酸钠注射液治疗脑梗死的临床疗效观察[J].中国医学创新,2014,11(28):111-114.
[30] Guo YH, Liu CT, He JG. Effect of combined therapy of granulocyte colony stimulating factor and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells carrying hepatocyte growth factor gene on angiogenesis of myocardial infarction in rats. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2011; 25(6):736-740.
[31] Fang J, Chen LL, Fan L, et al. Enhanced therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cells on myocardial infarction by ischemic postconditioning through paracrine mechanisms in rats. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011;51(5):839-847.
[32] 黎洪展,吕永恒,陈琪,等.丹参酮ⅡA对大鼠局灶性脑缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用及其机制[J].中国综合临床,2012, 28(1):55-57.
[33] 张凌云.丹参酮ⅡA磺酸钠注射液治疗急性脑梗死的临床研究[J].中国医药指南,2014,19(93):53-54.
[34] 孙洪波,夏圣梅,杨姗杉,等.G-CSF联合自体骨髓闻充质于细胞移植治疗急性脑梗死的临床研究[J].中国医师杂志,2008,10(4):441-443.
[35] Zhang JS, He QY, Huang T, et al. Effects of panax notoginseng saponins on homing of c-kit+ bone mesenchymal stem cells to the infarction heart in rats. J Tradit Chin Med. 2011;31(3):203-208.
[36] 蔡磊,李雅娜,刘桂香,等.骨髓间充质干细胞治疗脑梗死的研究进展[J].滨州医学院学报,2009,32(1):52-54.
[37] 王荣,孙建田,贺云波.丹参酮IIA治疗缺血性脑卒中的疗效及经济学评价[J].中华神经医学杂志,2007,6(9):967-969.
[38] 李凤芹,张晓飞.丹参酮ⅡA磺酸钠注射液治疗急性脑梗死疗效观察及对血清D-二聚体的影响[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2015,18(17):54-55.
[39] 宋雪云,龙云,谭超,等.黄芪甲苷联合丹参酮Ⅱa诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向心肌样细胞分化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,11(36):6515-6520.
[40] Li DC, Bao XQ, Sun H, et al. Research progress in the study of protective effect of tanshinone IIA on cerebral ischemic stroke. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2015;50(6):635- 639.
[41] Zhou L, Bondy SC, Jian L, et al. Tanshinone IIA attenuates the cerebral ischemic injury-induced increase in levels of GFAP and of caspases-3 and -8. Neuroscience. 2015;288:105-111.
[42] Ghosh N, Ghosh R, Bhat ZA, et al. Advances in herbal medicine for treatment of ischemic brain injury. Nat Prod Commun. 2014;9(7):1045-1055.
[43] Park JH, Park OK, Cho JH, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of tanshinone I in neuroprotection against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in the gerbil hippocampus. Neurochem Res. 2014;39(7): 1300-1312.
[44] Wang JG, Bondy SC, Zhou L, et al. Protective effect of Tanshinone IIA against infarct size and increased HMGB1, NFκB, GFAP and apoptosis consequent to transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. Neurochem Res. 2014;39(2):295-304.
[45] Shang YH, Tian JF, Hou M, et al. Progress on the protective effect of compounds from natural medicines on cerebral ischemia. Chin J Nat Med. 2013;11(6): 588-595.
[46] Lee JC, Park JH, Park OK, et al. Neuroprotective effects of tanshinone I from Danshen extract in a mouse model of hypoxia-ischemia. Anat Cell Biol. 2013;46(3):183-10.
[47] Liu X, Ye M, An C, et al. he effect of cationic albumin-conjugated PEGylated tanshinone IIA nanoparticles on neuronal signal pathways and neuroprotection in cerebral ischemia. iomaterials. 2013;34(28):6893-605.
[48] Wen PY, Yang FZ, Wang F, et al. tudy on regulation of tanshinone II(A) on GFAP and ATPase and PDI of cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury in rats. Zhong Yao Cai. 2012;35(10):1628-1632.
[49] Hatfield MJ, Tsurkan LG, Hyatt JL, et al. odulation of esterified drug metabolism by tanshinones from Salvia miltiorrhiza ("Danshen"). Nat Prod. 2013;76(1):36-44.
[50] Liu X, An C, Jin P, et al. rotective effects of cationic bovine serum albumin-conjugated PEGylated tanshinone IIA nanoparticles on cerebral ischemia. iomaterials. 2013;34(3):817-830.
[51] Tang Q, Han R, Xiao H, et al. Neuroprotective effects of tanshinone IIA and/or tetramethylpyrazine in cerebral ischemic injury in vivo and in vitro. Brain Res. 2012;1488:81-91. |
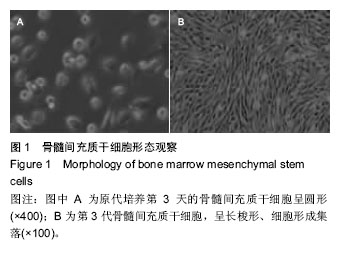
.jpg)
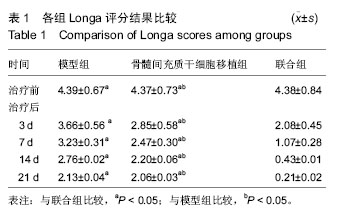
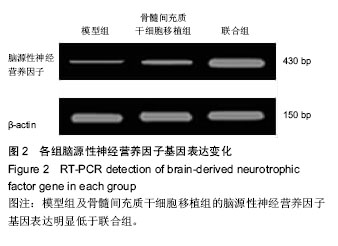
.jpg)
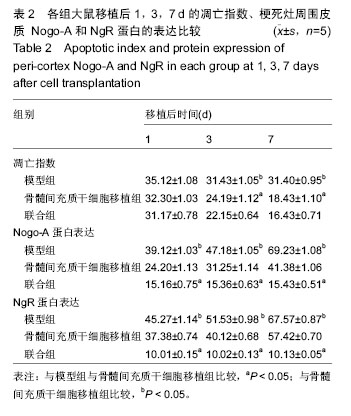
.jpg)