| [1] 郭风劲,陈安民,黄仕龙.免疫分选软骨前体细胞并诱导永生化的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2007,24(2): 226-228.
[2] 刘春晓,陈伟豪,郑少波,等.丝素蛋白膜对犬不同长度尿道缺损的修复效果[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008, 12(19):3613-3616.
[3] 杨光,严世贵,冯建钜,等.膝关节软骨病变的MRI表现与关节镜术后疗效相关性研究[J],中国骨伤,2010,23(2): 90-92.
[4] 袁道英,杨佑成,张彬,等. VEGF在脱细胞骨基质复合富血小板血浆修复颅骨缺损中的表达[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2010,8(4):347 351.
[5] Shi SY,Ying XZ,Hu DX,et al.Experiment on articular cartilage defect repaired with autologous cancellous bone or cancellous bone enriching bone marrow stem cell.Zhongguo Gu Shang.2012;24(4):332-335.
[6] Ei Bahy GS,Abdelrazek ME,Allam MA,et al. Characterization of in situ prepared nano hydroxyapatite/ polyacrylic acid (HAp/PAAc) biocomposites. J Appl Polymer Sci.2011;122(5):3270-3276.
[7] 曾凡营,张勇,孟凌志,等.关节镜手术治疗膝关节痛风性关节炎[J].临床骨科杂志,2008,11(2):135-136.
[8] 孙钢,尹天,张淳,等.关节镜下清理术治疗膝骨关节炎的中期疗效随访[J].中国骨伤,2010,23(12):903-905.
[9] 陈义泉,袁太珍,王健,等.自体软骨~软骨膜移植重建手指关节面11例[J].中国骨伤,2010,23(10):784-786.
[10] 李成,王伟. 软骨组织工程中相关生长因子理论研究的最新资讯[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(28):5260-5263.
[11] Feito MJ,Lozano RM,Alcaide M,et al. Immobilization and bioactivity evaluation of FGF-1 and FGF-2 on powdered silicon doped hydroxyapatite and their scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J Mater Sci: Mater in Med.2011;22(2):405-416.
[12] Wen P,Gao JP,Zhang YL,et al.Fabrication of chitosan scaffolds with tunable porous orientation structure for tissue engineering.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2011; 22(1-3):19-40.
[13] Mecwan MM,Rapalo GE,Mishra SR,et al.Effect of molecular weight of chitosan degraded by microwave irradiation on lyophilized scaffold for bone tissue engineering application.J Biomed Mater Res A.2011; 97(1):66-73.
[14] Zulkifli FH,Jahir Hussain FS,Abdull Rasad MS,et al. Improved cellular response of chemically crosslinked collagen incorporated hydroxyethyl cellulose/poly (vinyl)alcohol nanofibers scaffold. J Biomater Appl. 2015; 29(7):1014-1027.
[15] 王海燕,周咏梅,吴岚,等.以胶原膜为支架构建组织工程化人口腔黏膜研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志 2009,25(8): 494-496.
[16] 周炳华,廖文波.改性聚乳酸-羟基乙酸/I型胶原复合支架与兔耳软骨细胞的细胞相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(3):381-384.
[17] 朱现玮,徐卫袁,张兴祥,等.多孔型丝素蛋白/羟基磷灰石复合骨髓间充质干细胞修复兔半月板无血运区软骨损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(29):5375-5378.
[18] Tang Z,Akiyama Y,Okano T. Recent development of temperature responsive cell culture surface using poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). J Polymer Sci Part B: Polymer Physics.2014;52(14): 917-926.
[19] Elloumi-Hannachi I,Yamato M,Okano T.Cell sheet engineering: A unique nanotechnology for sca old- free tissue reconstruction with clinical applications in regenerative medicine. J Intern Med.2010;267(1): 54-70.
[20] Tatsumi T,Sugimoto M,Lillicrap D,et al.A novel cell-sheet technology that achieves durable factor VIII delivery in a mouse model of hemophilia A.PLoS One.2013;8(12): e83280.
[21] Li D,Wang W,Guo R,et al. Restoration of rat calvarial defects by poly(lactide-co-glycolide)/hydroxyapatite sca olds loaded with bone mesenchymal stem cells and DNA complexes. Chin Sci.2012;57(5):435-444.
[22] Tsumanuma Y,Iwata T,Washio K,et al. Comparison of different tissue-derived stem cell sheets for periodontal regeneration in a canine 1-wall defect model. Biomaterials.2011;32(25): 5819-5825.
[23] Burillon C,Huot L,Justin V,et al. Cultured autologous oral mucosal epithelial cell sheet (CAOMECS) transplantation for the treatment of corneal limbal epithelial stem cell de ciency. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.2012;53(3): 1325-1331.
[24] Chen LL,Hu GF.Angiogenin-mediated ribosomal RNA transcription as a molecular target for treatment of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Oral Oncology. 2010;46(9): 648-653.
[25] Lam J,Lu S,Meretoja VV,et al. Generation of osteochondral tissue constructs with chondrogenically and osteogenically predifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in bilayered hydrogels. Acta Biomater.2014;10(3): 1112-1123.
[26] Packer C,Boddice B,Simpson S.Regenerative medicine techniques in cardiovascular disease: where is the horizon? Regen Med.2013;8(3): 351-360.
[27] Dormer NH,Berkland CJ,Detamore MS. Emerging techniques in stratified designs and continuous gradients for tissue engineering of interfaces. Ann Biomed Eng.2010; 38(6): 2121-2141.
[28] Kon E,Delcogliano M,Filardo G,et al. Novel nano-composite multilayered biomaterial for osteochondral regeneration: a pilot clinical trial. Am J Sports Med.2011;39(6): 1180-1190.
[29] Kon E,Delcogliano M,Filardo G,et al. A novel nano- composite multi-layered biomaterial for treatment of osteochondral lesions: technique note and an early stability pilot clinical trial. Injury.2010;41(7): 693-701.
[30] 陈加荣,张余,黄华扬,等.磁力靶向传递SPIO标记的BMSC修复关节软骨缺损的研究进展[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2014,6(2):118-122.
[31] 杨建华,刘舒云,赵鹏,等.微球化人脐带Wharton胶间充质干细胞移植裸鼠皮下构建异位软骨[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(8):1179-1184.
[32] 刘利兵,王成伟,高健,等.微骨折技术与骨软骨移植治疗关节软骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(31): 5735-5740.
[33] 孟晔,林治琳,柳硕柱,等.关节镜下自体骨软骨移植治疗股骨软骨损伤:1-4年随访结果[J].中国组织工程研究与临床复,2009,13(31):6055-6058.
[34] 侯煜,王向荣,王林杰,等.关节镜下关节清理术联合髌周支持带平衡术治疗膝关节OA(附27例报告)[J].山东医药, 2010,50(30):57-58.
[35] Mohan N,Dormer NH,Caldwell KL,et al. Continuous gradients of material composition and growth factors for effective regeneration of the osteochondral interface. Tissue Eng Part A.2011;17(21/22): 2845-2855.
[36] 刘拴,杨洪平,张卫国.关节镜下关节清理术治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的疗效分析[J].实用临床医学杂志, 2014,18(1): 58-60. |
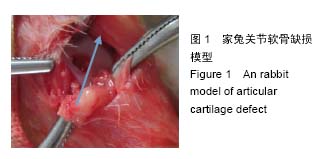
.jpg)
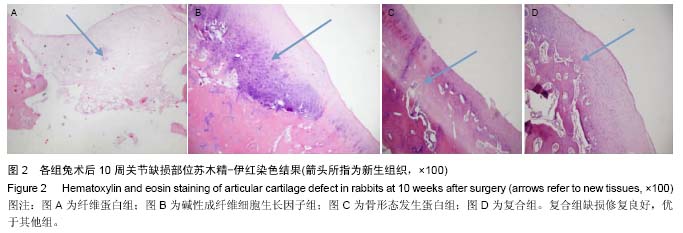
.jpg)